1. Foreman Salt 4.0 Manual
Salt support in Foreman is implemented through two plugins, smart_proxy_salt and foreman_salt. These plugins enable Foreman to manage Salt minions, including provisioning, keys, states, pillars, and grains, as well as providing advanced reporting features.
The core plugin major version will increment with the specific Foreman release, as shown in the table below. Proxy releases tend to be compatible for longer, as the Foreman Proxy plugin API changes less frequently.
| Foreman | foreman_salt | smart_proxy_salt |
|---|---|---|
| 1.6.x | 0.x | 0.x - 1.x |
| 1.7.x | 1.x | 0.x - 1.x |
| 1.8.x | 2.x | 2.x |
| 1.9.x | 3.x | 2.x |
| 1.10.x | 4.x | 2.x |
1.1 Release Notes
1.1.1 Foreman plugin
- 4.0:
- Foreman 1.10 compatibility
- 3.0:
- Foreman 1.9 compatibility
- Fixed foreman_salt to work with discovery plugin
- Updated to work with latest foreman-tasks
1.1.2 Smart Proxy plugin
- 2.1.2:
- Support for Salt 2015.05 report structure
- 2.1.1:
- Fixes for Ruby 1.8.7 support
- 2.1.0:
- Support for using salt-api
- API endpoints for environments and state lists
1.2 Contributors
We’d like to thank the following people who contributed to Foreman Salt:
Arnold Bechtoldt, Daniel Lobato, Dominic Cleal, Marek Hulán, Michael Moll, Sherif Nagy, Lukáš Zapletal, Stephen Benjamin
2. Installation
You will need to install the Smart Proxy plugin, smart_proxy_salt, as well as the Foreman plugin, foreman_salt. RPM and DEB packages are available in the official Foreman repositories.
If using the Foreman installer, install the core and smart proxy plugins with:
foreman-installer --enable-foreman-plugin-salt --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-salt
For manual installation, see the plugin manual for more info.
2.1 Smart Proxy
Install the Salt Smart Proxy package for your operating system (see above). The Salt smart proxy needs to run on the same server as your Salt master, and the foreman-proxy user needs to be able to run the ‘salt’ and ‘salt-key’ commands via sudo.
2.1.1 System Configuration
-
Add this to /etc/sudoers:
Cmnd_Alias SALT = /usr/bin/salt, /usr/bin/salt-key foreman-proxy ALL = (ALL) NOPASSWD: SALT Defaults:foreman-proxy !requiretty -
For the salt-api, ensure the salt-api package is installed, and a supported server such as python-cherrypy is installed.
2.1.2 Salt Master Configuration
In /etc/salt/master, make the following changes:
-
Configure Salt to use the Foreman external node classifier:
master_tops: ext_nodes: /usr/bin/foreman-node -
In order to enable pillar data as well:
ext_pillar: - puppet: /usr/bin/foreman-node -
Enable the autosign file, which the Smart Proxy will manage:
autosign_file: /etc/salt/autosign.conf
Set group ownership to foreman-proxy and allow group writing:
touch /etc/salt/autosign.conf
chgrp foreman-proxy /etc/salt/autosign.conf
chmod g+w /etc/salt/autosign.conf
In /etc/salt/foreman.yaml, make the following changes:
:proto: https
:host: foreman.example.com
:port: 443
:ssl_ca: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem
:ssl_key: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/private_keys/foreman.example.com.pem
:ssl_cert: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/foreman.example.com.pem
:timeout: 10
:salt: /usr/bin/salt
:upload_grains: true
If your Smart Proxy uses SSL, then the certs and key configured in the YAML should be the same ones it uses to talk to Foreman. If you’re already using Puppet in Foreman, consult /etc/puppet/foreman.yaml or /etc/puppet/node.rb for those settings.
2.1.3 Salt API Configuration
To support state and environment importing, configure salt-api as per the Salt documentation. The user for the Smart Proxy requires a minimum of the @runner permission. An example for CherryPy is below, using the Puppet certificates for SSL.
Add the following section to your /etc/salt/master, and create a system user for the API to use (in this case ‘saltuser’):
external_auth:
pam:
saltuser:
- '@runner'
rest_cherrypy:
port: 9191
host: 0.0.0.0
ssl_key: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/private_keys/foreman.example.com.pem
ssl_crt: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/foreman.example.com.pem
Edit /etc/foreman-proxy/settings.d/salt.yml, and configure the API-related settings:
:use_api: true
:api_auth: pam
:api_url: https://saltmaster.bitbin.de:9191
:api_username: saltuser
:api_password: saltpassword
Then restart the services mentioned in the next section for the changes to take effect.
2.1.4 Final Configuration
Restart the foreman, foreman-proxy, salt-master, salt-api, and foreman-tasks services.
2.2 Foreman
Add the Smart Proxy to Foreman (under Infrastructure, Smart Proxies). If it is an existing smart proxy, click ‘Refresh Features’. You should see it has the Salt feature.
3. Upgrade
Ensure you have the latest stable foreman-release package, and follow the Foreman upgrade instructions, including backing up your database.
To support state and environment importing, configure salt-api as per the Salt documentation, and ensure the service is started on boot. See the Smart Proxy installation section for an example of how to configure the API.
Restart the foreman, foreman-proxy, salt-master, salt-api, and foreman-tasks services.
4. Features
4.1 Provisioning
When creating a new Host, you’ll see a drop down to select the ‘Salt Master’.
Hosts assigned a Salt Master will provision and register as minions automatically. The default Foreman templates support this. If you are installing on an existing Foreman installation, you may need to update your templates to the latest, perhaps by using the templates plugin.
Provisioning works as follows on a host with a salt master defined:
- When the host requests it’s template, Foreman temporarily adds a record to Salt’s autosign file
- At the end of the provisioning process (e.g. kickstart %post)
- salt-minion package is installed
/etc/salt/minionis configuredsalt-call --grainsis run in order to trigger key signing
- When the host finishes the build, Foreman removes the autosign entry
4.2 States
From the States index page, you have an overview of all the states from your Salt master, and the environments they are available in. To refresh this data, use the Import button on the top right of the screen.
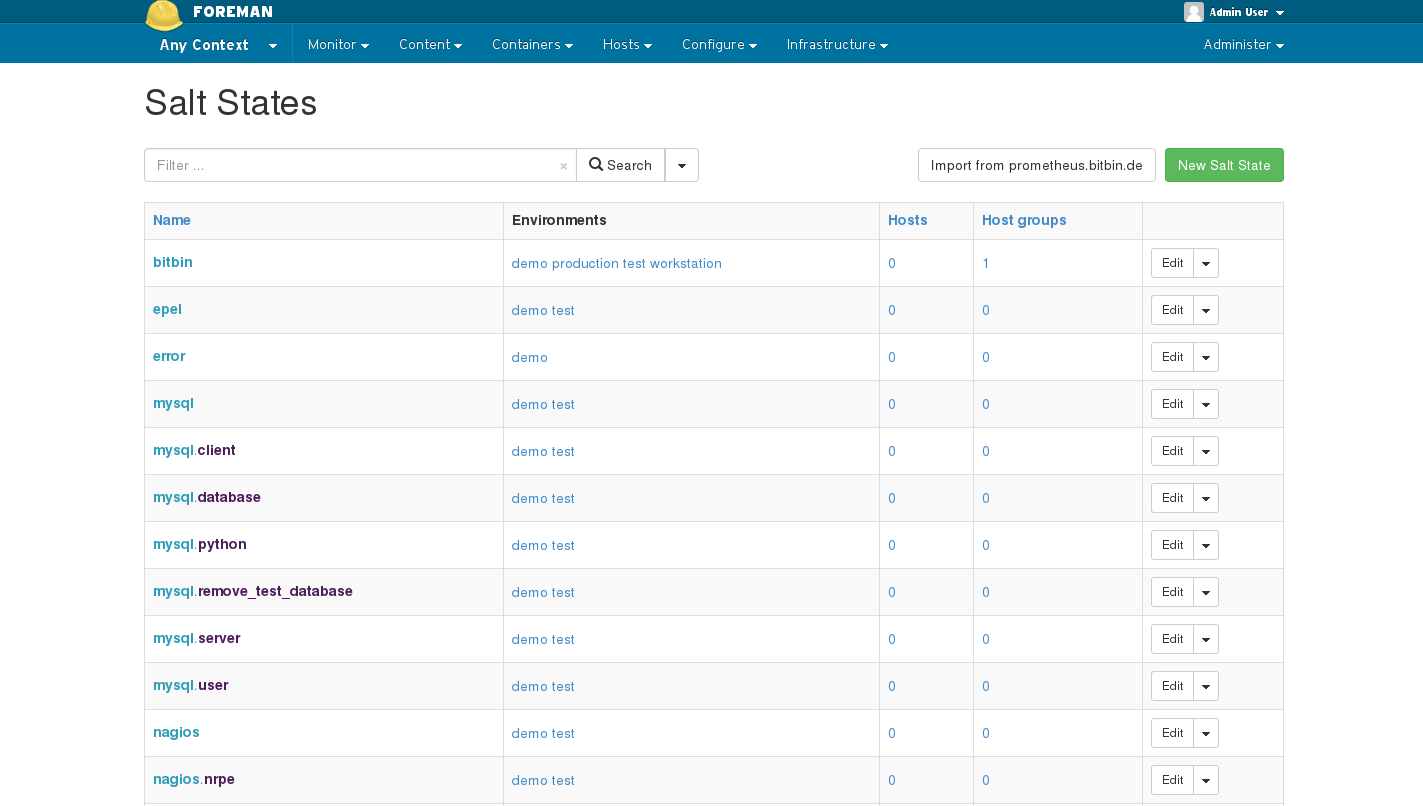
Foreman provides an interface for adding Salt states to either a Foreman host group or a host. Salt will know to apply these states through the external node classification feature. This is done in addition to top.sls.
In the example below, the inherited states are coming from the host’s host group, and you may add additional states specifically to this new host:
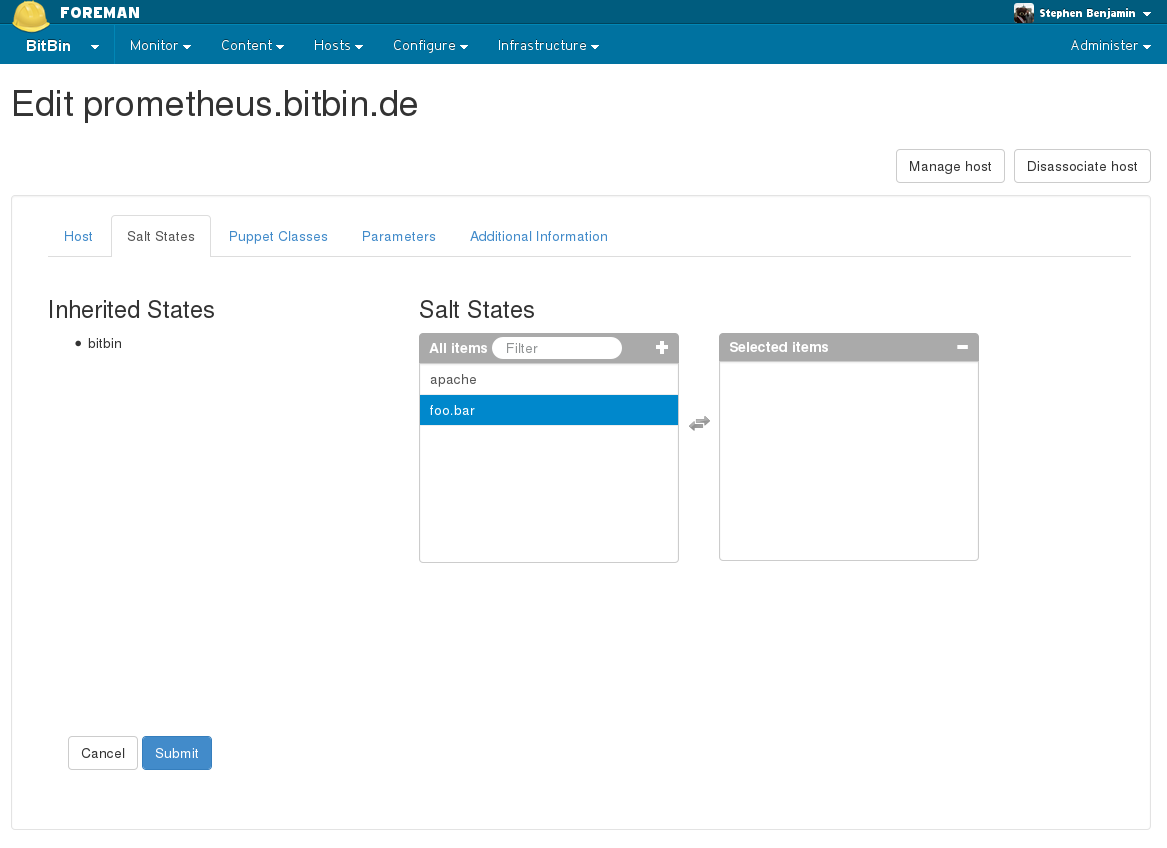
4.3 Key Management
This plugin provides a UI interface to both Salt Keys and the Autosign entries. Navigate to the Smart Proxy’s page, and click on ‘Salt Keys’ or ‘Salt Autosign’ next to the Smart Proxy in the action buttons.
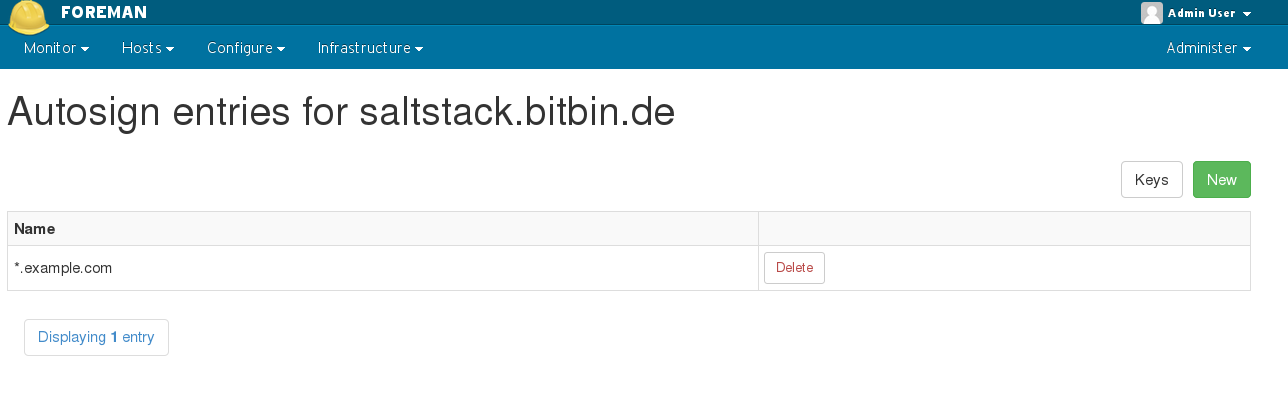
4.3.1 Autosign
Foreman manages the lifecycle of a salt minion’s keys. When the minion provisions, the autosign record will be added automatically, and when the build finishes it is removed. You may also manually enter an autosign entry, for example, to support automatically signing an entire domain managed outside foreman (e.g. ‘*.example.com’).
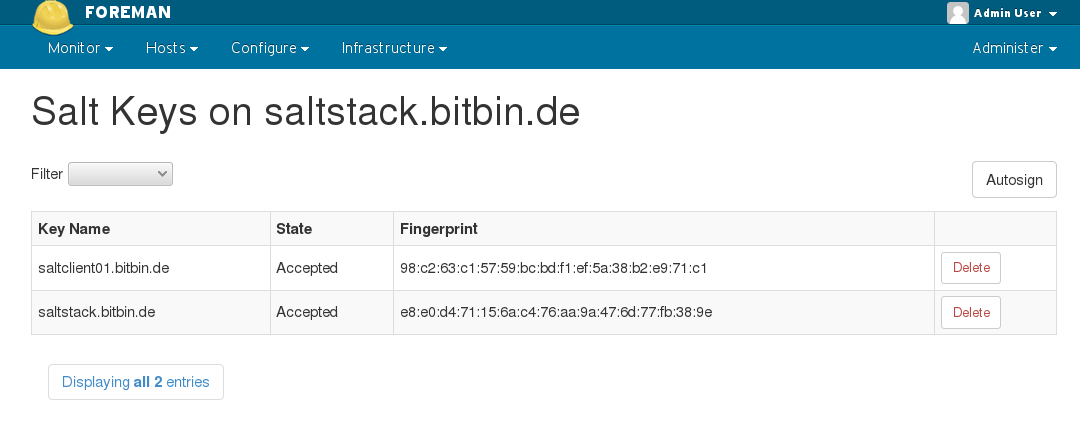
4.3.2 Keys
The Salt Keys interface allows you to manually accept, reject, or delete keys. This is useful for managing hosts outside of Foreman’s orchestration.
4.4 Highstate
“Run Salt” button on the hosts page will trigger a state.highstate run.
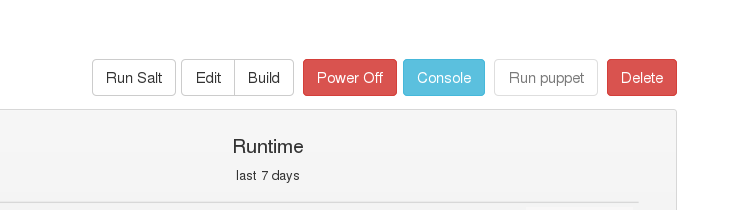
Results of a highstate run will show up in Monitor / Reports if using the upload-salt-reports feature of the Smart Proxy.
You can also review executed state.highstate runs with the jobs runner on the Salt Master:
salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20140921213537978546
4.5 Pillars
Foreman parameters are available inside Salt by setting ext_pillar in /etc/salt/master:
ext_pillar:
- puppet: /usr/bin/foreman-node
By default, Foreman pillars are sent to the top-level pillar namespace, but if you’d like them confined to their own namespace, change the Foreman setting called salt_namespace_pillars to true. Currently, Foreman parameters are limited to String values only.
4.6 Grains
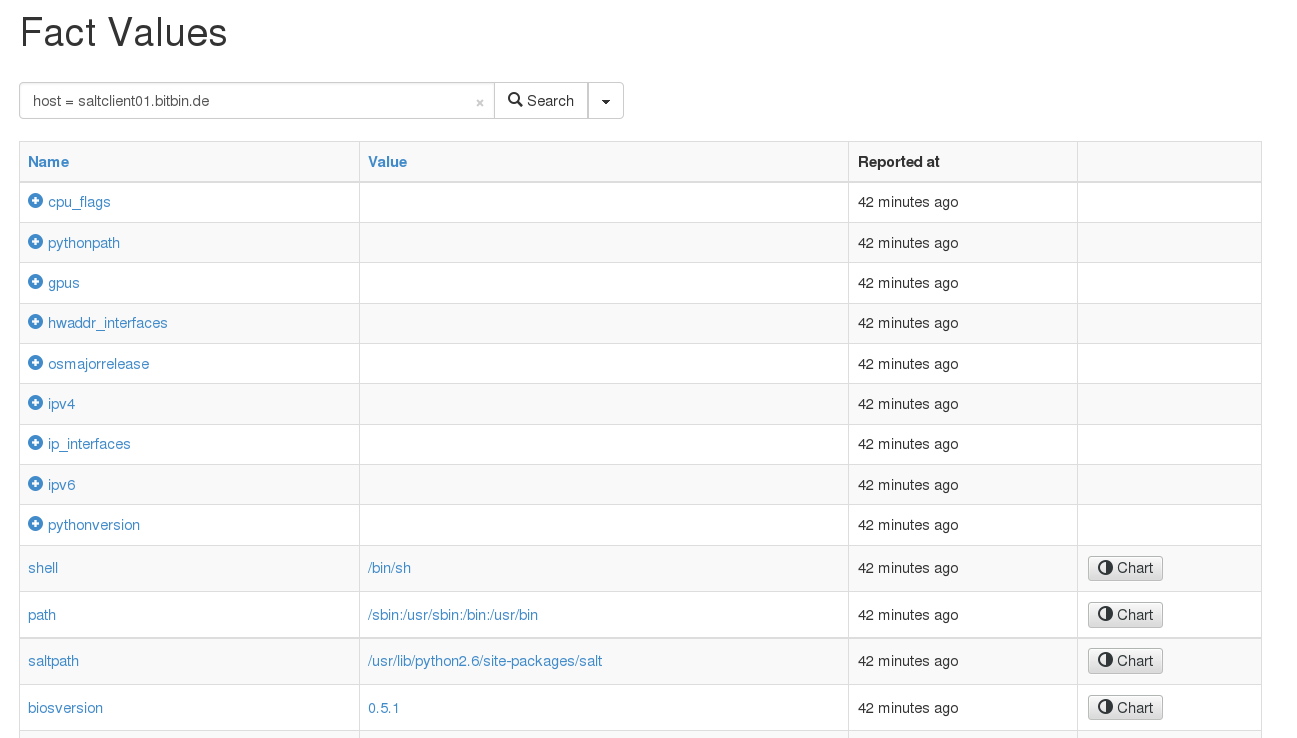
Cached grains are uploaded to Foreman when an external node classifier is run (e.g. when running state.highstate). You can view them in Foreman’s Fact browser. Structured facts are navigable by clicking on the name and drilling down in child values.
4.7 Reporting
When running state.highstate, you can have Foreman process the results and show them in the UI. These reports show statistics about what was done, how long it took, complete with pie charts and file diffs.
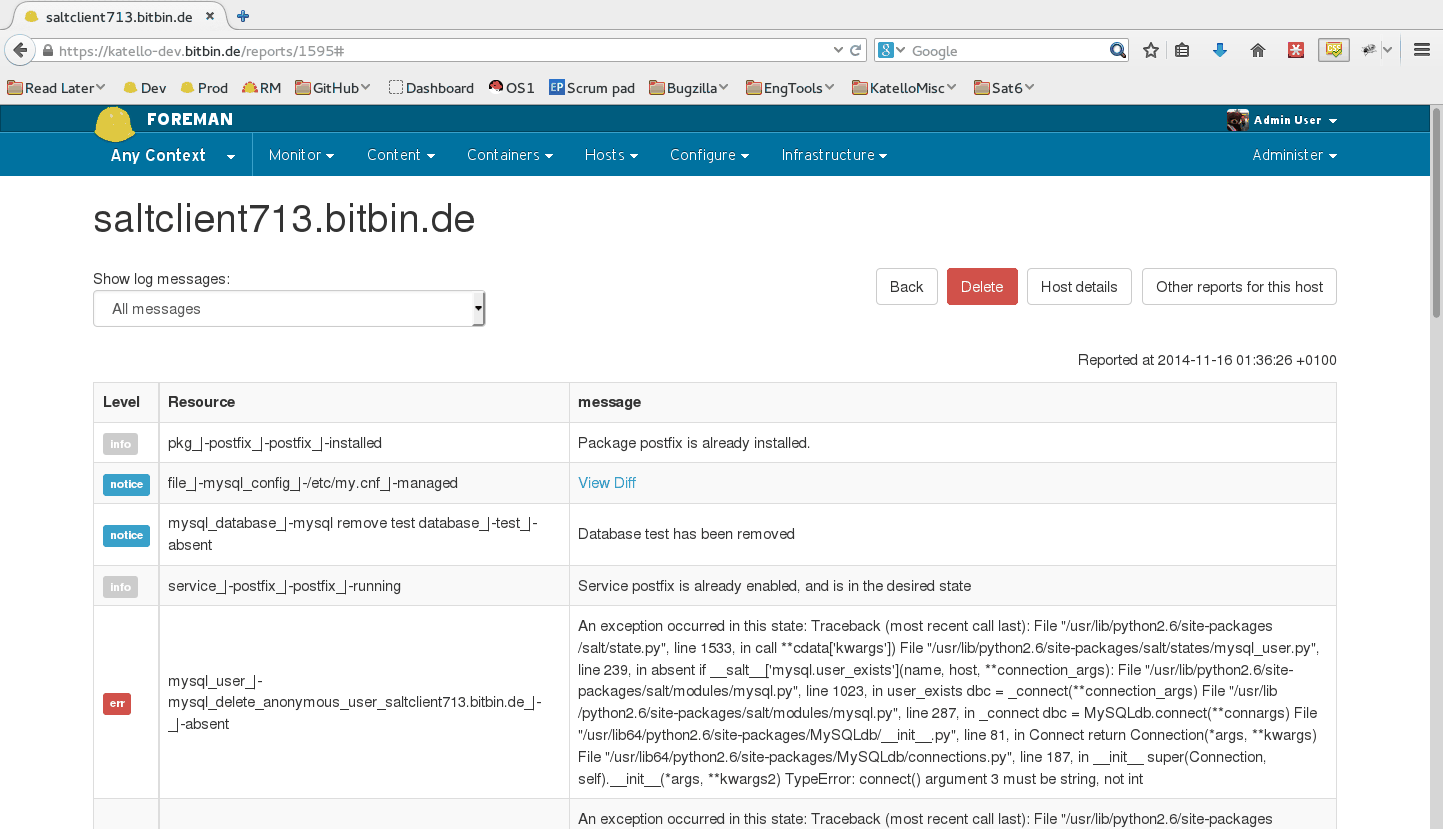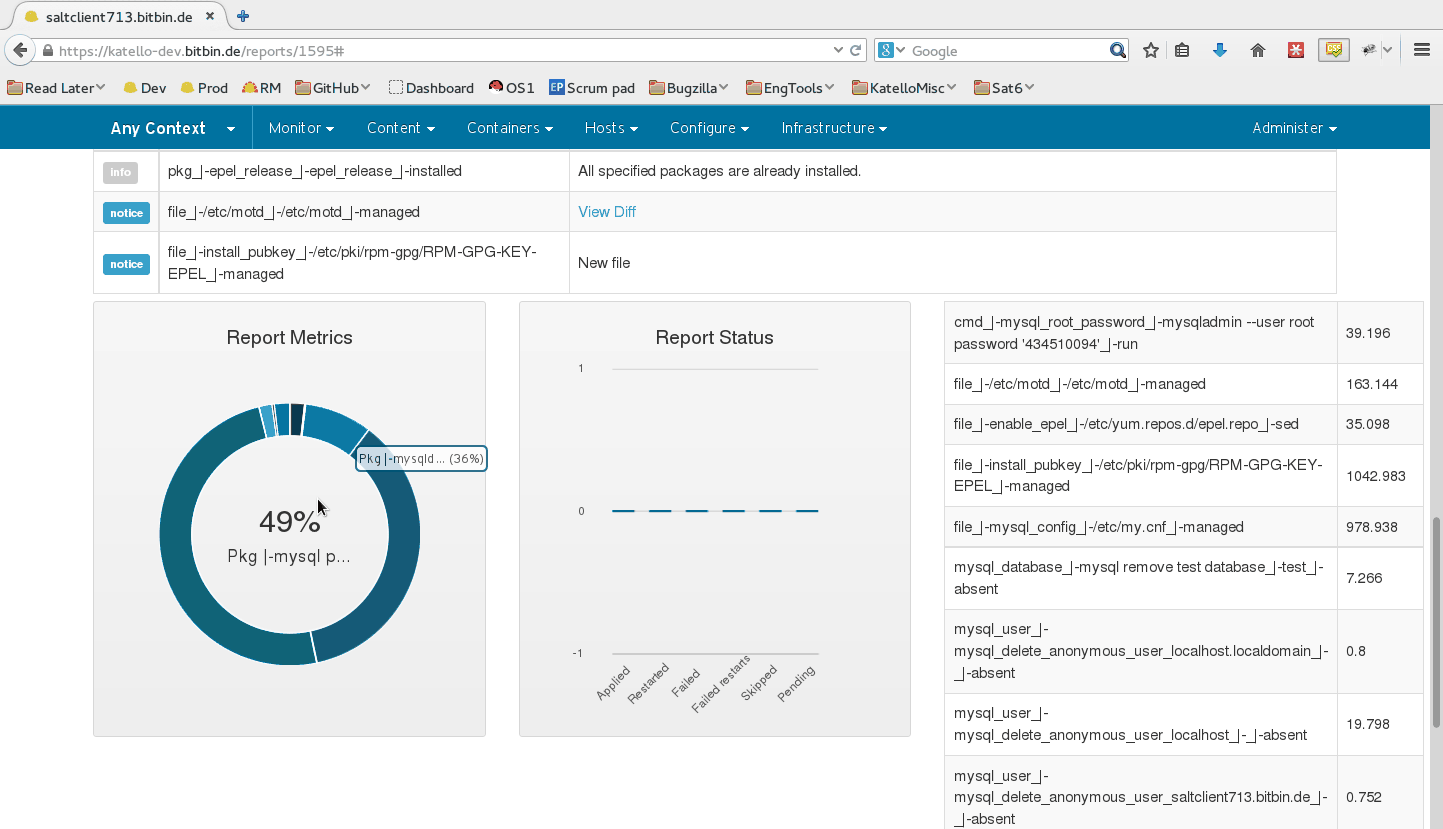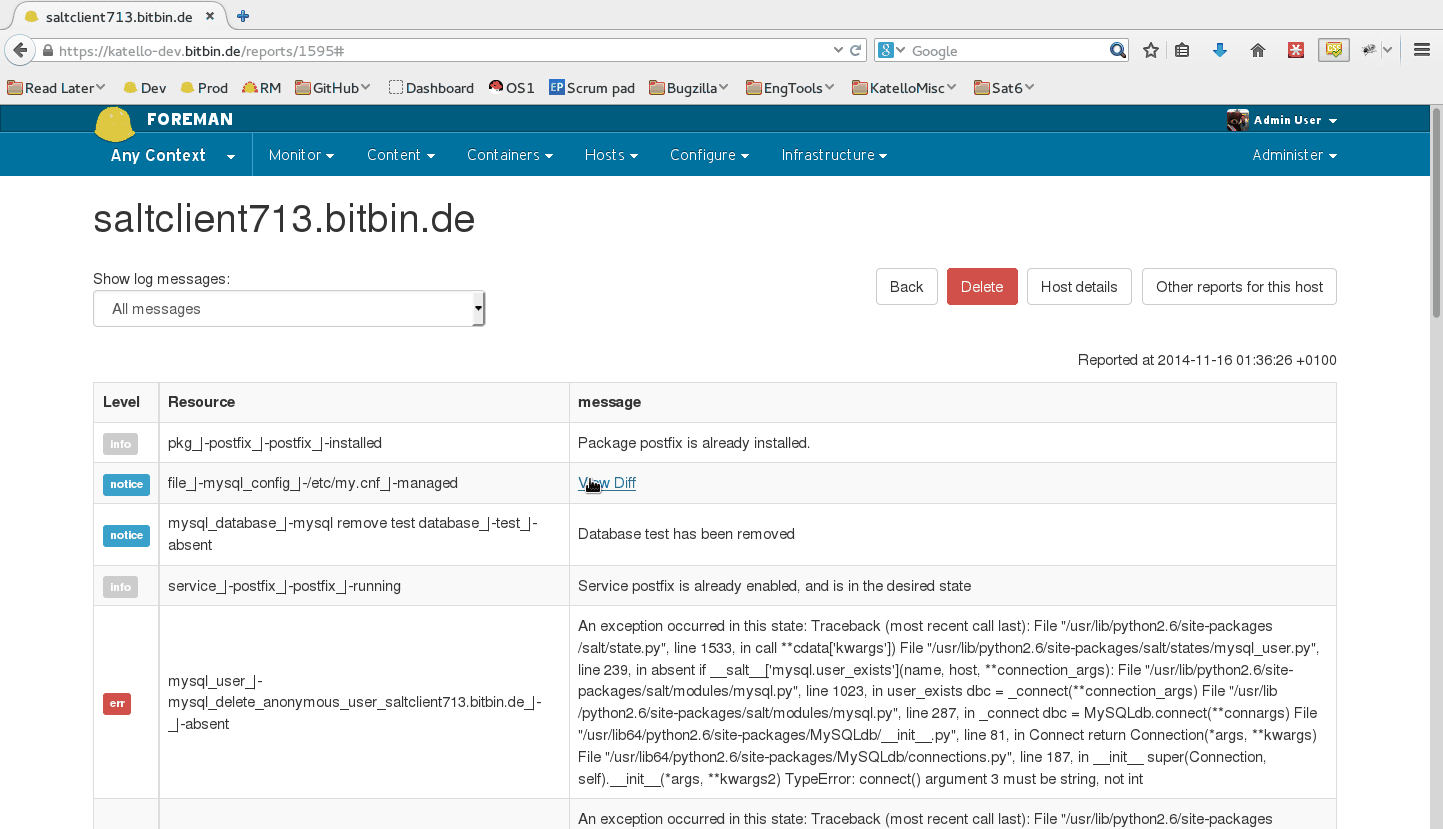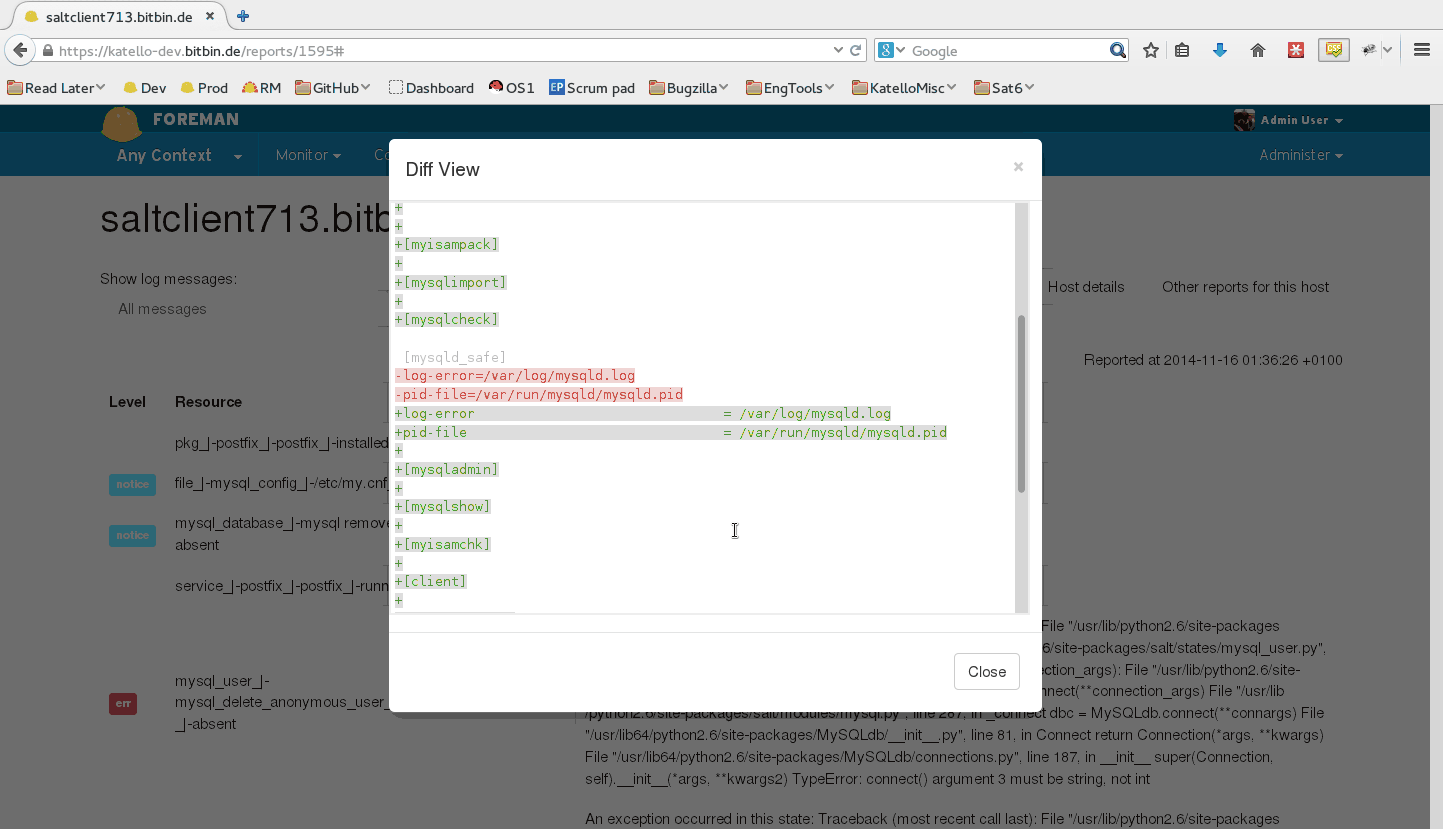
By default, reports are uploaded to Foreman once every 10 minutes from the Salt master’s job cache. You may modify the smart_proxy_salt cron job to customize this.
4.7.1 Scheduling
If you want to schedule your minions to run Salt on a recurring basis, you could modify the cron job to execute something like this:
(salt '*' -b 1000 state.highstate && sleep 60 && /usr/sbin/upload-salt-reports) >> /var/log/foreman-proxy/salt-cron.log
Why not use a returner?
Support for a custom returner would make this cron on the master unnecessary, however, there are limitations on both the Salt and Foreman Proxy side that make this impossible to do securely (for now).
4.8 API
Foreman Salt extends v2 of the Foreman RESTful API with Salt-specific features. See the Foreman manual for general info on the API, and view the full API documentation is available on your Foreman server: http://foreman.example.com/apidoc/v2.html.
Using Curl to get a list of keys from “smartproxy.example.com”:
curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" https://localhost/salt/api/v2/salt_keys/smartproxy.example.com
4.9 CLI
A hammer plugin for Salt is available, follow the instructions for installing a plugin to install hammer_cli_foreman_salt, and then see hammer --help for more information.
Examples:
- Creating a Salt State:
hammer salt-state create --name foo.bar
- Viewing info about a minion:
hammer salt-minion info --name minion.example.com
- Adding states to a minion:
hammer salt-minion update --name minion.example.com --salt-states foo.bar
5 Help
5.1 Troubleshooting
If you find a bug, please file it in Redmine. You can find us on libera.chat on #theforeman as well.
See the troubleshooting section in the Foreman manual for more info.
5.2 Contributing
Follow the same process as Foreman for contributing.