1. Foreman 1.4 Manual
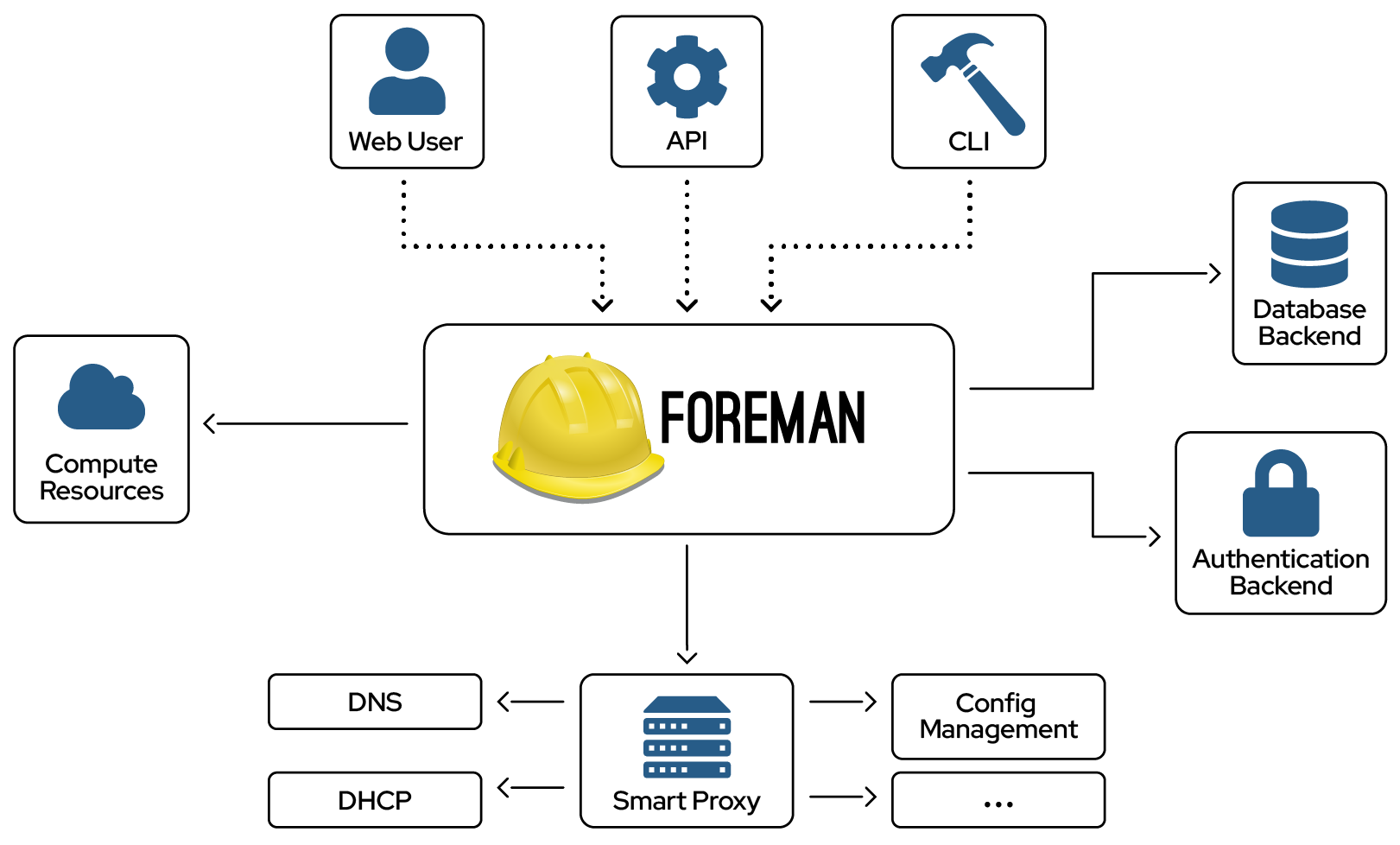
Foreman Architecture
A Foreman installation will always contain a central foreman instance that is responsible for providing the Web based GUI, node configurations, initial host configuration files, etc. However, if the foreman installation supports unattended installations then other operations need to be performed to fully automate this process. The smart proxy manages remote services and is generally installed with all Foreman installations to allow for TFTP, DHCP, DNS, and Puppet, and the Puppet CA.
Smart-Proxy
A Smart-Proxy is located on or near a machine that performs a specific function and helps foreman orchestrate the process of commissioning a new host. Placing the proxy on or near to the actual service will also help reduce latencies in large distributed organizations.
Release notes for 1.4
Headline features
Compute profiles
Administrators are now able to define sets of default attributes for new VMs on each compute resource (of any type), and label it as an one-stop “compute profile” for users to create hosts with.
This speeds up host creation and avoids mistakes with complex network and storage options being set by users each time. Read more about configuring profiles in Using Compute Profiles.
Image user data support
Image-based compute resources (EC2, OpenStack Nova) now support supplying a template as user data to the VM instead of Foreman using SSH to configure the newly created host. In particular, this allows hosts to be created when there is no direct network access from Foreman to the hosts, provided they can contact Foreman.
A new user_data template type has been added and images in Foreman can be configured to resolve a user data template instead of a finish script. More information in the EC2 and OpenStack documentation.
Web UI Kerberos support
Foreman can now be configured under Apache HTTP with mod_auth_kerb to authenticate users using GSSAPI and Kerberos, allowing single sign on (SSO) in enterprise environments. This has been tested with FreeIPA project and more information on configuring it can be found in the SPNEGO documentation.
Interface enhancements and plugin support
Foreman 1.4 introduces a new plugin registration system, which allows plugins to extend the menu system, add permissions, roles and other enhancements to the Foreman installation when they’re loaded. Installed plugins are also now visible under Administer > About, foreman-rake plugins and in the API.
A new “two pane” design has also been added to many index pages around the application, enabling quick creation and editing without waiting for the page to reload entirely. Full page edits may still be opened in new tabs.
A range of new proxy providers
The smart proxy has been updated with new providers for:
- Chef report and fact uploads (details to follow)
- DHCP management with libvirt (dnsmasq)
- DNS record management with libvirt (dnsmasq) and dnscmd (Windows AD)
- Puppet future parser support
- Puppet runs over SSH, SaltStack and with custom commands
Upgrade notes
The following are major changes to be aware of and check after upgrading. Upgrade instructions themselves can be found in 3.6 Upgrade.
foreman-mysql replaced with foreman-mysql2
Two MySQL database adapters (mysql and mysql2) were provided in previous versions of Foreman, but the former (foreman-mysql) has now been removed as mysql2 is generally more reliable.
Check /etc/foreman/database.yml before upgrade and ensure any “adapter: mysql” lines are updated to “adapter: mysql2”. The foreman-mysql package should be updated to foreman-mysql2 on upgrade.
Software Collections on EL6
Foreman 1.2 and 1.3 provided their own rebuild of the ‘ruby193’ software collection, which in Foreman 1.4 has been replaced by a dependency on Red Hat Software Collections or a rebuild such as Software Collections for CentOS or Scientific Linux. This will provide more timely security and bug fix updates, as well as better compatibility with other applications relying on the same SCL.
When upgrading on RHEL6 you should enable the RHSCL repository or channel: yum-config-manager --enable rhel-server-rhscl-6-rpms (subscription-manager), or subscribe to rhel-x86_64-server-6-rhscl-1 if using RHN or Satellite.
On EL6 clones, configure the CentOS SCL repository or the Scientific Linux SCL repository as appropriate. On clean installations of 1.4, the appropriate repo will be configured automatically by the installer.
Important: After configuring the appropriate repository, run yum upgrade scl-utils ruby193\* to ensure the latest available packages are installed.
URL tokens now enabled by default
Foreman’s per-host token feature for provisioning URLs is now enabled by default, which works in addition to identification by IP and MAC address, helping with complex network setups (including NAT). Customizations to PXELinux templates to change the URL, e.g. to add ?static=yes may need updating to form a valid URL, i.e. change to &static=yes.
New unattended_url setting after upgrade
A new setting has been added which controls the URL used in provisioning templates to refer to the Foreman server. This complements the existing foreman_url setting, which is now used to control the URL for users accessing the Foreman web interface.
Ensure this is correct under Administer > Settings > Provisioning > unattended_url, it should refer to the hostname of the Foreman server and is usually HTTP (even if users access Foreman over HTTPS).
Release notes for 1.4.5
Foreman 1.4.5 is security release for Foreman core and the Smart Proxy. The installer component will remain at version 1.4.3 (Debian/Ubuntu) or 1.4.2 (RPM), and the SELinux policy at version 1.4.4.
We recommend that users update to Foreman 1.4.5 or 1.5.1 as soon as possible due to the security issues that have been fixed in these versions. See the Security advisories page for more information.
Security
- Fix stored XSS in host YAML preview (CVE-2014-3492, #6149)
- Fix stored XSS in notification dialogs (CVE-2014-3491, #5881)
- Fix TFTP boot file fetch API permitting remote code execution (CVE-2014-0007, #6086)
A full list of changes in 1.4.5 is available via Redmine
Release notes for 1.4.4
Foreman 1.4.4 is security and bug fix release for Foreman core, and has bug fixes in the Smart Proxy and the SELinux policy. The installer component will remain at version 1.4.3 (Debian/Ubuntu) or 1.4.2 (RPM).
We recommend that users update to Foreman 1.4.4 as soon as possible due to the security issues that have been fixed in this version. See the Security advisories page for more information.
This is the first release to be compatible with RHSCL 1.1.
Compute resources and Hosts creation
- Fixed “missing required parameter uuid” error on VMware host creation (#4590)
- Fix oVirt 3.4.0 compatibility (#4346)
- Fix hang when creating hosts on oVirt 3.4.0 (#5132)
- Fix error on host edit when org/location not visible (#5609)
Installer and packaging
- Update Passenger on EL6 to 4.0.18 (#3199)
- Fix Ruby 1.8 compatibility with rake 10.2.0 (#4828)
- Pin scoped_search for Ruby 1.8 compatibility (#5580)
- Remove %pretrans section from Foreman spec to work in kickstart (#4465)
- Update ruby-wrapper for RHSCL 1.1 ruby193 compatibility
Puppet and Puppet integration
- Fix arrays in smart parameters being reset from YAML/JSON style to Ruby on edit (#4639)
- Fix Puppet 3.5 and future parser compatibility (#5289)
Security
- Fix stored XSS inside search auto-completion of parameter names (CVE-2014-0208, #5471)
- Fix world-accessible provisioning templates via spoof interface (CVE-2014-0192, #5436)
- Fix SELinux fcontext paths for Passenger 4.0.18 (#5466)
A full list of changes in 1.4.4 is available via Redmine
Release notes for 1.4.3
Foreman 1.4.3 is bug fix release for the installer in the 1.4 series.
It has only been released for Debian 6, 7 and Ubuntu 12.04. Packages for RPM distros weren’t required. Similarly, the core Foreman component remains at version 1.4.2.
Installer and packaging
- Fix user shell path on Debian, failing under Puppet 3.5 (#5390)
A full list of changes in 1.4.3 is available via Redmine
Release notes for 1.4.2
Foreman 1.4.2 is a security and bug fix release for the 1.4 series. Core Foreman, the smart proxy and the installer have been updated - the SELinux package remains at version 1.4.0.
We recommend that users update to Foreman 1.4.2 as soon as possible due to the security issues that have been fixed in this version. See the Security advisories page for more information.
Notably, this release adds support for Puppet 3.5.0 and Facter 2.0.1.
Authentication and Authorization
- Preserve HTTP status when using login URL as ErrorDocument (#3475)
- Fix error when using username/password for user created via external auth source (#4442)
Compute resources and Hosts creation
- Reverted #2270 OpenStack floating IP fix to fix EC2 and Rackspace support, to return in 1.5.0 (#4616, #4710)
- Fix hostname “period” error when creating hosts with unattended=false (#4680)
- Fix default owner of hosts being the logged in user (#4524)
- Fix cloning of virtual machine hosts (#4485)
- Fix “New Window” button on SPICE consoles (#4245)
Proxy and Services
- Fix Puppet 3.5 compatibility when listing environments and classes (#4658)
Installer and packaging
- Fix Facter 2 compatibility during FQDN system check (#4372)
- Set minimum version of Puppet on foreman-installer package (#4301)
Security
- Stored Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability on 500 error page (CVE-2014-0089, #4456)
- Session fixation vulnerability, new session IDs aren’t generated on login (CVE-2014-0090, #4457)
Web Interface
- Fix searching for hosts by associated Puppet class (#4314)
- Fix Puppet class search using large amounts of memory (#4565)
- Fix navigation links within plugins not linking to Foreman correctly (#4459)
- Fix session timeout redirect from plugins (#4194)
Various fixes and features
- Fix Facter 2 compatibility during settings and DB initialization (#4626)
- Fix searching on facts by a host’s host group (#4563)
- Fix ‘env’ error in host mailer error handler (#4669)
A full list of changes in 1.4.2 is available via Redmine
Release notes for 1.4.1
Foreman 1.4.1 is a bug fix release for the 1.4 series. Core Foreman, the smart proxy and the installer have been updated - the SELinux package remains at version 1.4.0.
API
- Fix 500 error when creating a duplicate organization or location (#3519)
Authentication and Authorization
- Permit parentheses in user names (#4298)
Compute resources and Hosts creation
- Add SCSI controller selection for VMware hosts (#4159)
- Fix foreign key error when deleting compute resources with associated compute profiles (#4221)
- Fix OpenStack requirement for floating IP by searching for working IP (#2270)
- Please note that this has been reverted in 1.4.2 due to knock-on issues and will be addressed again for 1.5.0
- Fix error on compute resource edit page when oVirt host inaccessible (#3567)
- Fix saving of VMware thin provisioning volume setting in compute profiles (#4159)
- Fix NIC type selection being ignored when creating VMware hosts (#4307)
- Fix rendering of OpenStack attributes in compute profiles (#3980)
Proxy and Services
- Fix needless creation of temporary pid directory (#4215)
Facts and Importers
- Fix per-host fact search link under Ruby 1.8 (#4304)
Installer and packaging
- Fixes for Puppet 3.5 support in kafo (#4343, #4347, #4367)
- foreman module changes:
- Use alphanumeric ordering for vhosts (#4225)
- puppet module changes:
- Fix puppet::server::env with config_version set
- Only show ca_server if non-empty
Internationalization
- Updates to all translations
Puppet and Puppet integration
- Fix override of parameters from host create/edit form (#4234)
- Fix validation error using YAML/JSON on smart class parameter overrides (#2726)
Web Interface
- Current organization/location context now saved through session expiry (#3845)
- Fix menu URLs linking to / when using relative URL root (#3903)
- Fix dashboard widget layout (#4220)
VM management
- Fix error on deletion of OpenStack VMs with auto-assigned IPs (#4125)
- Fix “no map for 173” error with minus key on SPICE consoles (#4300)
Various fixes and features
- Fix “user has this host group already” error when user creates and is subscribed to a host group (#3596)
- Fix template spoof/preview by hostname returning the wrong host (#4268)
- Fix errors on searches by organization/location (#4293)
A full list of changes in 1.4.1 is available via Redmine
Release notes for 1.4.0
API
- Add API for importing of Puppet classes from proxies at /api/smart_proxes/:id/import_puppetclasses (#3140)
- Add API for orchestration tasks at /api/orchestration/:id/tasks (#3566)
- Add API for updating OS default templates at /api/operatingsystems/:os/os_default_templates (#3928)
- Add API for autosign listing at /api/smart_proxies/:id/autosign (#2983)
- Allow API version to be specified in URL via /api/v1 or /api/v2 (#3020)
- Add available images and IAM information to images API (#3101)
- Add validation to OS families on partition tables, installation media (#2818)
- Remove unused show actions from controllers after old API removal (#2986)
- APIv2 request and response formats updated to the APIv2 specification
- Remove the additional root node for child objects (#3768)
- Show errors when parent object doesn’t exist for nested route (#3137)
- Provide metadata for pagination in collection responses (#3018)
- Change default collections root node name to “results”, configurable via root_name parameter (#3011)
- Remove default single root node name, configurable via root_name parameter (#3646)
- Add *_name attribute for each *_id (#2931)
- Separate internal controllers from APIv1 (#3017)
- Allow updates of associations using same JSON as from GET (#3693)
- Standardize API responses for lists, single objects and associations (#3491)
- DRY documentation by using parameter groups (#3925)
- Wrap error responses in “error” node (#3960)
- Fix API documentation for host compute resource parameters (#2951)
- Invalid JSON uploaded now returns an error message instead of 500 error (#3587)
- Fix 500 error when associated objects not found on creation (#3515)
- Fix 500 error thrown for /api/users/loginname (#3736)
- Fix 500 error when incorrect search terms used (#3920)
- Fix locale not being initialized, resulting in random translated errors (#3828)
- Fix method for /hosts/:id/puppetrun call from GET to PUT (#4022)
- Fix incorrect DELETE documentation for reports (#3905)
- Fix accessing smart proxy by name when it contains “.” (#3524)
- Fix error when authentication/user logins are disabled (#3280)
- Fix error message when API authentication fails (#2855)
- Remove APIv2 “catch all” route so plugins can extend it (#3974)
Authentication and Authorization
- Add support for mod_auth_kerb using
authorize_login_delegation_auth_source_user_autocreatesetting (#3312) - Populate user attributes (first name, last name etc.) from REMOTE_* variables (#3528)
- Enable auditing for partition tables (#3673)
- Enable auditing for auth sources, bookmarks, domains, images, roles, proxies, subnets and usergroups (#3975)
- Fix users being created automatically from LDAP when auto creation is disabled (#3493)
- Refactor permissions check for edit self (#3930)
CLI
- Fix errors when creating or updating user data (#3948)
- Fix associating domain to an organization (#3922)
- Improved ‘404’ error messages when resources are not found (#3915)
- Fix managed state of host being reset on update (#4034)
- Fix error on “proxy info” command (#3952)
- Fix error when setting global parameters (#3964)
- Translate names to IDs when using –name for reliability (#3954)
- Add –login argument to user info for search by login (#3734)
- Fix existing architectures being lost when associating a new architecture (#4202)
- Continue loading when an unknown module is specified in config (#3854)
- Fix error when using CSV or table formatters (#4013)
- Fix help text growing on each invocation from shell (#3523)
- Update for new error responses from APIv2 (#4190)
- Remove ‘foreman’ from help text (#3857)
- Handle associated IDs in non-root-node structures (#4192)
Compute resources and Hosts creation
- Add compute profiles functionality [documentation] (#3178)
- Add
use_shortname_for_vmssetting to use short hostnames for VM names (#2975) - Add NIC model selection for creation of VMware VMs (#3116)
- Add libvirt volume zero/size/full allocation options (#2374)
- Add FreeBSD operating system provisioning support via mfsbsd (#2572)
- Add Junos ZTP provisioning support for Juniper network devices (#3906)
- SUSE templates have been updated and one for SLES was added (#3733), more information can be found in the wiki
- Add user data (i.e. cloud-init) support for image-based CRs [EC2 documentation, OpenStack documentation] (#3927)
- Add PXEGrub local boot template (#3737)
- Remove requirement for IP address when creating host in some circumstances (#3182)
- Prevent browser port being used in template URLs, add unattended_url setting (#3569)
- Template URL tokens enabled by default (#3196)
- Add spoof by hostname to provisioning templates, now default (#359)
- Improve host creation field validation for hostnames and IPs (#3697, #3701)
- Disable fields that can’t be edited during VM host edit (#3338)
- Add param_true? and snippet_if_exist template methods (#3955)
- Allow dash-separated MAC addresses (#3170)
- Retrieve oVirt SSL CA over HTTPS instead of HTTP connection (#3896)
- Update list of Rackspace datacentres (#3822)
- Fix VMware “AnyType” error by using older rbvmomi (#3931)
- Fix error when changing build state of oVirt hosts (#4173)
- Fix
@staticsupport in non-kickstart templates (#4020) - Fix behavior of host creation form when cloning VMware host (#3134)
- Fix IP address suggestion and remove host name when cloning hosts (#3136)
- Fix storage volume error when cloning libvirt hosts (#3177)
Proxy and Services
- Add Chef support for proxying facts and reports to Foreman (#3699, #3658)
- Add support for Puppet future (experimental) parser (#2878)
- Add support to trigger Puppet runs over SSH (#3047)
- Add support to trigger Puppet runs over SaltStack (#3732)
- Add libvirt (dnsmasq) DNS and DHCP providers (#3943)
- Add dnscmd (Windows AD) DNS provider for creating static records (#3991)
- Proxy features list can be refreshed from Foreman’s UI and API (#1244)
- Add :puppet_user setting to set user for MCollective or puppet kick commands (#3150)
- Set appropriate DHCP options for Junos Zero-Touch-Provisioning (#3941)
- Set appropriate DHCP options for Solaris SPARC JumpStart (#3067)
- Add puppet dependency to the Gemfile (#3966)
Facts and Importers
- Add support for nested/structured facts (#3339)
- Add create_new_host_when_report_is_uploaded setting to disable host creation when report received (#3364)
- Use boardproductname for hardware models if productname or model is missing (#1431)
- Report importer refactored into separate class (#3205)
Installer and packaging
- foreman-gce package added for Google Compute Engine (GCE) support (#3050, #3617)
- RHSCL / Software Collections now used instead of ruby193 rebuild (#3989)
- Add console rake task, so “foreman-rake console” loads Rails console (#3347)
- Update foreman-cli package to install Hammer CLI (#3495, #3537)
- Use foreman-rake in default cronjobs (#3250)
- Add trends:clean to cronjobs (#3983)
- Installer changed to use puppetlabs-apache module (#3972)
foreman-installer --no-colorsnow respected (#3238)- foreman-mysql now unsupported, replace with mysql2 (#3539)
- Add missing LICENSE files (#4115)
- Remove libvirtd dependency from rubygem-ruby-libvirt/foreman-libvirt (#3344)
- Update ruby-libvirt to latest version (#3882)
- Add facter to bundler group for source installs (#3568)
- Update Rails to 3.2.16 (#4021)
- ‘rr’ dependency removed (#3597)
- ‘coffeescript’ dependency removed (#3992)
- Support short switches and space separators in installer config options (#3244)
- Run puppet with –trace option (#3394)
- foreman module changes:
- depend on puppetlabs-apache instead of theforeman-apache (#3972)
- foreman() parser function docs updated, added per_page option
- puppet module enhancements:
- depend on puppetlabs-apache instead of theforeman-apache (#3972)
- add cron_cmd parameter, use runinterval for cron timing
- add server_certname, classfile parameters
- switch to concat for building puppet.conf
Internationalization
- Add Swedish translation
- Add Zanata support for translations (#3672)
- Improve internationalization of compute resource form (#2600)
- Fix some untranslated validation error messages (#3248)
Puppet and Puppet integration
- Puppet master and Puppet CA proxies assigned to hosts created via Puppet runs (#1830)
- Matchers on host groups updated on rename or nesting of host groups (#2866)
- Add :puppetuser setting to node.rb to run script as another user (#3543)
- Fix display of validation error messages on Puppet class/parameter editing (#3889)
- Add notice and above level filter to report view (#3571)
Web Interface
- Web interface updated to use Bootstrap 3 (#3811)
- Add new RCUE-inspired login page (#3935)
- Add two pane UI for adding and editing objects (#3254)
- New menu design allowing plugins to register and extend it (#3510)
- Add plugin tab to About page to list currently installed plugins (#3510)
- Add full screen edit mode to provisioning template editor (#3274)
- Add categorized list of permissions to role edit page (#3279)
- Add FreeBSD logo to host list (#3168)
- Enable host group searching on reports (#3094)
- Sort host groups alphabetically in list (#3107)
- Add description to operating systems using LSB name (#3720)
- Change OS family class names to use label instead (#3721)
- Fix URL generation for various resources that were affected by multi-byte and / characters (#3516)
- Link to web site manual instead of wiki pages (#2763)
- Fix SQL errors when searching on environments, domains etc on PostgreSQL (#3826)
- IDs added to UI elements to improve test automation (#3684)
- Improve title wording for compute resource and smart proxy pages (#3937)
- Change environments page to refer to Puppet environments (#3709)
- Fix title text for libvirt volume deletion (#3932)
- Update application template layout for best practices (#3872)
- Update image username help text (#3967)
- Fix disabling of items in multi-select boxes (#3911)
- Rename i18n function for compatibility with underscore.js (#3984)
VM management
- Add MAC address and memory in MB to VMware listing (#3123)
- Display free and available space in VMware datastores (#3683)
- Notification message improved after host power action (#3261)
- Fix positioning of power status on Rackspace VMs (#4024)
Various fixes and features
- foreman_url setting now defaults to FQDN, not foreman.domain (#3210)
- Add AIX operating system family (#1489)
- Initial data loaded via db:seed rake task instead of db:migrate (#3752)
- Rails 2 syntax changed to Rails 3 style (#2741)
- Automatically strip leading and trailing whitespace from object names (#3091)
- Add rsync upload support to foreman-debug (#3973)
- Fix inclusion of installer and proxy logs in foreman-debug (#3958)
- Fix random directory name in foreman-debug (#2613)
- Prevent host group deletion when children are present (#2231)
- Remove unused columns from user and user role tables (#3144)
- Improve regexes used in validations (#3249)
- Improve smart proxy class SQL and whitepsace (#3578)
- Fix OS class overriding of class methods (#3962)
- Fix DB migration when plugin overrides the user model (#3669)
- Load smart proxy features dynamically, so plugins can extend them (#3622)
- Fix settings deletion message in development mode (#3777)
- Change “RedHat” name to “Kickstart” in default partition tables (#3722)
- Fix various brand names in UI text (#3724)
- Fix output of exception:codes rake task (#3637)
- Fix plugin issue for models not defining “name” (#4161)
- Fix intermittent fact test failures (#3885)
- Remove unused comps dir (#4001)
A full list of changes in 1.4.0 is available via Redmine
Contributors
We’d like to thank the following people who contributed to the Foreman 1.4 release:
Aaron Stone, Adam Heinz, Adam Price, Amos Benari, Andreas Ntaflos, Andreas Paul, Andrew N Golovkov, Beat Gätzi, Benjamin Papillon, Brad Buckingham, Bryan Kearney, Carmela Rubiños, Daniel Lobato, David Davis, Dennis Konert, Ding Tim, Dmitri Dolguikh, Dolf Schimmel (Freeaqingme), Dominic Cleal, Duncan Innes, Eric D. Helms, Ewoud Kohl van Wijngaarden, Florentin Raud, Florian Ernst, Francois Deppierraz, Frank Wall, Frederic Schaer, Félix Barbeira, Gavin Williams, Gaël Chamoulaud, Glen Ogilvie, Greg Petras, Greg Sutcliffe, Grégoire Morpain, Guido Günther, Gustavo Varela, Hannes Schaller, Iouns Gardon, Ivan Nečas, Jan Orel, Jan Pazdziora, Jared Nelson, Jason Montleon, Jean-Japtiste Langlois, Jimmi Dyson, Johnny Westerlund, Joseph Mitchell Magen, Luke Alford, Lukáš Zapletal, Marek Hulán, Martin Bačovský, Martin Matuska, Michael Crilly, Michael Moll, Michaux Kelley, Mickaël Canévet, Mikael Fridh, Mike McCune, Nils Domrose, Ohad Levy, Patrick Cable, Paul Puschmann, Petr Chalupa, Povilas Daukintis, Rickard von Essen, Robert Birnie, Romain Vrignaud, Ruediger Mueck, Sam Kottler, Stefan Wiederoder, Stephen Benjamin, Tom McKay, Tom McLaughlin, Tomas Edwardsson, Tomas Strachota, Ulrich Habel, Walden Raines, award, dima, francisvm, hhenkel, odgrim, snobear.
As well as all users who helped test releases, report bugs and provide feedback on the project.
2. Quickstart
The Foreman installer is a collection of Puppet modules that installs everything required for a full working Foreman setup. It uses native OS packaging (e.g. RPM and .deb packages) and adds necessary configuration for the complete installation.
Components include the Foreman web UI, Smart Proxy, Passenger (for the puppet master and Foreman itself), and optionally TFTP, DNS and DHCP servers. It is configurable and the Puppet modules can be read or run in “no-op” mode to see what changes it will make.
Supported platforms
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and derivatives (CentOS, Scientific Linux)
- EPEL is required
- On RHEL 6, additionally the Optional and RHSCL 1.0 repositories/channels:
yum-config-manager --enable rhel-6-server-optional-rpms rhel-server-rhscl-6-rpms
- Fedora 19
- Debian 7 (Wheezy)
- Debian 6 (Squeeze) (update Puppet from backports)
- Ubuntu 12.04 (Precise)
Other operating systems will need to use alternative installation methods (see the manual).
2.1 Installation
The Foreman installer uses Puppet to install Foreman. This guide assumes that you have a newly installed operating system, on which the installer will setup Foreman, a puppet master with Passenger and the Smart Proxy by default.
Downloading the installer
For Red Hat variants, run this (replace ‘el6’ with ‘f19’ if appropriate):
yum -y install http://yum.theforeman.org/releases/1.4/el6/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm
yum -y install foreman-installerFor Debian variants, run this (replace ‘wheezy’ with ‘precise’ if on Ubuntu 12.04, or ‘squeeze’ for Debian 6):
echo "deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ wheezy 1.4" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/foreman.list
wget -q http://deb.theforeman.org/pubkey.gpg -O- | apt-key add -
apt-get update && apt-get install foreman-installerRunning the installer
The installation run is non-interactive, but the configuration can be customized by supplying any of the options listed in foreman-installer --help, or by running foreman-installer -i for interactive mode. More examples are given in the Installation Options section. Adding -v will disable the progress bar and display all changes. To run the installer, execute:
foreman-installerAfter it completes, Foreman will be accessible at https://fqdn/ with a default username/password of “admin” and “changeme”.
2.2 Puppet Management
After installation, the Foreman installer will have set up a puppet master on the host, fully integrated with Foreman. First run the Puppet agent on the Foreman host which will send the first Puppet report to Foreman, automatically creating the host in Foreman’s database.
puppet agent --testIn Foreman, click on the Hosts tab and your Foreman host should be visible in the list with an “O” status. This indicates its status is OK, with no changes made on the last Puppet run.
Downloading a Puppet module
Next, we’ll install a Puppet module for managing the NTP service. If you have Puppet 2.7.14 or higher, install the module automatically from Puppet Forge to our “production” environment (the default):
puppet module install -i /etc/puppet/environments/production/modules saz/ntpOn older versions, download the tar.gz and unpack to /etc/puppet/environments/production/modules/. Rename the directory to “ntp”, removing the author and version number.
In Foreman, go to Configure > Puppet Classes and click Import from hostname (top right) to read the available Puppet classes from the puppet master and populate Foreman’s database. The “ntp” class will appear in the Puppet class list if installed correctly.
Using the Puppet module
Click on the “ntp” class in the list, change to the Smart Class Parameters tab and select the server_list parameter on the left hand side. Tick the Override checkbox so Foreman manages the “server_list” parameter of the class and change the default value if desired, before submitting the page.
- More info: Parameterized classes documentation
- Screencast: Parameterized class support in Foreman
Change back to the Hosts tab and click Edit on the Foreman host. On the Puppet Classes tab, expand the ntp module and click the + icon to add the ntp class to the host, then save the host.
Clicking the YAML button when back on the host page will show the ntp class and the server_list parameter, as passed to Puppet via the ENC (external node classifier) interface. Re-run puppet agent --test on the Foreman host to see the NTP service automatically reconfigured by Puppet and the NTP module.
Adding more Puppet-managed hosts
Other hosts with Puppet agents installed can use this puppet master by setting server = foreman.example.com in puppet.conf. Sign their certificates in Foreman by going to Infrastructure > Smart Proxies > Certificates or using puppet cert list and puppet cert sign on the puppet master.
Puppet classes can be added to host groups in Foreman instead of individual hosts, enabling a standard configuration of many hosts simultaneously. Host groups are typically used to represent server roles.
3. Installing Foreman
There are several different methods of installing Foreman. The recommended way is with the puppet based Foreman Installer but you may also use your distribution’s package manager or install directly from source.
3.1 System Requirements
This sections outlines the system requirements for an installation of Foreman. This will cover the hardware requirements, OS requirements and firewall requirements. This includes variations for all supported database types.
3.1.1 Supported Platforms
The following operating systems are supported by the installer, have packages and are tested for deploying Foreman:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and derivatives (CentOS, Scientific Linux)
- EPEL is required
- On RHEL 6, additionally the Optional and RHSCL 1.0 repositories/channels:
yum-config-manager --enable rhel-6-server-optional-rpms rhel-server-rhscl-6-rpms
- Fedora 19
- Debian 7 (Wheezy)
- Debian 6 (Squeeze)
- Ensure Puppet is updated from backports
- Ubuntu 12.04 (Precise)
All platforms will require Puppet 2.7 or higher. Puppet 3.x is supported and may be installed from the Puppet Labs repositories.
Other operating systems will need to use alternative installation methods, such as from source.
The following operating systems are known to install successfully from Foreman:
- RHEL derivatives (CentOS) 3+
- Fedora
- Ubuntu
- Debian
- Solaris 8, 10
- OpenSUSE 11.4
3.1.2 Puppet Compatibility
Foreman integrates with Puppet and Facter in a few places, but generally using a recent, stable version will be fine. The exact versions of Puppet and Facter that Foreman is compatible with are listed below.
| Puppet version | Foreman installer | Smart proxy | Report/fact processors | External node classifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25.x | Not supported | Untested | Untested | Supported * |
| 2.6.0 - 2.6.5 | Not supported | Untested | Untested | Supported * |
| 2.6.5+ | Not supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| 2.7.x | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| 3.0.x | Limited support | 1.1 or higher | Supported | Supported |
| 3.1.x - 3.4.x | 1.1 or higher | 1.1 or higher | Supported | Supported |
| 3.5.0+ | 1.4.3 or higher | 1.4.2 or higher | Supported | Supported |
Lines indicated with * require Parametrized_Classes_in_ENC in Foreman to be disabled.
The Foreman installer and packages are generally incompatible with Puppet Enterprise, however with some manual reconfiguration, individual Foreman components such as the smart proxy should work if needed (some further unsupported documentation can be found on the wiki). The installer in particular will conflict with a Puppet Enterprise installation. It is recommended that Foreman is installed using Puppet “open source”.
Facter compatibility
Foreman is known to be compatible with all Facter 1.x releases.
For Facter 2.x, both Foreman installer and Foreman 1.4.2 or higher are required.
Compatibility with structured facts in Facter 2.x is being introduced via #4528.
3.1.3 Firewall Configuration
Protect your Foreman environment by blocking all unnecessary and unused ports.
| Port | Protocol | Required For |
|---|---|---|
| 53 | TCP & UDP | DNS Smart Proxies |
| 67, 68 | UDP | DHCP Smart Proxies |
| 69 | UDP | * TFTP Smart Proxies |
| 80, 443 | TCP | * HTTP & HTTPS access to Foreman web UI - using Apache + Passenger |
| 3000 | TCP | HTTP access to Foreman web UI - using standalone WEBrick service |
| 3306 | TCP | Separate MySQL database |
| 5910 - 5930 | TCP | Server VNC Consoles |
| 5432 | TCP | Separate PostgreSQL database |
| 8140 | TCP | * Puppet Master |
| 8443 | TCP | Smart Proxy, open only to Foreman |
Ports indicated with * are running by default on a Foreman all-in-one installation and should be open.
3.2 Foreman Installer
The Foreman installer is a collection of Puppet modules that installs everything required for a full working Foreman setup. It uses native OS packaging (e.g. RPM and .deb packages) and adds necessary configuration for the complete installation.
Components include the Foreman web UI, Smart Proxy, Passenger (for the puppet master and Foreman itself), and optionally TFTP, DNS and DHCP servers. It is configurable and the Puppet modules can be read or run in “no-op” mode to see what changes it will make.
It’s strongly recommended to use the installer instead of only installing packages, as the installer uses OS packages and it saves a lot of time otherwise spent replicating configuration by hand.
By default it will configure:
- Apache HTTP with SSL (using a Puppet-signed certificate)
- Foreman running under mod_passenger
- Smart Proxy configured for Puppet, TFTP and SSL
- Puppet master running under mod_passenger
- Puppet agent configured
- TFTP server (under xinetd on Red Hat platforms)
Other modules can be enabled, which will also configure:
- ISC DHCP server
- BIND DNS server
3.2.1 Installation
The Foreman installer uses Puppet to install Foreman. This guide assumes that you have a newly installed operating system, on which the installer will setup Foreman, a puppet master with Passenger and the Smart Proxy by default.
Downloading the installer
For Red Hat variants, run this (replace ‘el6’ with ‘f19’ if appropriate):
yum -y install http://yum.theforeman.org/releases/1.4/el6/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm
yum -y install foreman-installerFor Debian variants, run this (replace ‘wheezy’ with ‘precise’ if on Ubuntu 12.04, or ‘squeeze’ for Debian 6):
echo "deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ wheezy 1.4" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/foreman.list
wget -q http://deb.theforeman.org/pubkey.gpg -O- | apt-key add -
apt-get update && apt-get install foreman-installerRunning the installer
The installation run is non-interactive, but the configuration can be customized by supplying any of the options listed in foreman-installer --help, or by running foreman-installer -i for interactive mode. More examples are given in the Installation Options section. Adding -v will disable the progress bar and display all changes, while --noop will run without making any changes. To run the installer, execute:
foreman-installerAfter it completes, Foreman will be accessible at https://fqdn/ with a default username/password of “admin” and “changeme”. Logs of the installation are stored under /var/log/foreman-installer.
3.2.2 Installer Options
The installer is a collection of Puppet modules, which have a large number of parameters available to customize the configuration. Parameters can be set by running foreman-installer with arguments, e.g. --foreman-db-type, changing settings in interactive mode or by setting up an answers file.
The precedence for settings is for those set by arguments to foreman-installer or interactive mode, then the answers file, then the Puppet manifest defaults.
foreman-installer arguments
Every parameter available in the installer can be set using command line arguments to foreman-installer. Run foreman-installer --help for a list of every available option.
When running the installer, all arguments passed on the command line will be persisted by default to /etc/foreman/foreman-installer.yaml and used automatically on subsequent runs, without needing to specify those arguments again. This persistence can be disabled with the -b option.
Interactive mode
The installer also provides a text driven interface to customize configuration parameters, and can be run by executing:
foreman-installer -iAvailable options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| --foreman-app-root | Name of foreman root directory |
| --foreman-authentication | Enable users authentication (default user:admin pw:changeme) |
| --foreman-configure-epel-repo | If disabled the EPEL repo will not be configured on RedHat family systems. |
| --foreman-configure-scl-repo | If disabled the SCL repo will not be configured on Red Hat clone systems. (Currently only installs repos for CentOS and Scientific) |
| --foreman-custom-repo | No need to change anything here by default if set to true, no repo will be added by this module, letting you to set it to some custom location. |
| --foreman-db-adapter | Database 'production' adapter |
| --foreman-db-database | Database 'production' database (e.g. foreman) |
| --foreman-db-host | Database 'production' host |
| --foreman-db-manage | if enabled, will install and configure the database server on this host |
| --foreman-db-password | Database 'production' password (default is random) |
| --foreman-db-port | Database 'production' port |
| --foreman-db-sslmode | Database 'production' ssl mode |
| --foreman-db-type | Database 'production' type (valid types: mysql/postgresql/sqlite) |
| --foreman-db-username | Database 'production' user (e.g. foreman) |
| --foreman-environment | Rails environment of foreman |
| --foreman-foreman-url | URL on which foreman is going to run |
| --foreman-gpgcheck | turn on/off gpg check in repo files (effective only on RedHat family systems) |
| --foreman-group | Primary group for the Foreman user |
| --foreman-locations-enabled | Enable locations? |
| --foreman-oauth-active | Enable OAuth authentication for REST API |
| --foreman-oauth-consumer-key | OAuth consumer key |
| --foreman-oauth-consumer-secret | OAuth consumer secret |
| --foreman-oauth-map-users | Should foreman use the foreman_user header to identify API user? |
| --foreman-organizations-enabled | Enable organizations? |
| --foreman-passenger | Configure foreman via apache and passenger |
| --foreman-passenger-interface | Defines which network interface passenger should listen on, undef means all interfaces |
| --foreman-passenger-scl | Software collection name (on RHEL currently 'ruby193', undef on others) |
| --foreman-puppet-home | Puppet home directory |
| --foreman-repo | This can be stable, rc, or nightly |
| --foreman-selinux | when undef, foreman-selinux will be installed if SELinux is enabled setting to false/true will override this check (e.g. set to false on 1.1) |
| --foreman-server-ssl-ca | Defines Apache mod_ssl SSLCertificateChainFile setting in Foreman vhost conf file. |
| --foreman-server-ssl-cert | Defines Apache mod_ssl SSLCertificateFile setting in Foreman vhost conf file. |
| --foreman-server-ssl-key | Defines Apache mod_ssl SSLCertificateKeyFile setting in Foreman vhost conf file. |
| --foreman-ssl | Enable and set require_ssl in Foreman settings (note: requires passenger, SSL does not apply to kickstarts) |
| --foreman-unattended | Should foreman manage host provisioning as well |
| --foreman-use-vhost | Enclose apache configuration in |
| --foreman-user | User under which foreman will run |
| --foreman-user-groups | Additional groups for the Foreman user |
| --foreman-version | foreman package version, it's passed to ensure parameter of package resource can be set to specific version number, 'latest', 'present' etc. |
| --foreman-proxy-autosign-location | Path to autosign configuration file |
| --foreman-proxy-bmc | Use BMC |
| --foreman-proxy-bmc-default-provider | BMC default provider. |
| --foreman-proxy-custom-repo | No need to change anything here by default if set to true, no repo will be added by this module, letting you to set it to some custom location. |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp | Use DHCP |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-config | DHCP config file path |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-gateway | DHCP pool gateway |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-interface | DHCP listen interface |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-key-name | DHCP key name |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-key-secret | DHCP password |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-leases | DHCP leases file |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-managed | DHCP is managed by Foreman proxy |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-nameservers | DHCP nameservers |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-range | Space-separated DHCP pool range |
| --foreman-proxy-dhcp-vendor | DHCP vendor |
| --foreman-proxy-dir | Foreman proxy install directory |
| --foreman-proxy-dns | Use DNS |
| --foreman-proxy-dns-forwarders | DNS forwarders |
| --foreman-proxy-dns-interface | DNS interface |
| --foreman-proxy-dns-managed | DNS is managed by Foreman proxy |
| --foreman-proxy-dns-reverse | DNS reverse zone name |
| --foreman-proxy-dns-server | Address of DNS server to manage |
| --foreman-proxy-dns-zone | DNS zone name |
| --foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url | Base Foreman URL used for REST interaction |
| --foreman-proxy-gpgcheck | Turn on/off gpg check in repo files (effective only on RedHat family systems) |
| --foreman-proxy-keyfile | DNS server keyfile path |
| --foreman-proxy-log | Foreman proxy log file |
| --foreman-proxy-manage-sudoersd | Whether to manage File['/etc/sudoers.d'] or not. When reusing this module, this may be disabled to let a dedicated sudo module manage it instead. |
| --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key | OAuth key to be used for REST interaction |
| --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret | OAuth secret to be used for REST interaction |
| --foreman-proxy-oauth-effective-user | User to be used for REST interaction |
| --foreman-proxy-port | Port on which will foreman proxy listen |
| --foreman-proxy-puppet-group | Groups of Foreman proxy user |
| --foreman-proxy-puppetca | Use Puppet CA |
| --foreman-proxy-puppetca-cmd | Puppet CA command to be allowed in sudoers |
| --foreman-proxy-puppetdir | Puppet var directory |
| --foreman-proxy-puppetrun | Enable puppet run/kick management |
| --foreman-proxy-puppetrun-cmd | Puppet run/kick command to be allowed in sudoers |
| --foreman-proxy-puppetrun-provider | Set puppet_provider to handle puppet run/kick via mcollective |
| --foreman-proxy-register-in-foreman | Register proxy back in Foreman |
| --foreman-proxy-registered-name | Proxy name which is registered in Foreman |
| --foreman-proxy-registered-proxy-url | Proxy URL which is registered in Foreman |
| --foreman-proxy-repo | This can be stable, rc, or nightly |
| --foreman-proxy-ssl | Enable SSL, ensure proxy is added with "https://" protocol if true |
| --foreman-proxy-ssl-ca | If CA is specified, remote Foreman host will be verified |
| --foreman-proxy-ssl-cert | Used to communicate to Foreman |
| --foreman-proxy-ssl-key | Corresponding key to a certificate |
| --foreman-proxy-ssldir | Puppet CA ssl directory |
| --foreman-proxy-tftp | Use TFTP |
| --foreman-proxy-tftp-dirs | Directories to be create in $tftp_root |
| --foreman-proxy-tftp-root | TFTP root directory |
| --foreman-proxy-tftp-servername | Defines the TFTP Servername to use, overrides the name in the subnet declaration |
| --foreman-proxy-tftp-syslinux-files | Syslinux files to install on TFTP (copied from $tftp_syslinux_root) |
| --foreman-proxy-tftp-syslinux-root | Directory that hold syslinux files |
| --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts | Only hosts listed will be permitted, empty array to disable authorization |
| --foreman-proxy-use-sudoersd | Add a file to /etc/sudoers.d (true) or uses augeas (false) |
| --foreman-proxy-user | User under which foreman proxy will run |
| --puppet-agent | Should a puppet agent be installed |
| --puppet-agent-noop | Run the agent in noop mode. |
| --puppet-agent-template | Use a custom template for the agent puppet configuration. |
| --puppet-auth-template | Use a custom template for the auth configuration. |
| --puppet-ca-server | Use a different ca server. Should be either a string with the location of the ca_server or 'false'. |
| --puppet-classfile | The file in which puppet agent stores a list of the classes associated with the retrieved configuration. |
| --puppet-client-package | Install a custom package to provide the puppet client |
| --puppet-configtimeout | How long the client should wait for the configuration to be retrieved before considering it a failure. |
| --puppet-cron-cmd | Specify command to launch when runmode is set 'cron'. |
| --puppet-dir | Override the puppet directory. |
| --puppet-group | Override the name of the puppet group. |
| --puppet-listen | Should the puppet agent listen for connections. |
| --puppet-main-template | Use a custom template for the main puppet configuration. |
| --puppet-nsauth-template | Use a custom template for the nsauth configuration. |
| --puppet-pluginsync | Enable pluginsync. |
| --puppet-port | Override the port of the master we connect to. |
| --puppet-runinterval | Set up the interval (in seconds) to run the puppet agent. |
| --puppet-runmode | Select the mode to setup the puppet agent. Can be either 'cron' or 'service'. |
| --puppet-server | Should a puppet master be installed as well as the client |
| --puppet-server-app-root | Directory where the application lives |
| --puppet-server-ca | Provide puppet CA |
| --puppet-server-certname | The name to use when handling certificates. |
| --puppet-server-common-modules-path | Common modules paths (only when $server_git_repo_path and $server_dynamic_environments are false) |
| --puppet-server-config-version | How to determine the configuration version. When using git_repo, by default a git describe approach will be installed. |
| --puppet-server-dir | Puppet configuration directory |
| --puppet-server-dynamic-environments | Use $environment in the modulepath |
| --puppet-server-enc-api | What version of enc script to deploy. Valid values are 'v2' for latest, and 'v1' for Foreman =< 1.2 |
| --puppet-server-environments | Environments to setup (creates directories). Applies only when $server_dynamic_environments is false |
| --puppet-server-environments-owner | The owner of the environments directory |
| --puppet-server-envs-dir | Directory that holds puppet environments |
| --puppet-server-external-nodes | External nodes classifier executable |
| --puppet-server-facts | Should foreman receive facts from puppet |
| --puppet-server-foreman-ssl-ca | SSL CA of the Foreman server |
| --puppet-server-foreman-ssl-cert | Client certificate for authenticating against Foreman server |
| --puppet-server-foreman-ssl-key | Key for authenticating against Foreman server |
| --puppet-server-foreman-url | Foreman URL |
| --puppet-server-git-branch-map | Git branch to puppet env mapping for the default post receive hook |
| --puppet-server-git-repo | Use git repository as a source of modules |
| --puppet-server-git-repo-path | Git repository path |
| --puppet-server-group | Name of the puppetmaster group. |
| --puppet-server-httpd-service | Apache/httpd service name to notify on configuration changes. Defaults to 'httpd' based on the default apache module included with foreman-installer. |
| --puppet-server-manifest-path | Path to puppet site.pp manifest (only when $server_git_repo_path and $server_dynamic_environments are false) |
| --puppet-server-package | Custom package name for puppet master |
| --puppet-server-passenger | If set to true, we will configure apache with passenger. If set to false, we will enable the default puppetmaster service unless service_fallback is set to false. See 'Advanced server parameters' for more information. |
| --puppet-server-passenger-max-pool | The PassengerMaxPoolSize parameter. If your host is low on memory, it may be a good thing to lower this. Defaults to 12. |
| --puppet-server-port | Puppet master port |
| --puppet-server-post-hook-content | Which template to use for git post hook |
| --puppet-server-post-hook-name | Name of a git hook |
| --puppet-server-puppet-basedir | Where is the puppet code base located |
| --puppet-server-puppet-home | Puppet var directory |
| --puppet-server-report-api | What version of report processor to deploy. Valid values are 'v2' for latest, and 'v1' for Foreman =< 1.2 |
| --puppet-server-reports | List of report types to include on the puppetmaster |
| --puppet-server-service-fallback | If passenger is not used, do we want to fallback to using the puppetmaster service? Set to false if you disabled passenger and you do NOT want to use the puppetmaster service. Defaults to true. |
| --puppet-server-ssl-dir | SSL directory |
| --puppet-server-storeconfigs-backend | Do you use storeconfigs? (note: not required) false if you don't, "active_record" for 2.X style db, "puppetdb" for puppetdb |
| --puppet-server-template | Which template should be used for master configuration |
| --puppet-server-user | Name of the puppetmaster user. |
| --puppet-server-vardir | Puppet data directory. |
| --puppet-show-diff | Show and report changed files with diff output |
| --puppet-splay | Switch to enable a random amount of time to sleep before each run. |
| --puppet-user | Override the name of the puppet user. |
| --puppet-version | Specify a specific version of a package to install. The version should be the exact match for your distro. You can also use certain values like 'latest'. |
Answers file
The answers file describes the classes that will be applied to the host to
install Foreman, along with their parameters. The foreman-installer package stores it at /etc/foreman/foreman-installer.yaml. By default, the all-in-one setup will include Foreman, a puppetmaster, Puppet agent, and the Smart Proxy:
---
foreman:
custom_repo: true
foreman_proxy:
custom_repo: true
puppet:
server: trueOther examples are given in the next section, or /usr/share/foreman-installer/README.md.
3.2.3 Installation Scenarios
The Foreman installer can accommodate more complex, multi-host setups when supplied with appropriate parameters.
Setting up Foreman with external Puppet masters
Using the scenarios outlined below, a simple scale-out setup can be created as follows:
- On the Foreman host, run a complete foreman-installer all-in-one installation to provide Foreman, a Puppet master and smart proxy. This will be the Puppet CA.
For each Puppet master:
- Generate a new certificate following the steps in the SSL CA section and transfer it to the new Puppet master host
- Run the standalone Puppet master installation as detailed below
Each Puppet master will register with Foreman as a smart proxy, while the instance running on the Foreman host itself will act as a central Puppet CA. These can be selected while adding new hosts or host groups.
SSL certificate authority setup
The scenarios below assume a single Puppet CA (certificate authority) for all hosts, which is also used for Foreman and smart proxy communications, though more complex deployments are possible. This might be the central Foreman host, or a particular Puppet master.
Other systems require certificates to be generated on the central Puppet CA host, then distributed to them before running foreman-installer (else it may generate a second CA). To prepare these, on the host acting as Puppet CA, run:
# puppet cert generate new-puppetmaster.example.com
Notice: new-puppetmaster.example.com has a waiting certificate request
Notice: Signed certificate request for new-puppetmaster.example.com
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::CertificateRequest new-puppetmaster.example.com at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/ca/requests/new-puppetmaster.example.com.pem'
Notice: Removing file Puppet::SSL::CertificateRequest new-puppetmaster.example.com at '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/certificate_requests/new-puppetmaster.example.com.pem'
# ls /var/lib/puppet/ssl/*/new-puppetmaster.example.com.pem
/var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/new-puppetmaster.example.com.pem
/var/lib/puppet/ssl/private_keys/new-puppetmaster.example.com.pem
/var/lib/puppet/ssl/public_keys/new-puppetmaster.example.com.pemTransfer the following files to the same paths on the new host:
- /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem
- /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/new-puppetmaster.example.com.pem
- /var/lib/puppet/ssl/private_keys/new-puppetmaster.example.com.pem
This provides the new host a certificate in the same authority, but doesn’t make it a CA itself. Certificates will continue to be generated on the central Puppet CA host.
Standalone Puppet master
A standalone Puppet master can be configured along with a smart proxy installation, enabling the Puppet infrastructure to be scaled out. A certificate should be generated and copied to the host first to make it part of the same CA, else a new Puppet CA will be generated.
Command line arguments:
foreman-installer \
--no-enable-foreman \
--enable-puppet \
--puppet-server-ca=false \
--puppet-server-foreman-url=http://foreman.example.com \
--enable-foreman-proxy \
--foreman-proxy-tftp=false \
--foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url=http://foreman.example.com \
--foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key=<key here> \
--foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret=<secret here>Fill in the OAuth consumer key and secret values from your Foreman instance, retrieve them from Administer > Settings > Auth, and set the Foreman URLs appropriately. These allow the smart proxy to register automatically with the Foreman instance, or disable with --foreman-proxy-register-in-foreman=false.
Foreman server without the Puppet master
The default “all-in-one” Foreman installation includes a Puppet master, but this can be disabled. Foreman by default uses Puppet’s SSL certificates however, so a certificate must be generated and copied to the host first, or all SSL communications need to be disabled.
Command line arguments:
foreman-installer \
--puppet-server=false \
--foreman-proxy-puppetrun=false \
--foreman-proxy-puppetca=falseThis will still configure the Puppet agent, but this too can be disabled with --no-enable-puppet to disable the whole Puppet module.
Smart proxy for DNS, DHCP etc.
The smart proxy allows management of various network services, such as DNS, DHCP and TFTP. The installer can set up a basic smart proxy service ready to be configured, or it can install and configure BIND or ISC DHCP ready to go. A certificate should be generated and copied to the host first so Foreman can contact the proxy server.
Command line arguments for a basic smart proxy installation:
foreman-installer \
--no-enable-foreman \
--no-enable-puppet \
--enable-foreman-proxy \
--foreman-proxy-tftp=false \
--foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url=http://foreman.example.com \
--foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key=<key here> \
--foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret=<secret here>Fill in the OAuth consumer key and secret values from your Foreman instance, retrieve them from Administer > Settings > Auth, and set the Foreman URL appropriately. These allow the smart proxy to register automatically with the Foreman instance, or disable with --foreman-proxy-register-in-foreman=false.
Command line arguments for a smart proxy configured with just BIND, setting DNS forwarders and overriding the default forward and reverse DNS zones:
foreman-installer \
--no-enable-foreman \
--no-enable-puppet \
--enable-foreman-proxy \
--foreman-proxy-tftp=false \
--foreman-proxy-puppetca=false \
--foreman-proxy-puppetrun=false \
--foreman-proxy-dns=true \
--foreman-proxy-dns-interface=eth0 \
--foreman-proxy-dns-zone=example.com \
--foreman-proxy-dns-reverse=0.0.10.in-addr.arpa \
--foreman-proxy-dns-forwarders=8.8.8.8 \
--foreman-proxy-dns-forwarders=8.8.4.4 \
--foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url=http://foreman.example.com \
--foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key=<key here> \
--foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret=<secret here>Ensure the dns-interface argument is updated with the correct network interface name for the DNS server to listen on.
Command line arguments for a smart proxy configured with just ISC DHCP and a single DHCP subnet:
foreman-installer \
--no-enable-foreman \
--no-enable-puppet \
--enable-foreman-proxy \
--foreman-proxy-puppetca=false \
--foreman-proxy-puppetrun=false \
--foreman-proxy-tftp=false \
--foreman-proxy-dhcp=true \
--foreman-proxy-dhcp-interface=eth0 \
--foreman-proxy-dhcp-gateway=10.0.0.1 \
--foreman-proxy-dhcp-range="10.0.0.50 10.0.0.200" \
--foreman-proxy-dhcp-nameservers="10.0.1.2,10.0.1.3" \
--foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url=http://foreman.example.com \
--foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key=<key here> \
--foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret=<secret here>Also ensure here that the dhcp-interface argument is updated for the interface to run DHCP on.
3.3 Install From Packages
Packages are available for Red Hat and Debian-based distributions. This will install a standalone Foreman service running under WEBrick, which has limited scalability.
The Puppet-based Foreman installer is recommended for most environments, instead of installing only the packages as it will perform full configuration too.
3.3.1 RPM Packages
Foreman is packaged for the following RPM based distributions:
- RHEL and derivatives, version 6
- Fedora 19
For most users, it’s highly recommended to use the installer as the packages only provide the software and a standalone Foreman service. The installer installs these packages, then additionally configures Foreman to run under Apache and Passenger with PostgreSQL, plus can configure a complete Puppet setup integrated with Foreman.
Pre-requisites
All RHEL and derivatives must be subscribed to EPEL to provide additional dependencies. Install epel-release from here to automatically configure it.
RHEL 6 hosts must also be subscribed to the RHEL 6 Optional repository or child channel in RHN.
All RHEL and derivatives require Red Hat Software Collections (RHSCL) 1.0 or rebuild, e.g. Software Collections for CentOS. RHSCL is available to RHEL customers as a separate repository or child channel. More information on Software Collections for CentOS is available here and for Scientific Linux it is available here.
To enable both optional and software collections on a RHEL 6 system using subscription-manager, run:
yum-config-manager --enable rhel-6-server-optional-rpms rhel-server-rhscl-6-rpms
Optionally, the Puppet Labs repository can be configured to obtain the latest version of Puppet available, instead of the version on EPEL. See the Puppet Labs Package Repositories documentation on how to configure these.
Available repositories
Three main repos are provided at http://yum.theforeman.org:
/releases/latestor/releases/VERSION(e.g./releases/1.4) carries the stable releases and updates of Foreman and its dependencies./rccarries release candidates only in the few weeks prior to a release. Ensure after a release is made that you use the main releases repo instead./nightlycarries the latest development builds and as such, may be unstable or occasionally broken.
Under each repo are directories for each distribution, then each architecture.
Release packages
To set up the repository, foreman-release packages are provided which add a repo definition to /etc/yum.repos.d. Install the appropriate release RPM from these lists:
yum localinstall http://yum.theforeman.org/releases/1.4/el6/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm
yum localinstall http://yum.theforeman.org/releases/1.4/f19/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm
For release candidate or nightly RPMs, change the URL as appropriate based on the above list of available repositories.
Signing
Release and release candidate packages are signed by the “Foreman Automatic Signing Key (2014) packages@theforeman.org” (0x1AA043B8). Nightly packages are not signed.
A copy of the key is available from public keyservers or here.
Available packages
Install foreman and other foreman-* packages to add functionality:
foreman Foreman server
foreman-proxy Foreman Smart Proxy
foreman-compute EC2, OpenStack and Rackspace provisioning support
foreman-libvirt libvirt provisioning support
foreman-ovirt oVirt/RHEV provisioning support
foreman-vmware VMware provisioning support
foreman-cli Foreman CLI utility
foreman-console Console additions
foreman-selinux SELinux targeted policy
foreman-mysql2 MySQL database support
foreman-postgresql PostgreSQL database support
foreman-sqlite SQLite database support
Setup
- Configure by editing
/etc/foreman/settings.yamland/etc/foreman/database.yml - After changing the database, migrate it:
sudo -u foreman /usr/share/foreman/extras/dbmigrate - Start the foreman service or set up passenger:
service foreman start
Upgrade
3.3.2 Software Collections
The RPMs use a packaging technique called Software Collections, or SCL. This provides Ruby and all dependencies required to run Foreman separately from the version of Ruby provided by the distribution.
The current stack is “ruby193”, which provides Ruby 1.9.3 and Ruby on Rails 3.2. All packages will have a “ruby193-“ prefix, allowing them to be easily identified, and will install entirely underneath /opt/rh/ruby193.
The system Ruby version is left alone and will still be used for packages provided both by the distribution, and other third parties who target the system Ruby (e.g. Puppet packages).
Foreman currently uses SCL only on RHEL and EL clones where a newer version of Ruby is desired. Fedora only uses the distro version of Ruby.
In order to run rake commands for Foreman, or scripts that run in the same environment, ruby193-rake and ruby193-ruby wrappers are provided as alternatives for the usual rake or ruby. In order to run a series of commands or a script directly within the software collection, scl enable ruby193 'other command' can be used. It is also possible to run scl enable ruby193 bash to get a shell within the context of the SCL. Foreman rake tasks should be run with “foreman-rake”, which automates this process.
More general information about software collections is available from these links:
- RHEL packaging: Software Collections (SCLs)
- Fedora Contributor Documentation: Software Collections Guide
Passenger under the SCL
When running Foreman under Passenger (the default installer setup), a specific configuration is needed for SCL (on EL), since Foreman operates under the SCL Ruby and other apps such as the puppetmaster will use the system Ruby. Passenger 4 is shipped in the Foreman repos as it can be configured with separate Ruby binaries per VirtualHost. The full configuration is described below.
The following packages must be installed:
- mod_passenger
- ruby193-rubygem-passenger
- ruby193-rubygem-passenger-native
- ruby193-rubygem-passenger-native-libs
- rubygem-passenger
- rubygem-passenger-native
- rubygem-passenger-native-libs
Ensure all version numbers match and are at least 4.0. mod_passenger provides the Apache module, while there are two copies of the Ruby components, one for the SCL Ruby (ruby193-rubygem-*) and one for the system Ruby (rubygem-*).
The /etc/httpd/conf.d/passenger.conf file is supplied by mod_passenger and should contain:
LoadModule passenger_module modules/mod_passenger.so
<IfModule mod_passenger.c>
PassengerRoot /usr/lib/ruby/gems/1.8/gems/passenger-4.0.5
PassengerRuby /usr/bin/ruby
</IfModule>
Check for .rpmsave or .rpmnew config backup files if this isn’t correct. Note that this refers to the system Ruby paths by default, allowing everything except Foreman (i.e. the puppetmaster) to run under the system Ruby.
Next, the Foreman config file at /etc/httpd/conf.d/foreman.conf must contain this entry in both HTTP and HTTPS VirtualHost sections:
PassengerRuby /usr/bin/ruby193-ruby
The full foreman.conf template from the installer is available here for comparison.
Ensure both RailsAutoDetect and RakeAutoDetect config entries are removed from foreman.conf and puppet.conf when using Passenger 4, since they have been deprecated.
When successfully configured, two Passenger RackApp processes will be visible and by inspecting the open files, the Ruby version being loaded can be confirmed:
# ps auxww | grep RackApp
foreman 16627 0.1 15.4 466980 157196 ? Sl 07:35 0:09 Passenger RackApp: /usr/share/foreman
puppet 16697 0.8 11.3 253080 115720 ? Sl 07:35 1:13 Passenger RackApp: /etc/puppet/rack
# lsof -p 16697 | grep libruby
ruby 16697 puppet mem REG 253,0 951224 272286 /usr/lib64/libruby.so.1.8.7
# lsof -p 16627 | grep libruby
ruby 16627 foreman mem REG 253,0 2041096 171190 /opt/rh/ruby193/root/usr/lib64/libruby.so.1.9.1
3.3.3 Debian Packages
The Foreman packages should work on the following Debian-based Linux distributions:
Distributions
- Debian Linux 7.0 (Wheezy)
- Debian Linux 6.0 (Squeeze)
- Ubuntu Linux 12.04 LTS
Foreman might still work on these distros, but it has not been tested (let us know if it works for you):
- Debian Linux 5.0 (Lenny)
- Ubuntu Linux 11.04
- Ubuntu Linux 10.10
If you encounter any errors during the installation, please file a bug report!
Apt Configuration
Add one of the following lines to your /etc/apt/sources.list (alternatively in a separate file in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/foreman.list):
# Stable packages
# Debian Wheezy
deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ wheezy 1.4
# Debian Squeeze
deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ squeeze 1.4
# Ubuntu Precise
deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ precise 1.4
# Nightly builds. Beware: HERE BE DRAGONS
# Debian Wheezy
deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ wheezy nightly
# Debian Squeeze
deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ squeeze nightly
# Ubuntu Precise
deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ precise nightlyYou may also want some plugins from the plugin repo:
# Plugins compatible with Stable
deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ plugins 1.4
# Plugins compatible with Nightly
deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ plugins nightlyThe public key for secure APT can be downloaded here
You can add this key with
apt-key add pubkey.gpg
or combine downloading and registering:
wget -q http://deb.theforeman.org/pubkey.gpg -O- | apt-key add -
The key fingerprint is
7059 542D 5AEA 367F 7873 2D02 B348 4CB7 1AA0 43B8 Foreman Automatic Signing Key (2014) <packages@theforeman.org>
Remember to update your package lists!
apt-get update
Install packages
The packages are now split by gem dependencies - there are 11 packages to choose from. These are:
Main package:
- foreman
Database gems - you need at least one of these:
- foreman-sqlite3
- foreman-mysql2
- foreman-pgsql
Optional functionality:
- foreman-console
- foreman-compute
- foreman-libvirt
- foreman-ovirt
- foreman-test
- foreman-vmware
Command line interface:
- ruby-hammer-cli
- ruby-hammer-cli-foreman
Installation instructions are:
# Install packages (adjust additional packages as needed)
apt-get install foreman foreman-sqlite3 foreman-libvirt
# Copy sample db config to /etc
cp /usr/share/foreman/config/database.yml.example /etc/foreman/database.yml
# Review settings and DB config
vi /etc/foreman/settings.yaml /etc/foreman/database.yml
# Perform initial DB setup
foreman-rake db:migrate
foreman-rake db:seedThe packages should auto-run db:migrate and db:seed if /etc/foreman/database.yml exists. So the initial DB setup is only needed during first install, upgrades should just work.
Upgrade
3.4 Install From Source
Installing the latest development code: Foreman has now moved to using Rails 3 and Bundler to get up and running. This is the preferred way to get Foreman if you want to benefit from the latest improvements. By using the git repository you can also upgrade more easily. You will need to have Bundler installed manually for now (check your distribution repositories, or install it via rubygems).
Foreman will run with the following requirements (aside from rubygem dependencies):
- Ruby 1.8.7 or 1.9
- rubygems
- Puppet >= 0.24.4
The installation has been successfully tested on RHEL[5,6], Fedora[13,14,15,16,17], Debian Linux 6.0 (Squeeze) and Ubuntu Linux 12.04 (the community has reported varying success with other Debian/Ubuntu versions - 12.10 seems fine for example). For older operating systems you might need additional packages (e.g. sqlite). It is also known to work on Solaris and Mac.
to get latest “development” version do:
You will want to make sure that you have one of the mysql-devel, postgresql-devel, and sqlite-devel libraries installed so the database gems can install properly. Also, you would also need gcc, ruby-devel, libxml-devel, libxslt-devel, and libvirt-devel packages
For RHEL6 or clones, you can issue the following commands to install all required packages:
yum groupinstall "Development Tools" "Development Libraries"
yum -y install gcc-c++ git ruby ruby-devel rubygems \
libvirt-devel mysql-devel postgresql-devel openssl-devel \
libxml2-devel sqlite-devel libxslt-devel zlib-devel \
readline-devel tar
Additionally, it is important that config/database.yml is set to use
the correct database in the “production” block. Rails (and subsequently
Foreman) will use these connection settings under “production” to manage
the database it uses and setup the necessary schema.
git clone https://github.com/theforeman/foreman.git -b develop
cd foreman
cp config/settings.yaml.example config/settings.yaml
cp config/database.yml.example config/database.yml
gem install bundler
# depending on database configured in yml file you can skip others
# (we are assuming sqlite to be configured)
bundle install --without mysql2 pg test --path vendor # or postgresql
# set up database schema, precompile assets and locales
RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:migrate
RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:seed assets:precompile locale:packYou can run Foreman with the command ”./script/rails s -e production”
foreman-rake <task> to run rake tasks, however when installed from source, replace this with bundle exec rake <task> RAILS_ENV=productionLatest stable version
to get latest “stable” version do:
git clone https://github.com/theforeman/foreman.git -b 1.4-stableCLI (Hammer)
To install hammer from git checkouts, you will just need rake installed on your system.
Clone and install CLI core
$ git clone https://github.com/theforeman/hammer-cli.git
$ cd hammer-cli
$ rake install
$ cd ..and clone plugin with foreman commands
$ git clone https://github.com/theforeman/hammer-cli-foreman.git
$ cd hammer-cli-foreman
$ rake install
$ cd ..You can install other hammer plugins via any of the methods mentioned above.
3.5 Configuration
The following sections detail the configuration steps required to get Foreman working in your environment. Lets get started!
3.5.1 Initial Setup
Configuration
Foreman configuration is managed from two places; a configuration file config/settings.yaml and from the SETTINGS/Foreman Settings page. A full description of the configuration options is given at foreman_configuration
Database
Foreman requires a database of its own to operate - database sharing is unsupported. By default, the installer uses PostgreSQL, while a package or source installation will use SQLite. If you want to use other database (e.g. MySQL) please modify the configuration file under config/database.yml.
In all cases, please use the production settings.
to initialize the database schema and content, run:
foreman-rake db:migrate foreman-rake db:seed
For more information please see the database configuration page here
Import Data from Puppet
At this point, you might want to go through the [[FAQ]] to see how can you import your data into Foreman.
Start The Web Server
if you installed via rpm, just start the foreman service, or start the builtin web server by typing:
RAILS_ENV=production rails server
and point your browser to http://foreman:3000
If you would like to keep the server running, its recommend to setup passenger or use the RPM. Example usage with passenger can be found on GitHub.
Getting your Puppet Reports into Foreman
Read Puppet_Reports to learn how to get your nodes to report to Foreman.
3.5.2 Configuration Options
Configuration is broken into two parts. The /etc/foreman/settings.yaml file and the Administer > Settings page. The configuration file contains a few low-level options that need to be set before Foreman starts but the majority of Foreman customization is managed from within the web interface on the Settings page.
The configuration file can also override those settings specified in the web interface. Any settings added in the config file that are available in the web interface will be made read-only.
The config/settings.yaml file
YAML start
The first non-comment line of this file must be three dashes.
---
login
This boolean option configures whether Foreman requires users to to login. If it is set then each user will be expected to authenticate themselves and all operations will occur, and be audited, under their identity. When this option is false then all activity will be executed under the admin account.
:login: true
require_ssl
This boolean option configures whether Foreman insists on using only https/ssl encrypted communication channels in the web interface. This does not configure the channels used to contact the smart-proxies. Note that certain operations will still accept a http connection even if this is set, for example, the downloading of a finish script.
:require_ssl: true
unattended
This boolean option configures whether Foreman will act as a simple node classifier for puppet, or support the full spectrum of operations required for managing a host’s lifecycle. When set to true then foreman will provide full host building facilities for various operating systems.
:unattended: true
The ‘Administer/Settings’ page
administrator
When Foreman needs to mail the administrator then this is the email address that it will contact.
Default: root@
authorize_login_delegation
mod_proxy and other load balancers will set a REMOTE_USER environment variable. If this is true , your users will be able to login through an external service and Foreman requests will be authenticated using this REMOTE_USER variable. Default: true
authorize_login_delegation_api
Same as above, but this setting allows REMOTE_USER authentication for API calls as well. Default: true
authorize_login_delegation_auth_source_autocreate
If you have authorize_login_delegation set, new users can be autocreated through your external authentication mechanism by changing this to the name of the Auth Source you want to use to auto create users. Default: ‘’
create_new_host_when_facts_are_uploaded
When facts are received from Puppet or other configuration management systems, a corresponding host will be created in Foreman if the certname or hostname is unknown. When false, this behavior is disabled and facts will be discarded from unknown hosts. Default: true See also: create_new_host_when_report_is_uploaded
create_new_host_when_report_is_uploaded
If a report is received from Puppet or other configuration management systems, a corresponding host will be created in Foreman if the hostname is unknown. When false, this behavior is disabled and reports will be discarded from unknown hosts. Default: true See also: create_new_host_when_facts_are_uploaded
default_puppet_environment
When Foreman receives a fact upload from a machine that it has not previously come across it will create a host in its database. If the facts from that host did not contain information about the puppet environment then it will assign the default_puppet_environment environment to this host. Default: production
Default_variables_Lookup_Path
A Smart-variable’s match criteria are evaluated in a specific order and if this search order is not provided then Default_variables_Lookup_Path is used. Default: [“fqdn”, “hostgroup”, “os”, “domain”]
document_root
Puppetdoc will create RDoc documents for your manifests if its available. This setting allows you to select the directory where you want these documents to be created. Default: foreman_root/public/puppet/rdoc
email_reply_address
The return address applied to outgoing emails. Default: Foreman-noreply@<your domain>
enc_environment
When this is true, Foreman will send the puppet environment in the ENC yaml output. This is meant to fix conflicts between a node’s puppet.conf environment and the environment set in Foreman. On Puppet 3+, agents will take the environment sent by the ENC. When false, the ENC yaml will not contain the environment, the node will not update its environment and use the one at puppet.conf. Default: true
Enable_Smart_Variables_in_ENC
Whether Smart-variables should be included in the yaml node information provided to puppet. Default: true
entries_per_page
The number of entries that will be shown in the web interface for list operations. Default: 20
failed_report_email_notification
If this option is set to true then an email will be sent to the host’s owner whenever a report is received that contains errors. If the host is not owned or Foreman is not configured to use logins then send the email to the administrator. Default: false
foreman_url
Emails may contain embedded references to Foreman’s web interface. This option allows the URL prefix to be configured. Default: https://FQDN/ or http://FQDN/ (depending on require_ssl) See also: unattended_url
host_group_matchers_inheritance
Matchers used in smart variables or class parameters to match host groups can be inherited by children of those matching host groups too (e.g. a matcher for hostgroup=Base will also apply to Base/Web). Set this to false to make matchers only match a particular hostgroup and not its children. Default: true
idle_timeout
Users that stay idle (no requests sent to Foreman) for more than this number of minutes will be logged out. Default: 60
interpolate_erb_in_parameters
If true, Foreman variables will be exposed to the ENC. Check Template Writing for a more comprehensive guide on how to create and use these variables in your ERB templates. Default: true
ignore_puppet_facts_for_provisioning
If this option is set to true then Foreman will not update a host’s IP and MAC with the values that it receives in a host’s facts and it will also include Foreman’s values for IP and MAC to puppet in its node information. Default: false
legacy_puppet_hostname
This setting truncates the hostname of your smart proxy to ‘puppet’ if it starts with ‘puppet’. Default: false
libvirt_default_console_access
The IP address that should be used for the console listen address when provisioning new virtual machines via Libvirt. Default: 0.0.0.0
login_delegation_logout_url
If your external authentication system has a logout URL, redirect your users to it here. This setting can be useful if your users sign in Foreman through SSO, and you want them to sign out from all services when they log out Foreman. Default: ‘’
manage_puppetca
If this option is set to true then Foreman will manage a host’s Puppet certificate signing. If it is set to false then some external mechanism is required to ensure that the host’s certificate request is signed. Default: true
max_trend
Days that trend graphs will capture. Default: 30
modulepath
This it the modulepath that foreman uses when processing puppet modules. It is usually able to determine this itself at runtime but if it is not able to find a value then modulepath is used. Default: /etc/puppet/modules
oauth_active
Enables OAuth authentication for API requests. Default: false
oauth_consumer_key
OAuth consumer key Default: ‘katello’
oauth_consumer_secret
OAuth consumer secret Default: ‘shhhh’
oauth_map_users
This allows OAuth users to specify which user their requests map to. When this is false, OAuth requests will map to admin. Default: true
Parametrized_Classes_in_ENC
In Puppet 2.6.5+, the ENC may send a hash of the class’s attributes and values. Before then, the ENC used to send just an array of class names. Set this to true if you are using any version of Puppet equal to or higher than 2.6.5. Default: true
puppet_interval
This is the number of minutes between each run of puppet. Default: 30
puppet_server
The default puppet server hostname. For larger organizations this is often a non fqdn so that a name like puppet can be a different host within each DNS domain. Default: puppet
puppetrun
If this option is set to true then Foreman will be able to trigger a puppet run on any host that it manages. Default: false
query_local_nameservers
If true, Foreman will query the local DNS. When false Foreman will query the SOA/NS authority. Warning! Querying a resolver can cause Foreman to get false positives when checking presence of DNS records due to caching. Default: false
remote_addr
If Foreman is running behind Passenger or a remote load balancer, the IP of this load balance should be set here. This is a regular expression, so it can support several load balancers, i.e: (10.0.0.1|127.0.0.1) Default: 127.0.0.1
remove_classes_not_in_environment
This setting forces your host to only pick up classes known to be in its environment. It will avoid Puppet errors caused by trying to pick up classes in other environments, this could happen if your host is in environment ‘production’, but its host group is in environment ‘staging’. Default: false
require_ssl_puppetmasters
When set to true, Foreman requires a client SSL certificate on requests from puppet masters, and will verify the CN of the certificate against the known smart proxies. If false, it uses the reverse DNS of the IP address making the request. require_ssl in config/settings.yaml should be enabled too. For more information about securing the connection between Foreman and puppet masters, see Section 5.4.1
Default: true
restrict_registered_puppetmasters
When set to true, you will have to register your puppet masters as Smart Proxies with the Puppet feature so they can access fact/report importers and ENC output. Default: true
root_pass
If a root password is not provided whilst configuring a host then this encrypted password is used when building the machine. The plain text password “123123” has been encrypted to produce the default value. Default: xybxa6JUkz63w (To generate a new one you should use: openssl passwd -1 “your_password” )
safemode_render
The default templating system used within Foreman allows unlimited interpolated variables and expressions. This could obviously be abused so a evaluation environment is provided that restricts the template variables and expressions to a whitelist. When this option is true then only known helper methods and instance variables will be available in template expansion. Default: true
signo_sso
Use Signo as SSO login. Default: false
signo_url
Signo SSO url for login. Default: https://theforeman/signo
ssl_client_dn_env
Environment variable containing the subject DN from a client SSL certificate Default: SSL_CLIENT_S_DN
ssl_client_verify_env
Environment variable containing the verification status of a client SSL certificate Default: SSL_CLIENT_VERIFY
ssl_ca_file
The SSL Certificate Authority file that Foreman will use when connecting to its smart-proxies. Default: The CA file used by puppet
ssl_certificate
The SSL certificate that Foreman will use when connecting to its smart-proxies. Default: The host certificate used by puppet
ssl_priv_key
The SSL private key file that Foreman will use when connecting to its smart-proxies. Default: The private key file used by puppet
token_duration
Time in minutes installation tokens should be valid for, 0 to disable. Default: 60
trusted_puppetmaster_hosts
Other trusted puppet masters in addition to Smart Proxies to access fact/report importers and ENC output. i.e: [puppetmaster1.yourdomain.com, puppetmaster2.yourdomain.com] Default: []
unattended_url
This controls the URL prefix used in provisioning templates such as TFTP/PXELinux files that refer to the Foreman server. It is usually HTTP rather than HTTPS due to lack of installer support for HTTPS. Default: http://FQDN/ See also: foreman_url
update_environment_from_facts
If Foreman receives an environment fact from one of its hosts and if this option is true, it will update the host’s environment with the new value. By default this is not the case as Foreman should manage the host’s environment. Default: false
update_ip_from_built_request
If true, Foreman will update the host IP with the IP that made the ‘build’ request. This request is made at the end of a provisioning cycle to indicate a host has completed the build. Default: false
use_shortname_for_vms
When false, any hosts created on a compute resource will use the FQDN of the host for the name of the virtual machine. When set to the true, the short name (i.e. without domain) will be used instead. Default: false
use_gravatar
Display user avatars by matching their emails with emails at Gravatar.com Default: true
use_uuid_for_certificates
When enabled, Foreman will generate UUIDs for each host instead of using the hostname as the Puppet certname, which is more reliable with changing hostnames. Note that when disabling this setting, existing stored certnames won’t be changed or discarded until new certificates are requested from a host (i.e. on a rebuild), in order that the existing certificate remains known to Foreman and can be revoked.
3.5.3 Database Setup
Foreman is a rails application. Therefore, anything that is supported under RAILS (sqlite, mysql, postgresql, …) can be used. See 3.3 Install From Packages for a list of packages for connecting foreman to the databse of your choice. At this time, Oracle DB is known to not work. Patches are welcome!
The database configuration file can be found at:
/etc/foreman/database.yml
SQLite (default)
By default, the database will be created in the db subdirectory.
production:
adapter: sqlite3
database: db/production.sqlite3
pool: 5
timeout: 5000MySQL
Edit your config/database.yml and modify:
production:
adapter: mysql2
database: foreman
username: foreman
password: password
host: localhost
socket: "/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock"Prior to version 1.4, the foreman-mysql package was available, however support of this and the legacy ‘mysql’ adapter has been discontinued.
Afterwards you would need to re-populate your database, simply execute:
foreman-rake db:migrate
foreman-rake db:seed
PostgreSQL
Edit your config/database.yml and modify:
production:
adapter: postgresql
database: foreman
username: foreman
password: password
host: localhostSwitching from SQLite to MySQL/PostgreSQL while maintaining existing data
We have a rake task for this. First setup your database.yml to have the sqlite db as production and the mysql/psql db as dev:
production:
adapter: sqlite3
database: db/production.sqlite3
pool: 5
timeout: 5000
development:
adapter: postgresql
database: foreman
username: foreman
password: password
host: localhostNow migrate both dbs so they’re consistent:
bundle exec rake db:migrate RAILS_ENV=production
bundle exec rake db:migrate RAILS_ENV=developmentNow move the data to the new db
bundle exec rake db:convert:prod2dev(On RPM distros, remove “bundle exec” from the start of these commands.)
Once you’ve migrated to your new database using prod2dev, you should update your database.yml file to point your ‘production’ environment at the new database. You should also update the ‘development’ environment to point to an alternative location (for example, at SQLite) to ensure you don’t accidentally overwrite your production database.
Special notes for migrating to Postgres
Firstly, the default installer setup doesn’t give superuser privileges to the ‘foreman’ user, which then prevents the prod2dev script from temporarily disabling foreign keys. You’ll need to do
sudo -u postgres psql -c 'ALTER USER foreman WITH SUPERUSER'before the prod2dev call, and
sudo -u postgres psql -c 'ALTER USER foreman WITH NOSUPERUSER'after it.
Secondly, the psql sequence numbers will be wrong after the prod2dev execution. You can fix them like this:
cat <<EOF > reset.sql
SELECT 'SELECT SETVAL(' ||quote_literal(S.relname)|| ', MAX(' ||quote_ident(C.attname)|| ') ) FROM ' ||quote_ident(T.relname)|| ';'
FROM pg_class AS S, pg_depend AS D, pg_class AS T, pg_attribute AS C
WHERE S.relkind = 'S'
AND S.oid = D.objid
AND D.refobjid = T.oid
AND D.refobjid = C.attrelid
AND D.refobjsubid = C.attnum
ORDER BY S.relname;
EOF
psql -Atq -f reset.sql -o temp foreman
psql -f temp foreman
rm temp reset.sql(big thanks to Fixing Sequences for the fix)
3.5.4 Puppet Reports
Foreman uses a custom puppet reports address (similar to tagmail or store) which Puppet will use to upload it’s report into Foreman. This enables you to see the reports through the web interface as soon as the client finishes its run.
Configuration
Client
Ensure that the puppet clients has the following option in their puppet.conf:
report = true
Without it, no reports will be sent.
puppetmaster
- copy https://raw.github.com/theforeman/puppet-foreman/master/templates/foreman-report_v2.rb.erb to your report directory
- e.g. /usr/lib/ruby/1.8/puppet/reports/foreman.rb, /usr/lib/ruby/site_ruby/1.8/puppet/reports/foreman.rb, /var/lib/gems/1.8/gems/puppet-2.6.4/lib/puppet/reports/foreman.rb or /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/puppet/reports.
- make sure you copied the foreman-report_v2.rb.erb to foreman.rb so puppet can find it!
- open the new file with your favorite editor
- edit the URL to point to foreman.
- add this report in your puppetmaster reports - e.g, in your master puppet.conf under the main section add:
reports=log, foreman
and restart your puppetmaster
You should start seeing reports coming in under the reports link.
Expire Reports automatically
You will probably want to delete your reports after some time to limit database growth. To do so, you can set a cronjob:
Available conditions:
- days => number of days to keep reports (defaults to 7)
- status => status of the report (defaults to 0 –> “reports with no errors”)
Example:
- Expires all reports regardless of their status
foreman-rake reports:expire days=7
- expires all non interesting reports after one day
foreman-rake reports:expire days=1 status=0
3.5.5 Facts and the ENC
Foreman can act as a classifier to Puppet through the External Nodes interface. This is a mechanism provided by Puppet to ask for configuration data from an external service, via a script on the puppetmaster.
The external nodes script we supply also deals with uploading facts from hosts to Foreman, so we will discuss the two things together.
Configuration
puppetmaster
- Copy external_node_v2.rb.erb to the Puppet configuration directory, e.g. ‘/etc/puppet’
- The name you choose for the file is arbitrary, but we will assume ‘node.rb’, e.g. ‘/etc/puppet/node.rb’. Ensure it is executable by the puppet user.
- Edit the new file, and configure the settings:
- url - The address of the Foreman server (e.g. http://foreman )
- puppetdir - The location of Puppet’s cache dir (e.g. /var/lib/puppet )
- ssl_* - SSL certs as per Securing Communications With SSL
- Add the following lines to the [master] section of puppet.conf:
- external_nodes = /etc/puppet/node.rb
- node_terminus = exec
Restart the puppetmaster. When the next agent checks in, the puppetmaster will upload fact data for this host to Foreman, and download the ENC data.
Client
No agent configuration is necessary to use this functionality.
Testing the config
Make sure that the puppet user can execute the ENC script and it works:
sudo -u puppet /etc/puppet/node.rb [the name of a node, eg agent.local]
should output something like:
parameters:
puppetmaster: puppet
foreman_env: &id001 production
classes:
helloworld:
environment: *id001
This output should match the information displayed when you click on the YAML button on the Host page in Foreman.
For further information see the Puppet Labs docs on external nodes
Assigning data to hosts through the ENC
Foreman passes all assoicated parameters, classes,and class parameters, to the Host, including those inherited from host groups, domains, or global settings. See section Managing Puppet for more information on assigning configuration to hosts.
Pushing Facts to Foreman when not using the ENC functionality
There are several options for pushing fact data to Foreman if you are using Foreman for reporting/inventory only.
Using node.rb
The ENC script (node.rb) accepts an option to run in ‘batch-mode’. In this mode, the script iterates over the cached fact data stored on the puppet master, and uploads all of it to Foreman.
Download and configure the node.rb script as above, and then call it like this:
sudo -u puppet /etc/puppet/node.rb --push-facts
Direct HTTP upload
As of Foreman 1.3, the fact-upload API endpoint accepts data in pure JSON. You can push data to Foreman as a hash containing:
{
"name": "fqdn-of-host.domain.com",
"certname": "optional-certname-of-host.domain.com",
"facts": {
"fact1": "string",
"fact2": "true",
"fact3": "1.2.3.4",
...
}
}
The ‘certname’ is optional but will be used to location the Host in Foreman if supplied. The ‘facts’ hash must be a flat hash, not nested with other arrays or hashes. See link-to-API-when-its-updated-here for more details.
This body can be POSTed to ‘/api/hosts/facts’ using Foreman API v2. See the node.rb template for an example of constructing and sending data in Ruby.
3.5.6 CLI
The Command Line Interface is based on the hammer framework. The foreman-related commands are defined in plugin hammer_cli_foreman
Format and locations
Configuration is set based on the following files, loaded in this order:
/etc/foreman/cli_config.yml.~/.foreman/cli_config.yml./config/cli_config.yml(config dir in CWD)- custom location specified on command line -
-c CONF_FILE_PATH
Later files have precedence if they redefines the same option.
Hammer uses yaml formatting for its configuration. The config file template is contained in the hammer_cli gem
gem contents hammer_cli|grep cli_config.template.yml
and can be copied to one of the locations above and changed as needed. The packaged version of hammer copies the template to /etc for you.
Plugins
Plugins are disabled by default. You have to edit the config file and enable them manually under modules option, as can be seen in the sample config below.
Plugin specific configuration should be nested under plugin’s name.
Options
:log_dir: <path>- directory where the logs are stored. The default is/var/log/foreman/and the log file is namedhammer.log:log_level: <level>- logging level. One ofdebug,info,warning,error,fatal:log_owner: <owner>- logfile owner:log_group: <group>- logfile group:log_size: 1048576- size in bytes, when exceeded the log rotates. Default is 1MB:watch_plain: false- turn on/off syntax highlighting of data being logged in debug mode
Sample config
:modules:
- hammer_cli_foreman
:foreman:
:host: 'https://localhost/'
:username: 'admin'
:password: 'changeme'
:log_dir: '/var/log/foreman/'
:log_level: 'debug'3.6 Upgrade
Upgrading to Foreman 1.4
Preparation
Before updating to 1.4, make sure you have successfully upgraded to 1.3 first.
Upgrading across more than one version is not supported, so it’s required to upgrade to each intermediate version and follow all upgrade instructions for the previous versions.
Please check the upgrade notes for this release, as there may be things to be aware of or additional steps:
Step 1 - Backup
It is recommended that you backup your database and modifications to Foreman files(config/settings.yaml, unattended installations etc). Most upgrades are safe but it never hurts to have a backup just in case.
For more information about how to backup your instance head over to Backup
Step 2 - Perform the upgrade
Before proceeding, it is necessary to shutdown the Foreman instance.
Now it’s time to perform the actual upgrade. This process if different depending on how you downloaded Foreman. You only need to perform one of the following options.
Option 1 - Upgrading from a package on Fedora or RHEL
Upgrading from 1.3
To upgrade an existing Foreman 1.3 installation, first update with the appropriate foreman-release package from the above list of release packages, e.g. for RHEL6
yum upgrade http://yum.theforeman.org/releases/1.4/el6/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm
cat /etc/yum.repos.d/foreman.repo.rpmnew > /etc/yum.repos.d/foreman.repo
Clean up the yum cache:
yum clean all
Next upgrade all Foreman packages:
yum upgrade ruby\* foreman\*
If you wish to install the SELinux policy, also install the foreman-selinux package.
You can skip to Step 3.
Option 2 - Upgrading from a package on Debian or Ubuntu
Upgrading from 1.3
Upgrading from 1.3 to 1.4 has been tested on both Debian and Ubuntu. Updating the packages will upgrade the application and automatically migrate the database.
apt-get update apt-get dist-upgrade
You can skip to Step 3.
Option 3 - Downloaded release (tar.bz2)
- Uncompress the new program archive in a new directory.
- Copy your database settings-file
config/database.ymlinto the newconfigdirectory. - If your database is a simple file (e.g. SQLite), don’t forget to make it available in the new directory.
VERY IMPORTANT: do NOT overwrite config/settings.yml with the old one.
Option 4 - Upgrading from git
Please note now that the development branch has moved to Rails 3, you MUST take care to select a branch and make sure you get the correct one.
- Go to the Foreman root directory and run the following command:
For staying on the stable branch:
- git checkout 1.4-stable
- git pull
The following step is the one that could change the contents of your database. Go to your new Foreman directory (or the git dir), then migrate and update the contents of your database:
foreman-rake db:migrate
foreman-rake db:seed
You should compile i18n strings and precompile assets now:
foreman-rake locale:pack
foreman-rake assets:precompile
Step 3 - Cleanup
Database should be migrated already, but you can make sure by executing the migration script again, it should produce no errors or output:
foreman-rake db:migrate
foreman-rake db:seed
You should clear the cache and the existing sessions:
foreman-rake tmp:cache:clear
foreman-rake tmp:sessions:clear
Step 4 - Restart
Restart the application server (e.g. mongrel, thin, passenger)
Common issues
See Troubleshooting
4. General Foreman
This section covers general information on using Foreman to manage your infrastructure. It covers the features of the web interface, managing puppet, provisioning systems and the installation and configuration of Foreman Smart Proxies.
4.1 Web Interface
4.1.1 LDAP Authentication
Foreman natively supports LDAP authentication using one or multiple LDAP directories.
Enabling LDAP
Enable LDAP and User/Group settings menus
Edit your config/setting.yml
:login: true
and restart Foreman
Setting up
Go to Administer > LDAP Authentication
Click on New Authentication Source and enter the following
- Name: an arbitrary name for the directory
- Host: the LDAP host name
- Port: the LDAP port (default is 389)
- LDAPS: check this if you want or need to use LDAPS to access the directory
- Account: leave this field empty if your LDAP can be read anonymously, otherwise enter a user name that has read access to the LDAP or use $login (which will be replaced with the actual user credentials upon login)
- Account Password: password for the account (if defined above and its not using the $login)
- baseDN: the top level DN of your LDAP directory tree
On the fly user creation
By checking On-the-fly user creation, any LDAP user will have his Foreman account automatically created the first time he logs into Foreman. For that, you have to specify the LDAP attributes name (firstname, lastname, email) that will be used to create their Foreman accounts.
Examples
Active Directory
Name = My Directory Host = host.domain.org Port = 636 TLS = yes Onthefly register = yes Account = MyDomain\$login Password = (leave blank) Base DN = CN=users,DC=host,DC=domain,DC=org attr login = sAMAccountName attr firstname = givenName attr lastname = sN mail = mail
OpenLDAP
Name = My Directory Host = host.domain.org Port = 389 TLS = no Onthefly register = yes Account = (leave blank if anonymous access is enabled) Password = (leave blank) Base DN = ou=Users,dc=domain,dc=co,dc=il attr login = uid attr firstname = givenName attr lastname = sn mail = mail
Note that LDAP attribute names are case sensitive.
Troubleshooting
If you want to use on-the-fly user creation, make sure that Foreman can fetch from your LDAP all the required information to create a valid user. For example, on-the-fly user creation won’t work if you don’t have valid email addresses in your directory (you will get an ‘Invalid username/password’ error message when trying to log in).
4.1.2 Roles and Permissions
A user’s access to the features of Foreman are constrained by the roles and permissions that they are granted. These permissions are also used to restrict the set of hosts, host groups and domains that a user is able to access and modify.
Note: a user with global admin enabled is not restricted by the authorization system. This is the default for installations that do not have :login:true in config/settings.yml.
A logged in user will be granted the Anonymous role plus one or more additional roles. The permissions associated with these roles are aggregated and determine the final permission set.
Roles may be administered only by a user with global admin privileges.
Roles
These may be created, deleted and edited on the Roles page. Each role will be associates with one or more base privileges.
There are two builtin system roles
- Anonymous: This is a set of permissions that every user at your installation will be granted, irrespective of any other roles that they have.
- Default user: When a new Role is created this set of permissions are used as the template for the Role. The name is somewhat misleading but basically an ordinary default user who was assigned this Role would have these permissions set.
Permissions
These determine the operations that are allowed to be performed upon the items to which they refer. For simple items, like an architecture, this operates as expected but for more complex items, such as, the hosts a user is able to operate on, there is an additional layer of security called filtering.
When editing a user account there is a section at the bottom that narrows the scope of the permissions granted to a subset of the hosts, domains and host groups. See filtering below.
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Permissions for Architectures, Authentication providers, environments, External variables, Common parameters, Medias, Models, Operating systems, Partition tables, Puppet classes and User groups | |
| view | The user is allowed to see this type of object when listing them on the index page |
| create | The user is allowed to create this type of object |
| edit | The user is allowed to edit this type of object |
| destroy | The user is allowed to destroy this type of object |
| Permissions for Domains | |
| view | The user is allowed to see a list of domains when viewing the index page |
| create | The user is allowed to create a new domain and will also be able to create domain parameters |
| edit | The user is allowed to edit a domain and will also be able to edit a domain's parameters. If they have domain filtering active in their profile then only these domains will be editable |
| destroy | The user is allowed to destroy a domain and will also be able to destroy domain parameters. If they have domain filtering active in their profile then only these domains will be deletable |
| Permissions for Host groups | |
| view | The user is allowed to see a list of host groups when viewing the index page |
| create | The user is allowed to create a new host group and will also be able to create host group parameters |
| edit | The user is allowed to edit a host group and will also be able to edit a host group's parameters. If they have host group filtering active in their profile then only these host groups will be editable |
| destroy | The user is allowed to destroy a host group and will also be able to destroy host group parameters. If they have host group filtering active in their profile then only these host groups will be deletable |
| Permissions for Hosts | |
| view | The user is allowed to see a list of hosts when viewing the index page. This list may be constrained by the user's host filters |
| create | The user is allowed to create a new host. This operation may be constrained by the user's host filters |
| edit | The user is allowed to edit a host. This operation may be constrained by the user's host filters |
| destroy | The user is allowed to destroy a host. This operation may be constrained by the user's host filters |
| Permissions for Users | |
| view | The user is allowed to see a list of users when viewing the index page. A user will always be able to see their own account even if they do not have this permission |
| create | The user is allowed to create a new user |
| edit | The user is allowed to edit existing users. A user will always be able to edit their own basic account settings and password |
| destroy | The user is allowed to delete users from the system |
Filtering
If the filtering section at the bottom of the user’s profile page has no content then the permissions that the user has been granted will apply to all hosts within the system.
However, if the filtering section is in use then the permissions will apply only to those items selected in the filters and the user will have no access to anything not selected by the filters.
This is primarily a mechanism for restricting access to hosts. However if one or more domains or host groups are selected then this also restricts where parameters can be created, edited and deleted.
Filtering operates by generating a list of hosts on which actions can be performed. The list may be built out of four components
-
Ownership: The hosts that a user owns directly or hosts that are owned by a user group of which the user is a member.
-
Domain membership: The hosts that exist within one or more indicated domains.
-
Compute resource membership: The hosts that are deployed on one or more compute resources.
-
Host group membership: The hosts that are defined as being of one or more host group types.
-
Fact filtering: These restrict the hosts to those machines that have this fact associated with them. As a fact is only generated during a puppet run, this filter will only refer to machines that have been built and therefore cannot be used to restrict the creation of machines.
These four pools of hosts can be combined by adding them together or the filters can be used to restrict the selected hosts to a smaller and smaller subset of the total. Think of it as set operations.
Note: If the “Administrator” check box is checked for a user, filtering will not take effect.
Example
A user’s filter section has the select checkbox unticked, indicating that the user’s owned hosts are not included in the final set of hosts, (unless they are selected some other way.)
The domain selection is prefixed with plus all and the two domains a.com and b.com are ticked. This implies that the hosts selected are the user’s hosts, (of which there are none,) plus all the hosts in a.com and b.com.
The host group section is prefixed by must be and the hostgroup web server is selected. This implies that the hosts selected are the user’s hosts, (of which there are none,) plus all the hosts in a.com and b.com but they must be of type web server.
The fact filter section is prefixed by must match and there are two filters virtual = vmware and architecture = i386. This implies that the hosts selected are the user’s hosts, (of which there are none,) plus all the hosts in a.com and b.com but they must be of type web server and must match an i386 vmware host.
In any of these sections above, if the prefix had been plus all then every host in the system that matched the selections would have been added to the final host list, (though possibly removed by a later filter.)
4.1.3 Trends
Trends in Foreman allow you to track changes in your infrastructure over time. It allows you to track both Foreman related information and any puppet facts. The Trend pages give a graph of how the number of hosts with that value have changed over time, and the current hosts list.
There are two pieces to the Trends area, the Trends to track and their corresponding counters. To define trend counters, use the “Add Trend Counter” button on the ‘/trends’ page. Optionally set the “Name” field to over-ride odd puppet fact names to be more readable. Once created you can optionally ‘Edit’ the Trend to change the display names of the underlying values.
Next, to start collecting trend data, set a cron job to execute ‘foreman-rake trends:counter’. Each time the rake task executes it will create 1 tick on the graphs, so you can fine tune the granularity with your cron job. We recommend using the same as your puppet run interval (30 minutes). Here’s an example to run once per hour:
0 * * * * /usr/sbin/foreman-rake trends:counterFinally note that these trends are the same for all users. So if you delete a Trend category you will loose all history for that trend and the trackers will start all over again. So please be careful when deleting.
4.1.4 Auditing
Foreman supports auditing of almost all changes that happen within Foreman, from both the UI and from the API. Auditing is done at a user level, and is thus ineffective if :login: is set to false, as all audits will be done as the ‘admin’ user.
Basic View
Got to the Audit tab to see a view of what has changed. This view can be filtered by the type of change or by the object that was altered (e.g. search for a hostname to see all changes relating to that host). You also get the parent object - so if a parameter was modified, you can see what host/group that parameter belongs to. The timestamp of the change and the user who performed it will be listed.
Extended Audits for Templates
Template changes also store a diff of the changes, and the ability to roll back to a previous version of the template.
4.2 Managing Puppet
In this section we’ll look at the various ways we can control and interact with Puppet.
4.2.1 Environments
Puppet environments are mapped directly into Foreman. They can be used at various levels throughout the Foreman interface. Puppet environments are generally used to separate classes from different types of Host, typically allowing changes to a module to tested in one environment (e.g. development) before being pushed to another (e.g production).
Defining Environments
There are several ways to create Puppet environments within Foreman.
Manual creation
To create an environment by hand, simply go to Configure > Environments and click New Puppet Environment. Give the new environment a name and save.
Importing from Puppet
Foreman can detect all the environments and classes contained on a PuppetMaster, and import them automatically. To do this, go to Configure > Environments and click on *Import from
Assigning Environments to Hosts
This is done from the Host Edit page, on the Host tab. Selecting an environment will filter the classes visible on the Puppet Classes tab to just the classes in the selected environment.
You can also also mass-assign an environment to a group of hosts - tick the checkboxes of the required Hosts in the Hosts index, and then select Change Environment from the buttons at top of the page.
Environments with Hostgroups
You can assign an environment to a hostgroup as well. This functions as a form of default - a user creating a new host and selecting the hostgroup will automatically have the environment pre-selected. The user is not prevented from changing the environment of the new host, it simply saves a few clicks if they are happy with it.
4.2.2 Classes
Puppet classes are generally imported from the Puppet Master(s) via the Import button on the Puppet Classes page. They can also be created by hand, and manually associated with a set of environments (for filtering purposes).
Importing Classes
Go to Configure > Puppet Classes and click the Import button. This will not be visible unless you have at least one Puppet Master with a puppet-enabled Smart Proxy. Only classes from modules will be imported.
The “Hosts” Column
Under Configure > Puppet Classes you will also see a column called “Hosts”. This column represents the number of hosts the given module/class has been assigned to. Clicking this figure will list the hosts.
This column currently suffers from a known bug. This bug means this count excludes host groups from final figure.
Ignoring classes on import
It’s often to have a module structure like this:
$ tree git/
git/
└── manifests
├── init.pp
├── install.pp
├── params.pp
└── repo.ppIn this situation, Foreman would offer to create:
git
git::install
git::params
git::repoHowever, if we know that the subclasses are not intended for direct consumption, but are only really part of the internal structure of the module, then we would want to exclude those from the import mechanism, so that Foreman only offers to import git. We can achieve this via the file /usr/share/foreman/config/ignored_environments.yml. This file takes a set of regular expressions - any class which matches one of them will not be imported. So, for this example, we might configure:
:filters:
- !ruby/regexp '/install$/'
- !ruby/regexp '/params$/'
- !ruby/regexp '/repo$/'Assigning Classes to Hosts
To cause Puppet to apply your classes, you will need to assign them to your Hosts. This can be done at either an individual host level, or at a group level. The process is the same; edit the Host(group), select an Environment, and then go to the Puppet Classes tab and select what classes you want in this Host(Group).
Checking the results
To see how Foreman is passing the classes to Puppet, go to a Host and click the YAML button. You will be shown the exact YAML data sent to the PuppetMaster - the classes will be in the “classes” hash.
4.2.3 Parameters
Foreman’s concept of parameters maps onto Puppet’s idea of default-scope parameters. Foreman allows us to define a hierarchy of parameter inheritance.
Global Parameters
These are defined in Configure > Global Parameters and will apply to every host in Foreman.
Domain Parameters
These are defined for all Hosts in a given domain. Edit the domain from Infrastructure > Domains and switch to the Parameters tab and specify a parameter. If it has the same name as a Global Parameter, it will override the Global one.
Hostgroup Parameters
These are defined for all Hosts in the Group. Edit the Hostgroup from Configure > Host Groups and switch to the Parameters tab and specify a parameter. If it has the same name as a Global or Domain Parameter, it will override it.
Host Parameters
The final (most-specific) level of Parameters applies only to a single Host. Edit a Host and switch to Parameters, and you will see all it’s inherited parameters from the other three layers (note: they will all be marked as “Scope: Global” as this refers to the Puppet scope, not the Foreman scope). You can override higher-level parameters or define new ones here.
Checking the results
To see how Foreman is passing the parameters to Puppet, go to a Host and click the YAML button. You will be shown the exact YAML data sent to the PuppetMaster -the parameters will be in the “parameters” hash.
4.2.4 Smart Variables
Smart variables are a tool to provide data (Key / Value), normally to your puppet ENC, depending on a set of rules. They are intended to be a stepping stone to full parameterized classes.
Smart variable is usually associated with a puppet class, and may have multiple values, all depending on hierarchical context or various conditions a user can wish to apply.
for example:
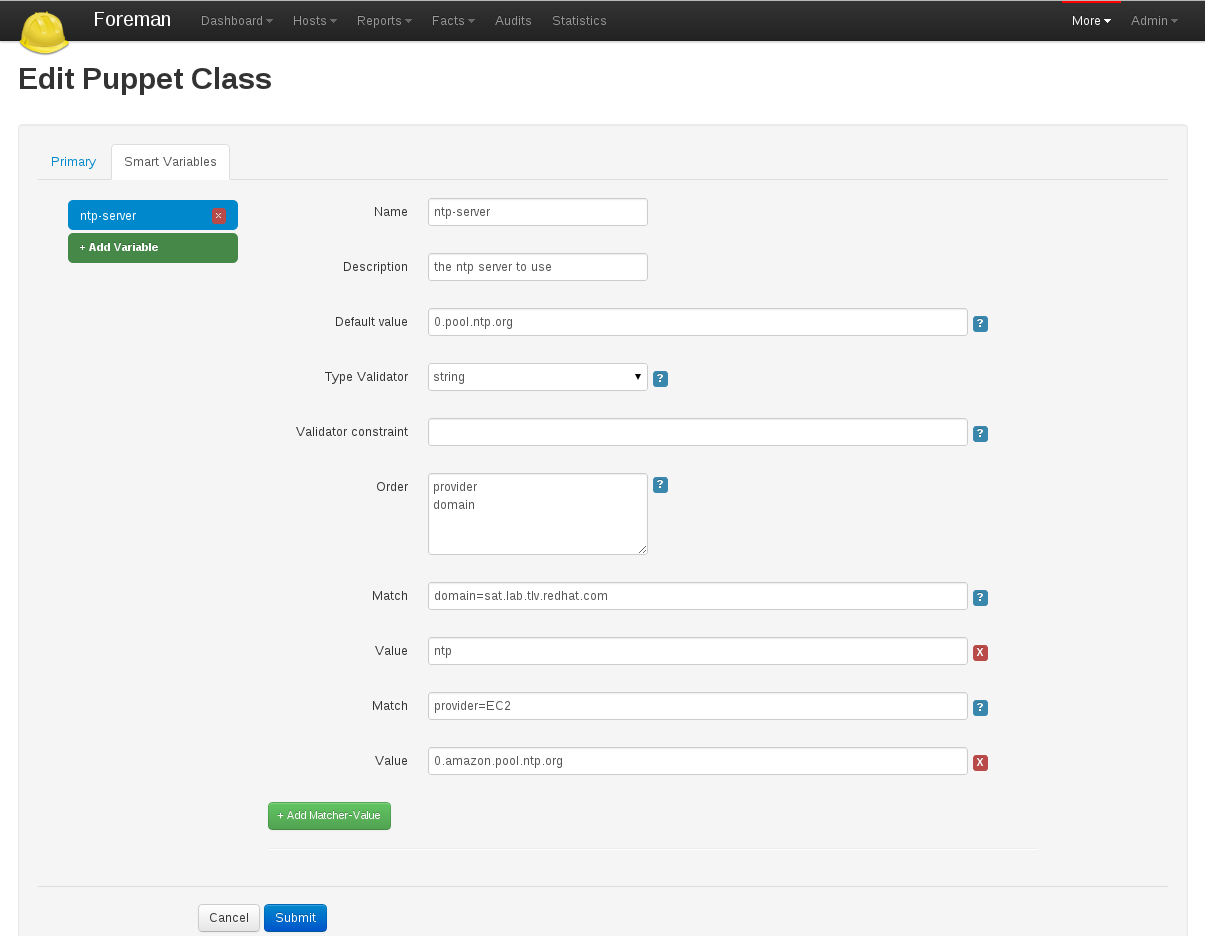
Creating a Smart Variable
Start by going to Configure > Puppet classes and then click one of your classes to edit it.
Click on the Smart Variables tab. If you have any existing Smart Variables, they will be listed at the left side of the tab.
Click New Variable, and you will be presented with a set of input fields:
| Name | What the parameter will be called in the ENC data |
| Description | A free form text box for your own information |
| Default Value | What the ENC will use if no other criteria is matched |
| Type Validator | A combo-box of data types. The type applies to the next field, the validator |
| Validator Constraint | Used to enforce certain values for the Smart Variable. See below for examples |
| Order | A list of variables which Foreman will search (in order) for the validator |
Once you’ve created the defaults for your Smart variable, you then need to add at least one criterion to match against - click the “plus” under your variable, and two more input fields will appear:
| Match | Should state a name = value relationship that Foreman use to match against the entries in searchlist |
| Value | What the parameter should be in the ENC, if this rule is matched |
Validators
The fourth and fifth fields in the Smart Variable combine to produce a validation criteria for the final value of the Smart Variable.
String validators
At present, the string type cannot be validated - leave the validator field blank, and all strings in the variable will be considered acceptable
Regexp / List validators
By entering a list (comma-separated, no spaces) or a regex (no delimiter required), the value to be assigned to the Smart Variable will be checked against this list. If the value does not match the validator, and error will be raised.
Ordering
All the ordering information is stored in the sixth field of the Smart Variable (order). The order matters and is used to find the first match.
Examples
Example 1 - Simple change to a single host
All our hosts use server.foo for something, except bob.domain.com which uses server2.bar:
| Name | target |
| Description | The target server to talk to |
| Default Value | server.foo |
| Type Validator | string |
| Validator Constraint | |
| Order | fqdn hostgroup os domain |
| Match | fqdn = bob.domain.com |
| Value | server2.bar |
Example 2 - Change for a group of hosts (via custom fact) with validation and ordering
Most hosts need to use a port of 80 but all machines with a fact region and value europe need to use 8080. To do this, you have to add the factname (in this example region) to the searchlist:
| Name | port |
| Description | The port to use |
| Default Value | 80 |
| Type Validator | list |
| Validator Constraint | 80,443,8080 |
| Order | fqdn region hostgroup os domain |
| Match | region = europe |
| Value | 8080 |
| Match | fqdn = foo.domain |
| Value | 67 |
Note that all machines will get either 80 or 8080 as required, except foo.domain which will generate an error, since 67 is not in the list validator. Note also that foo.domain will match before region, since it is higher in the searchlist. The rule ordering does not matter.
It is also possible to mix conditions, e.g.
| Name | port |
| Description | The port to use |
| Default Value | 80 |
| Type Validator | list |
| Validator Constraint | 80,443,8080 |
| Order | fqdn region, hostgroup, environment hostgroup environment domain |
| Match | fqdn = foo.domain |
| Value | 67 |
| Match | region = europe, hostgroup = "web servers", environment = production |
| Value | 8080 |
API usage
It’s also possible to retrieve these values if you’re not using a ENC, via a custom Puppet function or a http request.. You’ll need to retrieve the value from
https://foreman/hosts/<fqdn>/lookup_keys/<key>
You can find a ready-made function for your puppet module here
4.2.5 Parameterized Classes
Parameterized Class Support (PCS) permits detecting, importing, and supplying parameters direct to classes which support it, via the ENC.
Requirements
- Foreman 1.1+
- Foreman-Proxy 1.1+
- Puppet 2.6.5+
Setup
Firstly, you’ll need to enable the PCS support. Go to Administer > Settings, select the Puppet tab, and ensure Parameterized_Classes_in_ENC is set to true.

Now you’ll need to import some parameterized classes from your puppet master. If you don’t have any parameterized classes in your modules dir, the foreman-installer has several, you can download a few modules from the Puppet Forge. Once you have some parameterized modules, import your classes (see 4.2.2 Classes)
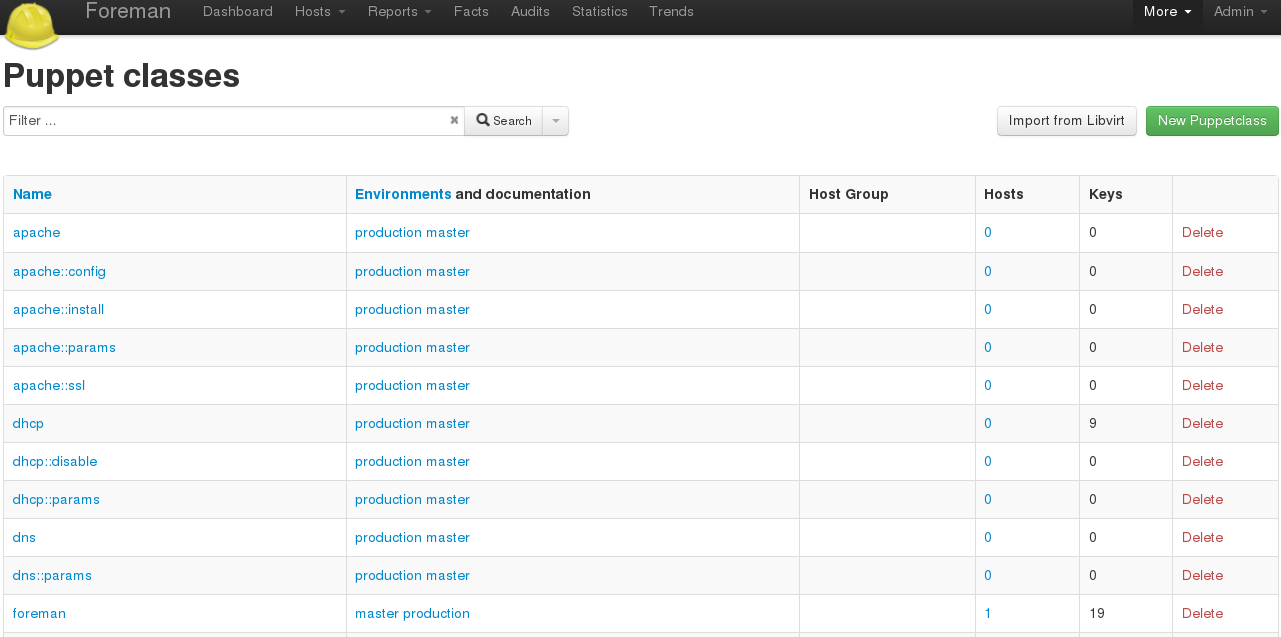
Configure a class
This example will work with the foreman class from the installer. Click on the class, and you should get a page with 3 tabs, like so:

The middle tab, “Smart Class Parameter”, is the important one. Click onto that, and you should see something like this:
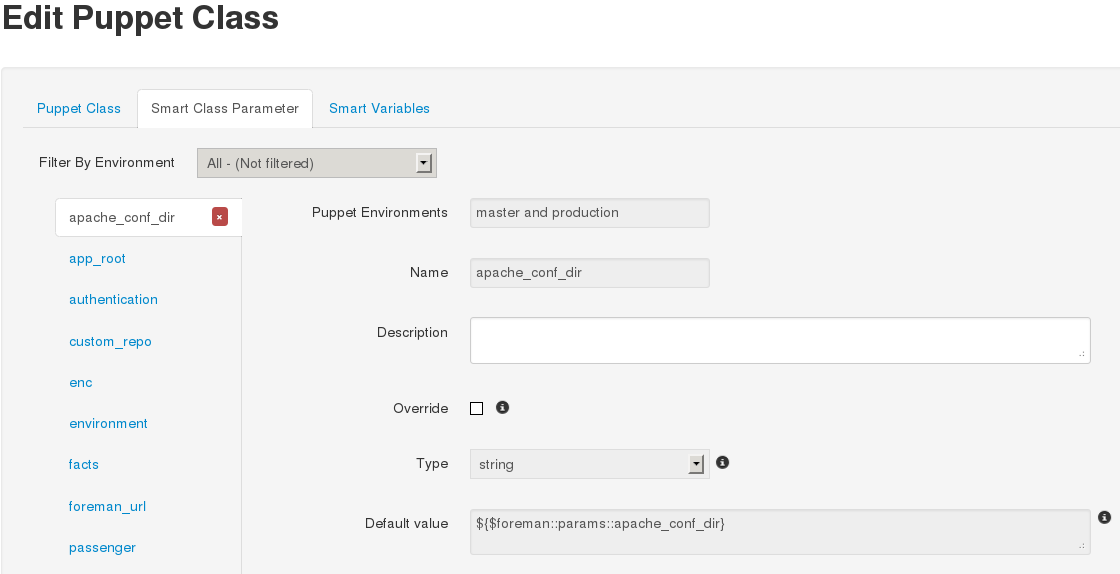
On the left, we have a list of possible parameters that the class supports. On the right, we have the configuration options for the parameter selected.
Lets configure the foreman class to change the user the foreman processes run as. Select the user parameter, at the end of the list. Now lets go through the options:
- Puppet Environments / Name
- These can’t be edited, they’re just for information.
- Description
- Purely information textbox for making notes in. Not passed to puppet, or reused anywhere else
- Override (important)
- If this is unchecked, Foreman will not attempt to control this variable, and it will not be passed to Puppet via the ENC.
- Type
- The type of data we want to pass. Most commonly a string, but many other data types are supported. There’s no easy way to tell what type of data puppet is expecting, so you will need to read through the code/documentation that comes with a particular module to find out. Changing the type field requires an appropriately set “Default Value” field.
- Default Value
- This will be imported from puppet initially, but if puppet is using any class inheritance, you’ll get something unhelpful like “${$foreman::params::user}”. This is because Foreman won’t follow the inheritance, so you’ll need to set a sensible default value
Ok, so let’s configure our user parameter. We want to tick Override, set type to “String” and set the default value to “foreman”, like so:
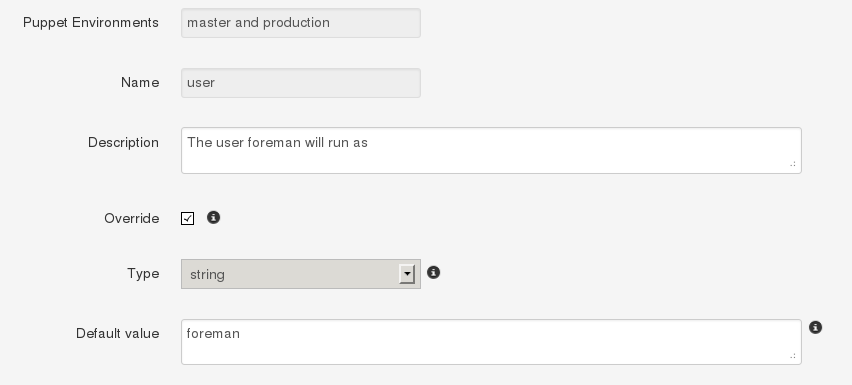
Setting up Matchers
We’ve configured the default, but that’s not very useful. We need to be able to override the default for hosts or groups of hosts. To do that we need the “Override Value For Specific Hosts” section at the bottom of the page.
Let’s say that any machine in the “development” puppet environment should use a value of “foremandev” instead of “foreman” for the “user” parameter. Add “environment” to the end of the matchers list, then click the “New Matcher-Value” button, and fill it out like this:
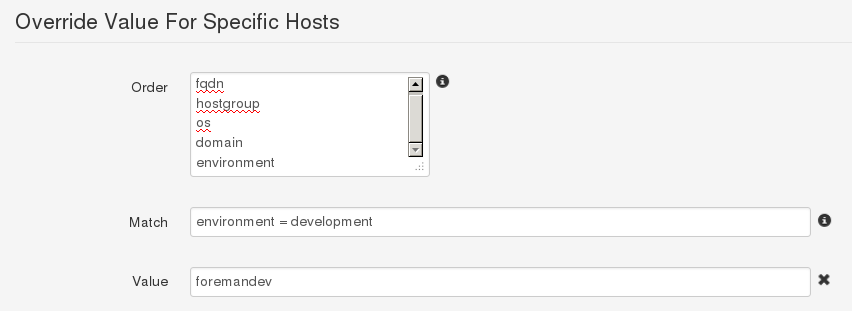
This is a basic configuration - for more complex examples of using matchers, see the 4.2.4 Smart Variables page.
Complex Data
Here’s an example of adding an array parameter. Note the use of YAML in the editbox:
This will be converted to the normal [“a”,”b”] syntax when you save. You can also use Hashes, YAML or JSON as data types too.
Template Variables
Because Foreman offers templating capabilities, you can utilise pre-existing variables, macros and or functions within your parameterized classes. This is especially useful if you need to send a string to Puppet/Chef, but have a need to embed host specific information within the string, such as the host’s FQDN.
Let’s look a quick example situation: we need to configure RabbitMQ and have it use our existing Puppet SSL certs. Using what we’ve learnt above, we jump into the RabbitMQ class and configure the “ssl cert” parameter as such:
As you can see we’re utilising a template variable within the parameter’s string just like we would in a normal template file. The important part of this string, as we’re sure you’ve gathered, is the “@host.name” element. This pulls the FQDN from Foreman’s facts and inserts it into the string.
More information regarding templates can be found on the wiki. This page also contains the pre-existing functions and macros you can use in your templates and parameter classes.
Editing Param from within a Host
If Foreman manages the value of a class parameter (“override = true”), it’s also possible to update a host-specific override from the host itself. That way you don’t have to grant access to the Puppet Classes page to everyone. From a Host, click Edit, go to the Parameters tab, and you’ll see the variable, the class-scope, and the current value. You can then override the value for that host:
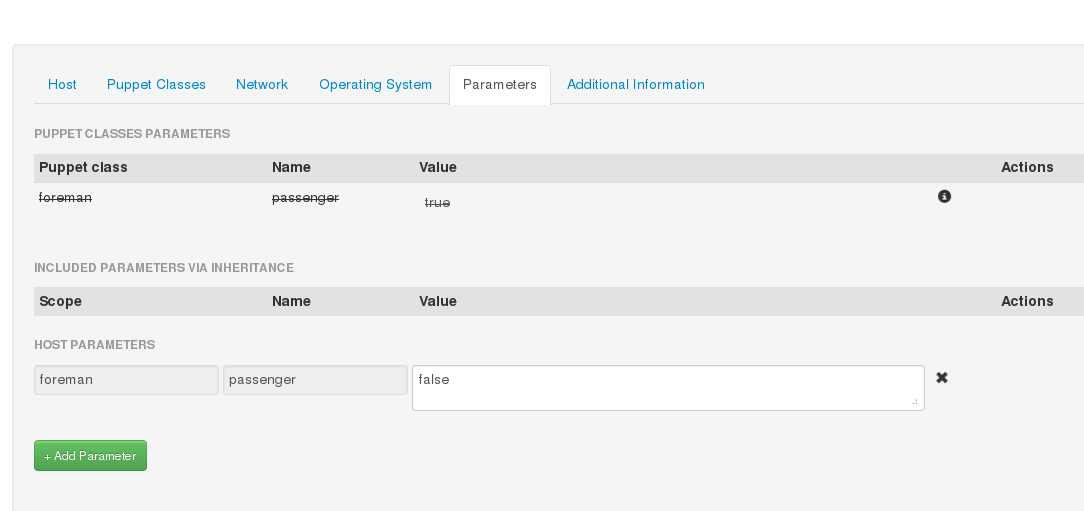
If you go back and look at the Puppet class, you’ll see Foreman has added a matcher for that host:
Currently this only works for Hosts, not Hostgroups. For more complex logic, like matching on facts, use the Puppet Class page
Input Validation
The “Optional Input Validator” section can be used to restrict the allowed values for the parameter. This functions in the same way as for Smart Variables, but it is important to note that the validation applies to changes made from the Host edit page as well as the Puppet Classes edit page.
For example, to restrict the “user” field to either “foreman” or “foremandev”, tick the Required checkbox, and then set:
- Type: List
- Rule: foreman,foremandev
4.3 Smart Proxies
The Smart Proxy is a project which provides a restful API to various sub-systems.
Its goal is to provide an API for a higher level orchestration tools (such as Foreman). The Smart proxy provides an easy way to add or extended existing subsystems and API’s.
Currently supported (Click on the links below for more details).
- DHCP - ISC DHCP and MS DHCP Servers
- DNS - Bind and MS DNS Servers
- TFTP - any UNIX based tftp server
- Puppet - Any Puppet server from 0.24.x
- Puppet CA - Manage certificate signing, cleaning and autosign on a Puppet CA server
- Chef Proxy - Allow authentication of facts and reports between chef-client and Foreman
If you require another sub system type or implementation, Please add a new feature request.
After you got it running, You would need to configure each one of the sub systems via the settings.yml file in the config directory.
4.3.1 Smart Proxy Installation
A smart proxy is an autonomous web-based foreman component that is placed on a host performing a specific function in the host commissioning phase. It receives requests from Foreman to perform operations that are required during the commissioning process and executes them on its behalf. More details can be found on the Foreman Architecture page.
To fully manage the commissioning process then a smart proxy will have to manipulate these services, DHCP, DNS, Puppet CA, Puppet and TFTP. These services may exist on separate machines or several of them may be hosted on the same machine. As each smart proxy instance is capable of managing all the of these services, there is only need for one proxy per host. In the special case of a smart proxy managing a windows DHCP server, the host machine must be running Windows and support the netsh dhcp utility, it does not need to be the Microsoft DHCP server itself.
Packages
RPM and Debian packages are available, see the Install from Packages section for configuration and install the foreman-proxy package.
Source code
You can get the latest stable code from GitHub (via git).
git clone git://github.com/theforeman/smart-proxy.git
Configuration file
Usually can be found at /etc/foreman-proxy/settings.yml or on the config/settings.yml subdirectory. You can use the settings.yml.example file inside the config directory as a template for your own settings.yml.
If you don’t plan to use one of the subsystems, please disable them in this configuration file. For more information see Smartproxy Configuration
Start the daemon
bin/smart-proxy.rb
Or if you installed it via a package simply start the foreman-proxy service.
Add the smart-proxy to Foreman
- Go to [FOREMAN_URL]/smart_proxies and click New Proxy
- Type in the Name for your Proxy and the URL of your Proxy, with the Port used.
For example:
Name: Puppet-Proxy URL: http://puppet.your-domain.com:8443
4.3.2 Smart Proxy Settings
The configuration for Smart-Proxy is held in the /etc/foreman-proxy/settings.yml or config/settings.yml file.
YAML start
The first non-comment line of this file must be three dashes.
---
SSL configuration
The existence of all the three ssl key entries below enables the use of an SSL connections.
NOTE that both client certificates need to be signed by the same CA, which must be in the ssl_ca_file, in order for this to work see SSL for more information
:ssl_certificate: ssl/certs/fqdn.pem :ssl_ca_file: ssl/certs/ca.pem :ssl_private_key: ssl/private_keys/fqdn.key
This is the list of hosts from which the smart proxy will accept connections. If this list is empty then every verified SSL connection is allowed to access the API.
:trusted_hosts: - foreman.prod.domain - foreman.dev.domain
Instance attributes
If this entry is present and not false then Smart-Proxy will attempt to disconnect itself from the controlling terminal and daemonize itself.
:daemon: true
The port listened to by the proxy. If this is not present then the default Sinatra port of 4567 is used.
:port: 8443
TFTP section
Activate the TFTP management module within the Smart-Proxy instance.
The tftproot value is directory into which tftp files are copied and then served from. The tftp daemon will also be expected to chroot to this location. This component is only supported in the Unix environment
:tftp: true :tftproot: /var/lib/tftpboot :tftp_servername: name of your tftp server (used for next server value in your dhcp reservation) - defaults to the host name of your proxy.
NOTE: the foreman proxy user must have read/write access to the tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg and tftpboot/boot directories.
DNS section
Activate the DNS management module within the Smart-Proxy instance.
The DNS module can manipulate any DNS server that complies with the ISC Dynamic DNS Update standard and can therefore be used to manage both Microsoft and Bind servers. Updates can also be done using GSS-TSIG, see the documentation.
The dns_key specifies a file containing a shared secret used to generate a signature for the update request (TSIG record). This option should not be used if you plan to use Kerberos/GSS-TSIG (for example for DNS servers shipped with FreeIPA or Microsoft AD).
If neither the dns_key or GSS-TSIG is used then the update request is sent without any signature. Unsigned update requests are considered insecure. Some DNS servers can be configured to accept only signed signatures.
The dns_server option is used if the Smart-Proxy is not located on the same physical host as the DNS server. If it is not specified then localhost is presumed.
:dns: true :dns_key: /home/proxy/keys/Kapi.+157+47848.private :dns_server: dnsserver.site.domain.com
NOTE: if you use a key, make sure that the foreman proxy account can read that file.
DHCP section
Activate the DHCP management module within the Smart-Proxy instance.
:dhcp: true
If the DHCP server is ISC compliant then set dhcp_vendor to isc. In this case Smart-Proxy must run on the same host as the DHCP server. If the proxy is managing a Microsoft DHCP server then set dhcp_vendor to native_ms. Smart-Proxy must then be run on an NT server so as to access the Microsoft native tools, though it does not have to be the same machine as the DHCP server. More details can be found at [[Foreman:Foreman Architecture]].
:dhcp_vendor: isc
The DHCP component needs access to the DHCP configuration file as well as the currently allocated leases. The section below shows these values for a RedHat client. In the case of a Smart-Proxy hosted on an Ubuntu machine then these values would be more appropriate: /etc/dhcp3/dhcpd.conf and /var/lib/dhcp3/dhcpd.leases
:dhcp_config: etc/dhcpd.conf :dhcp_leases: etc/dhcpd.leases
NOTE: Make sure that the foreman proxy account can read both ISC configuration files.
If your native_ms implementation is slow then you can request that the smart proxy only operate on a subset of the subnets managed by the dhcp server.
:dhcp_subnets: [192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0, 192.168.11.0/255.255.255.0]
If you secured your DHCP with an “omapi_key”, add the entries:
:dhcp_key_name: omapi_key :dhcp_key_secret: XXXXXXXX
Puppet Certificate Authority section
Activate the Puppet CA management module within the Smart-Proxy instance.
This should only be enabled in the Smart-Proxy that is hosted on the machine responsible for providing certificates to your puppet clients. You would expect to see a directory /var/lib/puppet/ssl/ca on such a host.
:puppetca: true
If your puppet SSL directory is located elsewhere, you’ll need to set ‘ssldir’ as well.
:ssldir: /etc/puppet/ssl
:puppetdir: /etc/puppet
The proxy requires write access to the puppet autosign.conf file, which is usually owner and group puppet, and has mode 0644 according to the puppet defaults.
Ensure the foreman-proxy user is added to the puppet group ( e.g. gpasswd -a foreman-proxy puppet or usermod -aG puppet foreman-proxy)
puppet.conf:
[master]
autosign = $confdir/autosign.conf {owner = service, group = service, mode = 664 }
Sudo access to the proxy is required - in your sudoers file ensure you have the following lines:
For older monolithic puppet (pre-3.0) without separate commands:
foreman-proxy ALL = NOPASSWD: /usr/sbin/puppetca * Defaults:foreman-proxy !requiretty
For newer puppet (3.0-onwards) with separate sub-commands available:
foreman-proxy ALL = NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/puppet cert * Defaults:foreman-proxy !requiretty
Puppet section
Activate the puppet management module within the Smart-Proxy instance.
This should only be enabled in the Smart-Proxy that is hosted on the machine capable of executing puppetrun. This will be a puppetmaster. This can also be set to true if you need to import puppet classes from the puppetmaster. Without this the import will not be possible
:puppet: true
:puppet_conf: /etc/puppet/puppet.conf # Defaults to %INSTALL_DIR%/.puppet/puppet.conf
puppet run/kick
Sudo access for the proxy is required - in your sudoers file ensure you have the following lines (use /opt/puppet/bin/puppet for Puppet Enterprise):
Defaults:foreman-proxy !requiretty foreman-proxy ALL = NOPASSWD: /usr/sbin/puppetrun
If you are using Puppet 3.0 or higher, the puppetrun binary has been removed and so the Smart Proxy will use puppet kick. The sudoers entry should be:
Defaults:foreman-proxy !requiretty foreman-proxy ALL = NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/puppet kick *
MCollective
The proxy can trigger Puppet runs using the MCollective “puppet” agent. To enable this, add this line to settings.yml:
:puppet_provider: mcollective
And then add a sudoers rule:
Defaults:foreman-proxy !requiretty
foreman-proxy ALL = NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/mco puppet runonce *
Logging
The proxy’s output is captured to the log_file and may be filtered via the usual unix syslog levels:
- WARN
- DEBUG
- ERROR
- FATAL
- INFO
- UNKNOWN
See Ruby’s Logger class for details.
:log_file: /tmp/proxy.log :log_level: DEBUG
4.3.3 ISC DHCP
ISC implementation is based on the omapi interface, which means:
- No need for root permissions on your DHCP server
- No need to restart (or “sync”) your dhcp server after every modifications.
Configuration
- dhcpd configuration file: ensure you have the following line in your dhcpd.conf file (somewhere in the top first lines):
omapi-port 7911;
- configure the settings file to point to your dhcpd.conf and dhcpd.leases files (make sure they are readable by the smart-proxy user)
- make sure the omshell command (/usr/bin/omshell) can be executed by the smart-proxy user.
- make sure that /etc/dhcp and /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf has group foreman-proxy
Securing the dhcp API
The dhcpd api server will listen to any host. You might need to add a omapi_key to provide basic security.
Example generating a key (on CentOS):
yum install bind97 dnssec-keygen -r /dev/urandom -a HMAC-MD5 -b 512 -n HOST omapi_key cat Komapi_key.+*.private |grep ^Key|cut -d ' ' -f2-
-
Edit your “/etc/dhcpd.conf”:
omapi-port 7911; key omapi_key { algorithm HMAC-MD5; secret "XXXXXXXXX"; #<-The output from the generated key above. }; omapi-key omapi_key; -
Make sure you also add the omapi_key to your proxy’s [[Smart-Proxy:Settingsyml#DHCP-section settings.yml]] - Restart the dhcpd and foreman-proxy services
NOTE: if you don’t see DHCP in Smart Proxies Features, choose “Refresh features” from drop-down menu.
Testing
If everything works, you could browse your dhcp server data if you goto http://proxy:8443/dhcp
The next step is to set up appropriate Subnets in Foreman from the settings menu.
Sample dhcpd.conf
ddns-update-style interim;
ignore client-updates;
authoritative;
allow booting;
allow bootp;
omapi-port 7911;
#Optional key:
key omapi_key {
algorithm HMAC-MD5;
secret "2wgoV3yukKdKMkmOzOn/hIsM97QgLTT4CLVzg9Zv0sWOSe1yxPxArmr7a/xb5DOJTm5e/9zGgtzL9FKna0NWis==";
}
omapi-key omapi_key;
subnet 10.1.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
# --- default gateway
option routers 10.1.1.254;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option domain-name "domain.com";
option domain-name-servers 10.1.1.1, 8.8.8.8;
option log-servers syslog;
option ntp-servers ntp;
range dynamic-bootp 10.1.1.10 10.1.1.250;
default-lease-time 21600;
max-lease-time 43200;
}
4.3.4 MS DHCP
The Microsoft smart-proxy installation procedure is very basic compared to the RPM or APT based solution.
It is required that this procedure is executed as an administrator.
It is not required that the smart-proxy be on the same host as the MS dhcp server. The smart-proxy just needs to be on a windows host that has netsh commands available.
- Go to the smart-proxy repository at https://github.com/theforeman/smart-proxy
- Select download and choose the latest revision
- Extract this to a directory that does not have any spaces in its name.
- Go to the rubyinstaller webpage at http://rubyinstaller.org/downloads/
- Download and install the “ruby 1.8.7 release 334”:http://rubyforge.org/frs/download.php/74293/rubyinstaller-1.8.7-p334.exe (Allow the ruby associations to be installed.)
- Open a CMD window and, using gem install –version X.X.X –platform ?????, add these gems
columnize (0.3.2) highline (1.6.1) json (1.4.6 x86-mswin32) linecache (0.43 mswin32) mime-types (1.16) mocha (0.9.11) net-ping (1.3.7) rack (1.2.0) rake (0.8.7) rest-client (1.6.1) sinatra (1.1.0) tilt (1.1) win32-api (1.4.6 x86-mswin32-60) win32-open3 (0.3.2 x86-mswin32-60) win32-service (0.7.1 x86-mswin32-60) windows-api (0.4.0) windows-pr (1.1.2)
Command to download them all:
wget http://rubygems.org/downloads/columnize-0.3.2.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/haml-3.0.24.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/highline-1.6.1.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/json-1.4.6-x86-mswin32.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/linecache-0.43-mswin32.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/mime-types-1.16.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/mocha-0.9.11.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/net-ping-1.3.7.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/rack-1.2.0.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/rake-0.8.7.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/rest-client-1.6.1.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/sinatra-1.1.0.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/tilt-1.1.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/win32-api-1.4.6-x86-mswin32-60.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/win32-open3-0.3.2-x86-mswin32-60.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/win32-service-0.7.1-x86-mswin32-60.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/windows-api-0.4.0.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/windows-pr-1.1.2.gem
To get it to work on Windows 2008 R2 some of the packages has to change
columnize (0.3.2) highline (1.6.1) json (1.4.6 x86-mingw32) linecache (0.43 mswin32) mime-types (1.16) mocha (0.9.11) net-ping (1.3.7) rack (1.2.0) rake (0.8.7) rest-client (1.6.1) sinatra (1.1.0) tilt (1.1) win32-api (1.4.6 x86-mingw32) win32-open3 (0.3.2 x86-mingw32) win32-service (0.7.1 x86-mswin32-60) windows-api (0.4.0) windows-pr (1.1.2)
Easy copy and paste method (platform may be different for you. Please check gem environment to find out.
gem install --version 0.3.2 --platform x86-mingw32 columnize gem install --version 1.6.1 --platform x86-mingw32 highline gem install --version 1.4.6 --platform x86-mingw32 json gem install --version 0.43 --platform x86-mingw32 linecache gem install --version 1.16 --platform x86-mingw32 mime-types gem install --version 0.9.11 --platform x86-mingw32 mocha gem install --version 1.3.7 --platform x86-mingw32 net-ping gem install --version 1.2.0 --platform x86-mingw32 rack gem install --version 0.8.7 --platform x86-mingw32 rake gem install --version 1.6.1 --platform x86-mingw32 rest-client gem install --version 1.1.0 --platform x86-mingw32 sinatra gem install --version 1.1 --platform x86-mingw32 tilt gem install --version 1.4.6 --platform x86-mingw32 win32-api gem install --version 0.3.2 --platform x86-mingw32 win32-open3 gem install --version 0.7.1 --platform x86-mingw32-60 win32-service gem install --version 0.4.0 --platform x86-mingw32 windows-api gem install --version 1.1.2 --platform x86-mingw32 windows-pr
Command to download them all:
wget http://rubygems.org/downloads/columnize-0.3.2.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/haml-3.0.24.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/highline-1.6.1.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/json-1.4.6-x86-mingw32.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/linecache-0.43-mswin32.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/mime-types-1.16.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/mocha-0.9.11.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/net-ping-1.3.7.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/rack-1.2.0.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/rake-0.8.7.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/rest-client-1.6.1.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/sinatra-1.1.0.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/tilt-1.1.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/win32-api-1.4.6-x86-mingw32.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/win32-open3-0.3.2-x86-mingw32.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/win32-service-0.7.1-x86-mswin32-60.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/windows-api-0.4.0.gem \
http://rubygems.org/downloads/windows-pr-1.1.2.gem
8) CD to the root of the smart-proxy install directory
9) Edit config/settings.yml so that it looks a bit like this
Sample config/settings.yml file
--- # HTTPS settings :ssl_certificate: c:\documents\smart-proxy\config\signed.pem :ssl_private_key: c:\documents\smart-proxy\config\private.pem :ssl_ca_file: c:\documents\smart-proxy\config\ca.pem :trusted_hosts: [ foreman.someware.com] :daemon: false # Enable DHCP management :dhcp: true # The vendor can be either isc or native_ms :dhcp_vendor: native_ms # The dhcp_server is only used by the native_ms implementation :dhcp_server: 172.29.90.240 # Where our proxy log files are stored # filename or STDOUT # Unix setting #:log_file: log/proxy.log # Windows setting :log_file: c:\tmp\proxy.log # valid options are # Logger::WARN, Logger::DEBUG, Logger::Error, Logger::Fatal, Logger:INFO, LOGGER::UNKNOWN #:log_level: Logger::DEBUG
10) Create the SSL key
10.1) Login to your puppetmaster
10.2) puppetca –generate Smart-proxy FQDN. (Do not use an alias here.)
10.3) Copy the private key, the public certificate and the ca.pem from /var/lib/puppet/ssl over to the locations that you specified in the setting file.
11) Test the installation by running ruby bin\smart-proxy.rb
12) Install the program as a service
12.1) ruby extra\register-service.rb
12.2) This may install the service but not run it. If so then try to start the service from the Ordinary Microsoft services snapin utility.
13) You may test connectivity by running the extra\query.rb utility from your foreman host. (Note that this file comes from the extra directory in the smart-proxy release.)
4.3.5 BIND
Bind configuration manipulation is based on nsupdate, which means that in theory could also be used to manipulate other dns servers which support nsupdate (such as Microsoft DNS server).
Configuration
In order to communicate securely with your dns server, you would need a key which will be used by nsupdate and your named daemon using ddns-confgen or dnssec-keygen
example using ddns-confgen
execute ‘ddns-confgen -k foreman -a hmac-md5’ - this should output something like the following:
# To activate this key, place the following in named.conf, and
# in a separate keyfile on the system or systems from which nsupdate
# will be run:
key "foreman" {
algorithm hmac-md5;
secret "GGd1oNCxaKsh8HA84sP1Ug==";
};
# Then, in the "zone" statement for each zone you wish to dynamically
# update, place an "update-policy" statement granting update permission
# to this key. For example, the following statement grants this key
# permission to update any name within the zone:
update-policy {
grant foreman zonesub ANY;
};
# After the keyfile has been placed, the following command will
# execute nsupdate using this key:
nsupdate -k /path/to/keyfile
You should create a new file (such as /etc/rndc.key or other) and store the key “foreman {…} in it. in the proxy Settings file you should point to this file location - make sure that the proxy have read permissions to this file.
In your named file, you could add the update-policy statement or something like this named example file if you need more fine grained permissions.
4.3.6 GSS-TSIG DNS
Both BIND as configured in FreeIPA and Microsoft AD DNS servers can accept DNS updates using GSS-TSIG authentication. This uses Kerberos principals to authenticate to the DNS server. Under Microsoft AD, this is known as “Secure Dynamic Update”.
Pre-requisites
- Kerberos principal in the realm/domain that Smart Proxy can use
- Kerberos keytab for the above principal
Microsoft AD configuration
A user has to be created in Active Directory that will be used by the Smart Proxy, e.g. foremanproxy. This will automatically create a service principal, e.g. foremanproxy@EXAMPLE.COM.
Test the Kerberos login with that user on the Smart Proxy using kinit:
kinit foremanproxy@EXAMPLE.COM
This requires that the /etc/krb5.conf file is setup correctly. By default many systems use DNS to locate the Kerberos DC. A KDC can also be statically set in this file. There are dozens of documents on how to do this on the net.
If login works, the keytab file can be created using ktutil. First clear the Kerberos ticket cache:
kdestroy
Now create the keytab file with ktutil:
ktutil: addent -password -p foreman@EXAMPLE.COM -k 1 -e RC4-HMAC
ktutil: wkt dns.keytab
ktutil: q
Once the keytab file has been created, test it using kinit:
kinit foreman@EXAMPLE.COM -k -t dns.keytab
If this works, clear the Kerberos ticket cache once again using kdestroy.
Store the keytab at /etc/foreman-proxy/dns.keytab, ensure permissions are 0600 and the owner is foreman-proxy.
The DNS zone Dynamic Updates option on the DNS zones can now be set to Secure Only. Now follow the steps below under Proxy Configuration.
FreeIPA configuration
A service principal is required for the Smart Proxy, e.g. foremanproxy/proxy.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM.
First of all, create a new principal (FreeIPA service) for Foreman, e.g. ipa service-add foremanproxy/proxy.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM.
Then fetch the keytab, e.g. ipa-getkeytab -p foremanproxy/proxy.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM -s ipa-server.example.com -k /etc/foreman-proxy/dns.keytab.
Store the keytab at /etc/foreman-proxy/dns.keytab, ensure permissions are 0600 and the owner is foreman-proxy.
The ACL on updates to the DNS zone then needs to permit the service principal. In the FreeIPA web UI, under the DNS zone, go to the Settings tab, verify that “Dynamic update” for that zone is set to “True”, and add to the BIND update policy a new grant:
grant foremanproxy\047proxy.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM wildcard * ANY;
Note the \047 is written verbatim, and don’t forget the semicolon. ACLs should be updated for both forward and reverse zones as desired.
Proxy configuration
Next, update the proxy configuration file (/etc/foreman-proxy/settings.yml) with the following settings:
:dns_provider: nsupdate_gss
:dns_tsig_keytab: /etc/foreman-proxy/dns.keytab
:dns_tsig_principal: foremanproxy/proxy.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM
4.3.7 SSL
The smart proxy can work in SSL mode, where both sides verify and trust each other. Requests from Foreman will only be accepted if the SSL certificate can be verified. Since proxies abstract a high level of control over your infrastructure, the configuration and security of keys and certificates is important.
Using Puppet CA certificates
Since Foreman integrates with Puppet heavily, it is recommended to use the Puppet Certificate Authority (CA) to secure proxy access. See the Security Communciations with SSL section for more advanced installations (multiple or internal CAs).
If the smart proxy host is not managed by Puppet, you will need to generate a certificate - skip forward to the generate section.
When using Puppet’s certificates, the following lines will be required in puppet.conf to relax permissions to the puppet group. The foreman and/or foreman-proxy users should then be added to the puppet group.
[main]
privatekeydir = $ssldir/private_keys { group = service }
hostprivkey = $privatekeydir/$certname.pem { mode = 640 }
Configuring the proxy
Configure the locations to the SSL files in /etc/foreman-proxy/settings.yml, plus the list of trusted Foreman hosts:
:ssl_certificate: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/FQDN.pem :ssl_ca_file: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem :ssl_private_key: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/private_keys/FQDN.pem :trusted_hosts: - foreman.corp.com #- foreman.dev.domain
Generating a certificate
To generate a certificate for a proxy host that isn’t managed by Puppet, do the following:
- Generate a new certificate on your puppetmaster:
puppet cert --generate <proxy-FQDN> - Copy the certificates and key from the puppetmaster to the smart proxy in
/etc/foreman-proxy:<ol>
</ol>
Follow the configuration section above, however use the /etc/foreman-proxy paths instead of the Puppet defaults.
Configuring Foreman
For Foreman to connect to an SSL-enabled smart proxy, it needs configuring with SSL certificates in the same way. If the Foreman system is managed by Puppet, it will already have these, else certificates can be generated following the above instructions.
The locations of the certificates are managed in the Settings page, under Provisioning with the ssl_ca_file, ssl_certificate and ssl_priv_key settings. By default these will point to the Puppet locations - for manually generated certificates, or non-standard locations, they may have to be changed.
Lastly, when adding the smart proxy in Foreman, ensure the URL begins with https:// rather than http://.
4.3.8 TFTP
An essential first step in netbooting a system is preparing the TFTP server with the PXE configuration file and boot images. This document assumes that you have already configured your DHCP infrastructure, either via manual configuration or through the DHCP smart proxy.
Configuration Values
Once enabled, there is currently only one valid setting to change, the default TFTP root. This is set with the :tftproot: parameter, which defaults to /var/lib/tftpboot.
Foreman tries to guess the right server name that should put into the dhcp record, if this is not what you want, you can override it - see tftp_servername under Settings.yml.
Setting Up the Proxy Server Host
Regardless of the filesystem setup is performed, you must also make sure you have the wget utility installed and in the default path. wget is used to download OS specific installation when a given host is enabled for the build process.
Automatic Setup
Foreman includes a TFTP server module that will perform all of the basic setup. It defaults to TFTP root of /var/lib/tftpboot, which may change if necessary. You will still need to provide the basic TFTP load images in your TFTP root directory. For vanilla PXE booting, this includes pxelinux.0, menu.c32, and chain.c32.
Manual Setup
The setup is very simple, and may be performed manually if desired.
- The TFTP root directory must exist (we will use /var/lib/tftpboot in this example).
- Populate /var/lib/tftpboot with PXE booting prerequisites. At a minimum, this should include:
- pxelinux.0
- menu.c32
- chain.c32
- Create the directory /var/lib/tftpboot/boot and make it writeable by the foreman proxy user (foreman-proxy, for instance, when installing through a rpm package).
- Create the directory /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg and make it writeable by the foreman proxy user (foreman-proxy).
Setting Up Foreman
| In most cases, the default templates should work fine. You do, however, need to make sure that a PXELinux or iPXE template is associated with your hosts. See [[Foreman:Unattended_installations | Unattended Installations]] for details. The template will be used to define the PXE configuration file when a host is enabled for build. |
Workflow
This is a rough outline of the steps triggered on the TFTP smart proxy host when you click on the “Build” link for a host.
- Call mkdir -p /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg if it does not already exist.
- Create a host-specific TFTP configuration file in /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/01-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX, named based off of the MAC address, using the associated PXE template.
- Call mkdir -p /var/lib/tftpboot/boot if it does not already exist.
- Download the OS specific kernel and initrd files using wget.
- The download URLs are derived from the installation media path, and OS specific log (see app/models/redhat.rb and debian.rb in foreman for examples of the gory details).
- The debian.rb file tries to guess if you want Ubuntu or Debian, based on the Name you give to your OS in the UI. If the name does not contain ‘ubuntu’ or ‘debian’, it may default to debian, hence fail to fetch the kernel/initrd.
- The exact wget command is
wget --no-check-certificate -nv -c <src> -O "<destination>" - At this point, the TFTP state is ready for the installation process.
- Once the host has completed installation, the OS specific installation script should inform foreman by retrieving the built URL.
- The host-specific TFTP configuration file is deleted.
- The kernel and initrd are not deleted, but left in place for future installs of the same OS and architecture combination. Please note that in the unlikely case that these files are modified, the simplistic freshness check of wget will likely get confused, corrupting the downloaded versions of the files. If this happens, you should simply delete the files and let them be re-downloaded from scratch.
To make sure that you trigger the above workflow make sure you’ve satisfied these requirements:
- at least 1 host is put in build mode
- the host is using a subnet with a TFTP proxy
Limitations
At the moment, the proxy is not able to fetch boot files using NFS. As a workaround, expose your installation medium (or use a public mirror) over http/ftp to configure one machine with the require boot files. this would be resolved as part of #992.
4.3.9 Libvirt
In this chapter, we will describe how to setup DHCP and DNS for use with the virsh provider for libvirt.
This provider is able to change DHCP and DNS settings in libvirt with dnsmasq. This is done via the virsh command. These settings can be for only a single session, or persistent on the libvirt instance.
The provider is intended for development setups where libvirt is usually used. With simple steps, one can configure full provisioning on a box with libvirt.
This provider is not recommended for production use.
Configuration of libvirt
Define the TFTP root first. Edit ‘default’ virtual network and add ‘tftp’, ‘bootp’ and ‘domain’ elements.
<network>
<name>default</name>
<uuid>16b7b280-7462-428c-a65c-5753b84c7545</uuid>
<forward mode='nat'/>
<bridge name='virbr0' stp='on' delay='0' />
<domain name="local.lan"/>
<dns>
</dns>
<mac address='52:54:00:a6:01:5d'/>
<ip address='192.168.122.1' netmask='255.255.255.0'>
<tftp root='/var/tftproot' />
<dhcp>
<range start='192.168.122.2' end='192.168.122.254' />
<bootp file='pxelinux.0' />
</dhcp>
</ip>
</network>
Create a TFTP root directory, make sure it is writeable by the foreman proxy
user (foreman-proxy for instance) and accessible to the account
dnsmasq is running on (in Fedora this is nobody), set gid flag for newly
copied files and copy necessary files to the new TFTP root directory:
mkdir -p /var/tftproot/{boot,pxelinux.cfg}
yum -y install syslinux
cp /usr/share/syslinux/{pxelinux.0,menu.c32,chain.c32} /var/tftproot
chown -R foreman-proxy:nobody /var/tftproot
find /var/tftproot/ -type d | xargs chmod g+s
Configuration of smart-proxy
Configure smart-proxy in config/settings.yaml file:
- enable tftp
- set correct tftp boot and set explicit tftp_servername
- enable dns virsh provider
- enable dhcp virsh provider
- check virsh_network name (
defaultin our case)
Important configuration values are (examples):
:tftp: true
:tftproot: /var/tftproot
:tftp_servername: 192.168.122.1
:dns: true
:dns_provider: virsh
:dhcp: true
:dhcp_vendor: virsh
:virsh_network: default
Make sure the user foreman proxy will be running with has sudo and virsh
commands available and password is not required for virsh command. Also make
sure sudo does not require tty. An example /etc/sudoers configuration:
Defaults !requiretty
foreman-proxy ALL = NOPASSWD : /usr/bin/virsh
Or for those who are running foreman-proxy under different user:
%users ALL = NOPASSWD : /usr/bin/virsh
Additional steps
Make sure the DNS server is configured with the foreman instance by setting
/etc/resolv.conf file or changing this in NetworkManager or dnsmasq
configuration. Example:
cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 8.8.8.8
nameserver 8.8.4.4
nameserver 192.168.122.1
Foreman is now configured for libvirt provisioning, this is the recommended setup for git development checkouts. There is one limitation though, reverse DNS entries are not created (libvirt XML does not support them).
4.3.10 Chef Proxy
Chef proxy allows proxying of the reports and facts uploads between the chef-client on all your hosts and Foreman.
In order to use this feature, you will need to:
- Use the gem chef_handler_foreman in you chef-client.rb (see documentation)
- Use the foreman_chef plugin in Foreman for Facts upload (see documentation)
You can also authenticate the reports and facts upload. In order to do that, reports and facts are signed with chef-client private key in chef_handler_foreman plugin. When receiving a report or facts, the smart-proxy retreives the node’s public key and check if signature is valid. This requires:
- the use of chef-server
- a declared client for the smart-proxy with admin rights (to be able to fetch all clients public keys)
Configuration
In the smart-proxy settings.yml, you need to:
- enable the chefproxy feature
- configure foreman_url setting
If you want to authenticate reports and facts, you need to:
- enable chef_authenticate_nodes feature
- configure chef_server_url setting (make sure smart-proxy can reach your chef-server)
- configure the chef_smartproxy_clientname: you should set a client with admin rights in chef-server
- configure the chef_smartproxy_privatekey: this key should be the private associated with the chef_smartproxy_clientname and should be readable with smart-proxy user
4.4 Provisioning
This chapter details the configuration of the required UI components necessary to provision an OS onto a host.
4.4.1 Operating Systems
The Operating Systems page (Hosts -> Operating Systems) details the OSs known to Foreman, and is the central point that the other required components tie into.
Creating an Operating System
Simply click New Operating system on the main page. You will be taken to a screen where you can create the bare essentials of a new OS. Not everything required for a successful provision is on this page (yet) - the remaining components will appear for selection as we create them.
You will need to fill in the first few parts of the form (Name, Major, Minor, Family, and possibly some family-dependent information). In the case of OSs like Fedora, it is fine to leave Minor blank.
If the default Partition Tables & Installation media are suitable, then you can assign them now. If not, return here after each step in this chapter to assign the newly created objects to your Operating System
Auto-created Operating Systems
Foreman does not come with any Operating Systems by default. However, Foreman will detect the Operating System of any host which reports in via Puppet - if the OS of that Host is supported, it will be created (with very basic settings) and assigned to the Host. Thus you may find some OSs already created for you.
4.4.2 Installation Media
The Installation Media represents the web URL from where the installation packages can be retrieved (i.e. the OS mirror). Some OS Media is pre-created for you when Foreman is first installed. However, it is best to edit the media you are going to use and ensure the Family is set.
New Installation Media
If your OS of choice does not have a mirror pre-created for you, click the New Medium button to create one. There are a few variables which can be used to pad out the URL. For example:
http://mirror.averse.net/centos/$major.$minor/os/$arch
Be sure to set the Family for the Media
Assign to Operating System
If you have not already done so, return to the Operating System page for your OS and assign the Media to it now.
4.4.3 Provisioning Templates
The Provision Templates is the core of Foreman’s flexibility to deploy the right OS with the right options. There are several types of template, along with a flexible matching system to deliver different templates to different Hosts.
Foreman comes with pre-created templates for the more common OSs, but you will need to review these.
Template Kinds
There are 6 template kinds:
- PXELinux - Deployed to the TFTP server to ensure the Host boots the correct installer with the correct kernel options
- Provision - The main unattended installation file; e.g. Kickstart or Preseed
- Finish - A post-install script used to take custom actions after the main provisioning is complete
- user_data - Similar to a Finish script, this can be assigned to hosts built on user_data-capable images (e.g. Openstack, EC2, etc)
- Script - An arbitrary script, not used by default, useful for certain custom tasks
- iPXE - Used in {g,i}PXE environments in place of PXELinux
In practice, most environments only make use of the first 3. The Create Host action deploys the PXELinux template to the TFTP server. The PXELinux template directs the host to retrieve the Provision template. The Provision template will direct the installer to retrieve and run the Finish template at the end of the install, and the Finish template will notify Foreman the build is complete just before reboot.
Editing Templates
Clicking a template will take you to the edit page. All templates are ERB-enabled, and you can access many variables about the to-be-installed-host within the template. See Template Writing for ideas.
As noted in 4.1.4 Auditing, changes to the templates are logged as diffs - you can browse the history of changes to the templates from the History tab within the Edit Template page. You can also revert changes here.
Template Association
When editing a Template, you must assign a list of Operating Systems which this Template can be used with. Optionally, you can restrict a template to a list of Hostgroups and/or Environments
When a Host requests a template (e.g. during provisioning), Foreman will select the best match from the available templates of that type, in the following order:
- Host-group and Environment
- Host-group only
- Environment only
- Operating system default
The final entry, Operating System default, can be set by editing the Operating System page.
Associating an Operating System default template
You will need to associate at least one PXELinux, Provision, and Finish template to your Operating System, and this must be done in two steps. First edit each of the templates, switch to the Association tab, and ensure the appropriate OSs are checked. Then edit the Operating System, switch to the Templates tab, and choose a default template for each template kind.
4.4.4 Partition Tables
Partition templates are a subset of normal Provisioning Templates. They are handled separately because it is frequently the case that an admin wants to deploy the same host template (packages, services, etc) with just a different harddisk layout to account for different servers’ capabilities.
Foreman comes with pre-created templates for common Operating Systems, but it is good to edit the template, check it’s content and it’s Family setting. If the Family is wrong, be sure to go back to Operating Systems and associate it with your Operating System.
Dynamic Partition tables
When creating a new Host, you will be given the option to create a Dynamic Partition table. This is essentially a ‘one-off’ partition table that is stored with the host and used only for that host. It replaces the choice of Partition Table from the normal list of those associated with the selected OS.
4.4.5 Architectures
Architectures are simple objects, usually created by Foreman automatically when Hosts check in via Puppet. However, none are created by default, so you may need to create them if you’re not using Foreman for reporting.
Creating a new Architecture
Simply click New Architecture to create a new one. This should match the Facter fact :architecture e.g. “x86_64”. If you’ve already created some Operating Systems, you can associate the Architecture with the OS now; if not, the list of Architectures will be present when you create an OS.
4.5 Command Line Interface
The framework used for implementation of command line client for foreman provides many features common for modern CLI applications. The task of managing Foreman from command line is quite complex so the commands have to be organized in more levels of subcommands. There is help available for each level to make it easy to use. Some other features for greater comfort are option validation, logging and customizable output formatting.
4.5.1 Usage Examples
Basic help and list of supported commands:
$ hammer -h
Usage:
hammer [OPTIONS] SUBCOMMAND [ARG] ...
Parameters:
SUBCOMMAND subcommand
[ARG] ... subcommand arguments
Subcommands:
shell Interactive Shell
architecture Manipulate Foreman's architectures.
global_parameter Manipulate Foreman's global parameters.
compute_resource Manipulate Foreman's compute resources.
domain Manipulate Foreman's domains.
environment Manipulate Foreman's environments.
fact Search Foreman's facts.
report Browse and read reports.
puppet_class Browse and read reports.
host Manipulate Foreman's hosts.
hostgroup Manipulate Foreman's hostgroups.
location Manipulate Foreman's locations.
medium Manipulate Foreman's installation media.
model Manipulate Foreman's hardware models.
os Manipulate Foreman's operating system.
organization Manipulate Foreman's organizations.
partition_table Manipulate Foreman's partition tables.
proxy Manipulate Foreman's smart proxies.
subnet Manipulate Foreman's subnets.
template Manipulate Foreman's config templates.
user Manipulate Foreman's users.
Options:
-v, --verbose be verbose
-c, --config CFG_FILE path to custom config file
-u, --username USERNAME username to access the remote system
-p, --password PASSWORD password to access the remote system
--version show version
--show-ids Show ids of associated resources
--csv Output as CSV (same as --adapter=csv)
--output ADAPTER Set output format. One of [base, table, silent, csv]
--csv-separator SEPARATOR Character to separate the values
-P, --ask-pass Ask for password
--autocomplete LINE Get list of possible endings
-h, --help print helpFirst level command help:
$ hammer architecture -h
Usage:
hammer architecture [OPTIONS] SUBCOMMAND [ARG] ...
Parameters:
SUBCOMMAND subcommand
[ARG] ... subcommand arguments
Subcommands:
list List all architectures.
info Show an architecture.
create Create an architecture.
delete Delete an architecture.
update Update an architecture.
add_operatingsystem Associate a resource
remove_operatingsystem Disassociate a resource
Options:
-h, --help print helpSecond level command help:
$ hammer architecture create -h
Usage:
hammer architecture create [OPTIONS]
Options:
--name NAME
--operatingsystem-ids OPERATINGSYSTEM_IDS
Operatingsystem ID’s
-h, --help print help4.5.2 Success Story
There was a set of common commands identified as necessary for basic Foreman management, we called it “success story” and track the progress of its implementation. The commands could also serve as a basic hammer cookbook.
The goal is to provision bare metal host on a clean install of Foreman. The following steps are necessary:
- create smart proxy
hammer proxy create --name myproxy --url https://proxy.my.net:8443
- create architecture
hammer architecture create --name x86_64
- create new subnet
hammer subnet create --name "My Net" --network "192.168.122.0" --mask "255.255.255.0" --gateway "192.168.122.1" --dns-primary "192.168.122.1"
-
import existing subnet from a proxy
missing, see #3355
-
create new domain
hammer domain create --name "my.net" --fullname "My network"
- associate domain with proxy
hammer domain update --id 1 --dns-id 1
- associate subnet with domain
hammer subnet update --id 1 --domain-ids 1
- associate subnet with proxy (DHCP, TFTP, DNS)
hammer subnet update --id 1 --dhcp-id 1 --tftp-id 1 --dns-id 1
- create new partition table
hammer partition_table create --name "Redhat test" --file /tmp/rh_test.txt
- create new OS
hammer os create --name RHEL --major 6 --minor 4
- create new template
hammer template create --name "kickstart mynet" --type provision --file /tmp/ks.txt
- edit existing pre-defined template
hammer template dump --id 4 > /tmp/ks.txt
vim /tmp/ks.txt
hammer template update --id 4 --file /tmp/ks.txt
- associate applicable OS with pre-defined template
hammer template update --id 1 --operatingsystem-ids 1
Listing associated OS’s is still missing - see #3360
- associate OS with architecture
hammer os update --id 1 --architecture-ids 1
- associate OS with part table
hammer os update --id 1 --ptable-ids 1
- associate OS with install media
hammer os update --id 1 --medium-ids 1
-
associate OS with install provision and pxelinux templates
Missing, needs investigation, may be related to #3360
-
create libvirt compute resource
hammer compute_resource create --name libvirt --url "qemu:///system" --provider Libvirt
-
import puppet classes
missing - see #3035
-
and finally create a bare metal host entry
works with some options, needs improvements - see #3063
5. Advanced Foreman
5.1 API
API v1 is the default version for Foreman 1.4.
This section documents the JSON API conventions for the Foreman API v2 and Katello API v2, both of which are not released. To test out new features in API v2, see Section 5.1.6, to specify version.
5.1.1 CRUD Request Examples
The following examples show the basic CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) using the JSON API.
Show a Collection of Objects
Get of a collection of domains: GET /api/domains
Send a HTTP GET request. No JSON data hash is required.
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" https://foreman.example.com/api/domains
This returns a collection JSON response. The format for a collection response is described in Section 5.1.2.
Show a Single Object
Get a single domain: GET /api/domains/:id or GET /api/domains/:name
Send a HTTP GET request with the object’s unique identifier, either :id or :name. No JSON data hash is required.
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains/42
# or
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains/foo
This returns a single object in JSON format. The format for a single object response is described in Section 5.1.3.
Create an Object
Create a new domain: POST /api/domains
Send a HTTP POST request with a JSON data hash containing the required fields to create the object. In this example, a domain is being created.
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X POST -d '{ "name":"foo.bar.com","fullname":"foo.bar.com description" }' \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains
This returns the newly created object in JSON format. The format for a single object response is described in Section 5.1.3.
Update an Object
Update a domain: PUT /api/domains/:id or PUT /api/domains/:name
Send a HTTP PUT request with the object’s unique identifier, either :id or :name, plus a JSON data hash containing only the data to be updated. In this example, only the domain name is being updated.
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X PUT -d '{ "name": "a new name" }' https://foreman.example.com/api/domains/12
# or
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X PUT -d '{ "name": "a new name" }' https://foreman.example.com/api/domains/foo
This returns the newly updated object in JSON format. The format for a single object response is described in Section 5.1.3.
Delete an Object
Delete a domain: DELETE /api/domains/:id or DELETE /api/domains/:name
Send a HTTP DELETE request with the object’s unique identifier, either :id or :name. No JSON data hash is required.
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" -X DELETE \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains/17
# or
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" -X DELETE \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains/foo
This returns the deleted object in JSON format. The format for a single object response is described in Section 5.1.3.
5.1.2 JSON Response Format for Collections
Collections are a list of objects (i.e. hosts, domains, etc). The format for a collection JSON response consists of a results root node and metadata fields total, subtotal, page, per_page. Note: for Katello objects, the metadata includes limit, offset instead of page, per_page.
Below is an example of the format for a collection JSON response for a list of domains: GET /api/domains
{
"total": 3,
"subtotal": 3,
"page": 1,
"per_page": 20,
"search": null,
"sort": {
"by": null,
"order": null
},
"results": [
{
"id": 23,
"name": "qa.lab.example.com",
"fullname": "QA",
"dns_id": 10,
"created_at": "2013-08-13T09:02:31Z",
"updated_at": "2013-08-13T09:02:31Z"
},
{
"id": 25,
"name": "sat.lab.example.com",
"fullname": "SATLAB",
"dns_id": 8,
"created_at": "2013-08-13T08:32:48Z",
"updated_at": "2013-08-14T07:04:03Z"
},
{
"id": 32,
"name": "hr.lab.example.com",
"fullname": "HR",
"dns_id": 8,
"created_at": "2013-08-16T08:32:48Z",
"updated_at": "2013-08-16T07:04:03Z"
}
]
}
The response metadata fields are described below:
total- total number of objects without any search parameterssubtotal- number of objects returned with given search parameters (if there is no search, thensubtotalequalstotal)page(Foreman only) - page numberper_page(Foreman only) - maximum number of objects returned per pagelimit- (Katello only) specified number of objects to return in collection responseoffset- (Katello only) number of objects skipped before beginning to return collection.search- search string (based on scoped_scoped syntax)sortby- the field that the collection is sorted byorder- sort order, either ASC for ascending or DESC for descending
results- collection of objects. See Section 5.1.4 for how to change the root name from ‘results’ to something else.
5.1.3 JSON Response Format for Single Objects
Single object JSON responses are used to show a single object. The object’s unique identifier :id or :name is required in the GET request. Note that :name may not always be used as a unique identifier, but :id can always be used. The format for a single object JSON response consists of only the object’s attributes. There is no root node and no metadata by default. See Section 5.1.4 for how to add a root name.
Below is an example of the format for a single object JSON response: GET /api/domains/23 or GET /api/domains/qa.lab.example.com
{
"id": 23,
"name": "qa.lab.example.com",
"fullname": "QA",
"dns_id": 10,
"created_at": "2013-08-13T09:02:31Z",
"updated_at": "2013-08-13T09:02:31Z"
}
5.1.4 Customize JSON Responses
Customize Root Node for Collections
The default root node name for collections is results but can be changed.
To change the root node name per API request, pass root_name= as a URL parameter. See example below:
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains?root_name=data
Customize Root Node for Single Object
There is no root node as the default for single object JSON responses, but it can be added.
To change the object’s root node name per API request, pass object_name= as a URL parameter. See example below:
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains/23?object_name=record
Customize Partial Response Attributes
Currently, there is no option to change or customize which attributes are returned for collections or single objects. In the future, customized partial responses such as fields=field1,field2,field3 or fields=all may be implemented (#3019). Similarly, there is currently no option to specify child nodes in an API call or to remove child nodes if they are returned by default.
Custom Number of Objects in Collection Per Response
Foreman paginates all collections in the JSON response. The number of objects returned per request is defined in Administer > Settings > General > entries_per_page. The default is 20. Thus, if there are 27 objects in a collection, only 20 will be returned for the default page=1.
To view the next page, pass page= as a URL parameter. See example below:
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains?page=2
The example above will show the remaining 7 objects in our example of 27 objects in the collection.
To increase or decrease the number of objects per response, pass per_page= as a URL parameter. See example below:
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains?per_page=1000
This will return all the objects in one request since 27 is less than the per_page parameter set to 1000.
Custom Search of Collections Per Response
Foreman uses the gem scoped_search for searching and filtering which allows all query search parameters to be specified in one string. To filter results of a collection, pass search= as a URL parameter. See example below:
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains?search=name%3Dexample.com
The number of objects returned will be shown in the subtotal metadata field, and the query string will be shown in the search metadata field.
Custom Sort of Collections Per Response
Custom sort order per collection can be specified by passing order= as a URL parameter. See example below:
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
https://foreman.example.com/api/domains?order=name+DESC
The default sort order is ascending (ASC) if only a field name is passed. The sort parameters will be shown in sort by and order metadata fields.
5.1.5 Nested API routes
The goal is to implement nested routes for all objects as an alternative to filtering collections.
For example, rather then filtering subnets by a specified domain using a search string
$ GET /api/subnets?search=name%3Dqa.lab.example.com
the alternative nested route below returns the same result as the above.
$ GET /api/domains/qa.lab.example.com/subnets
All actions will be accessible in the nested route as in the main route.
5.1.6 API Versioning
The default API version is v1 for Foreman 1.4.
There are two methods of selecting API v2:
-
In the header, pass
Accept: application/json,version=2 -
In the URL, pass /v2/ such as
GET /api/v2/hosts
Similarly, when API version v2 becomes the default, v1 can still be used by passing Accept: application/json,version=1 in the header or api/v1/ in the URL.
5.1.7 Handling Associations
Updating and creating associations are done in a few different ways in the API depending on the type of association.
One-to-One and One-to-Many
To update a one-to-one or a one-to-many association, simply set the name or id on the object. For example, to set a host group for a host, simply set the hostgroup_name or hostgroup_id of the host.
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST \
-d '{ "hostgroup_name": "telerin" }' \
https://foreman.example.com/api/hosts/celeborn.firstage
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST \
-d '{ "hostgroup_id": 42 }' \
https://foreman.example.com/api/hosts/celeborn.firstage
Many-to-One and Many-to-Many
To update an association for an object that contains a collection of other objects, there are a few options. First you can set the names or ids:
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST \
-d '{ "host_names": ["enel.first", "celeborni.first", "elwe.first"] }' \
https://foreman.example.com/api/hostgroups/telerin
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST \
-d '{ "host_ids": [4, 5, 6] }' \
https://foreman.example.com/api/hostgroups/telerin
This will set the host group’s hosts to enel, celeborn, and elwe (or 4, 5, 6) and only those.
Alternatively, you can pass in a set of objects:
$ curl -k -u admin:changeme -H "Accept: version=2,application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST \
-d '{ "domains": [{ "name": "earendil", "id": 1}, { "name": "turgon", "id": 3 }] }' \
https://foreman.example.com/api/subnets/iluvatar
This would set the domains for the subnet to be earendil and turgon. If another domain for example belonged to the subnet before the request, it would be removed.
5.2 Compute Resources
Foreman supports creating and managing hosts on a number of virtualization and cloud services - referred to as “compute resources” - as well as bare metal hosts.
The capabilities vary between implementations, depending on how the compute resource provider deploys new hosts and what features are available to manage currently running hosts. Some providers are able to support unattended installation using PXE, while others are image-based. Some providers have graphical consoles that Foreman interfaces to, and most have power management features. A summary of all providers and their support features is given below, and more detailed sections follow with specific notes.
| Provider | Package | Unattended installation | Image-based | Console | Power management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC2 | foreman-compute | no | yes | read-only | yes |
| Google Compute Engine | foreman-gce | no | yes | no | yes |
| Libvirt | foreman-libvirt | yes | no | VNC or SPICE | yes |
| OpenStack Nova | foreman-compute | no | yes | no | yes |
| oVirt / RHEV | foreman-ovirt | yes | yes | VNC or SPICE | yes |
| Rackspace | foreman-compute | no | yes | no | yes |
| VMware | foreman-vmware | yes | no | VNC | yes |
Support for these features is aimed at being as transparent as possible, allowing the same configuration to be applied to hosts irrespective of the provider in use (compute resource or not). The selection of compute resource is made when creating a new host and the host in Foreman’s database remains associated to the VM that’s created, allowing it to be managed throughout the lifetime of the host.
5.2.1 Using Compute Resources
The following steps describe how to configure a compute resource and provision new hosts on it.
-
Ensure the necessary package for the provider (from the above table) is installed, e.g.
yum -y install foreman-ovirt. Restart the Foreman application to complete installation. -
Add a compute resource under Infrastructure > Compute Resources > New Compute Resource. Select the provider type from the menu and appropriate configuration options will be displayed. Check the notes sections below for any provider-specific setup instructions.
-
Click the Test Connection button after entering the configuration. If no error is displayed, the test was successful.
-
After saving the compute resource, existing virtual machines can be browsed by clicking on the compute resource and the Virtual Machines tab.
-
For providers that use images, click on the compute resource, then the Images tab, where known images are listed. To register images that Foreman can use, click New Image and enter the details.
-
To provision a new host on this compute resource, from Hosts, click New Host and select the compute resource from the Deploy to menu.
Also note the following features:
-
When viewing a host, power management controls and the console access button are in the top right hand corner of the page.
-
If a host provisioned on a compute resource is deleted, the VM and associated storage on the compute resource will also be deleted.
-
Users in Foreman can have access restricted to hosts present on certain compute resources. For more information, see Filtering in 4.1.2 Roles and Permissions.
5.2.2 Using Compute Profiles
A compute profile is a way of expressing a set of defaults for VMs created on a specific compute resource that can be mapped to an operator-defined label. This means an administrator can express, for example, what “Small”, Medium” or “Large” means on all of the individual compute resources present for a given installation.
In combination with host groups, this allows a user to completely define a new host from just the Host tab of the New Host form.
You can find the configuration for compute profiles at Infrastructure > Compute Profiles
Default Profiles
By default, Foreman comes with 3 predefined profiles; “1-Small”, “2-Medium”, and “3-Large” (the numbers are just to make them sort nicely). They come with no associated configuration for any particular compute resource, and as such, they can be deleted or renamed as required.
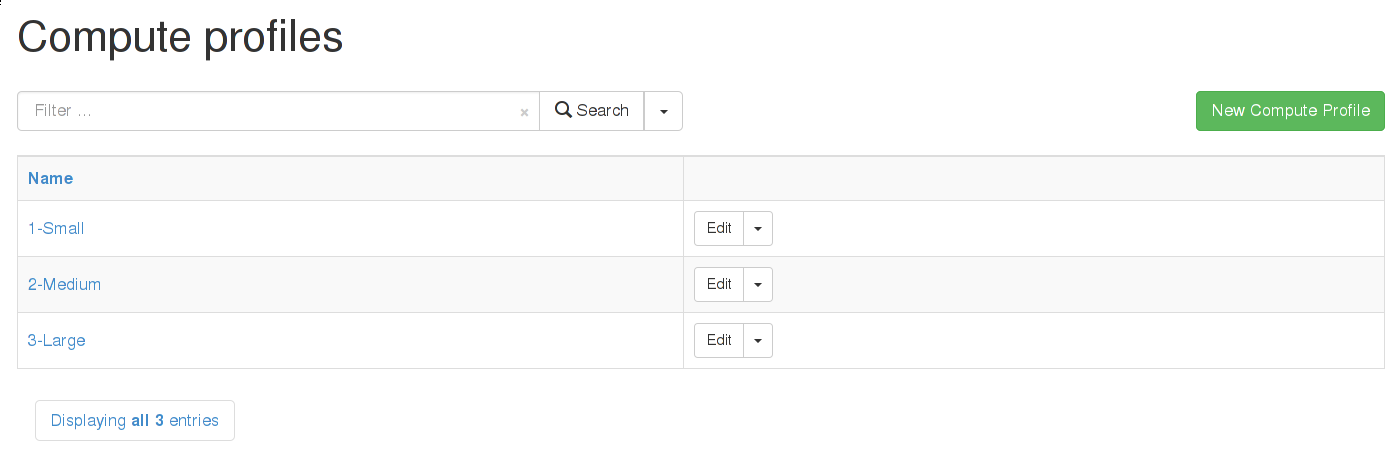
Assigning information to a Profile
This walkthrough will define what “1-Small” means for a particular installation. It will also assume there are two compute resources; one Libvirt and one EC2 (these make a good example as they are very different).
Start by editing the compute profile, by clicking its name in the profile list. This leads to a list of all your current compute resources. Later, once the configuration is done, this list will also display the current defaults configured for each compute resource.
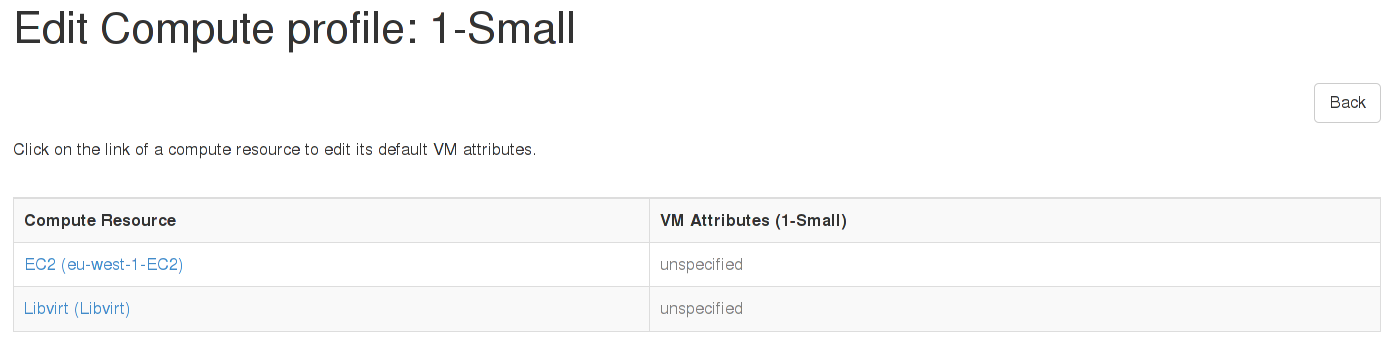
EC2
Clicking on the EC2 resource will bring up a page very similar to the one used when provisioning a single host. Here an administrator can set what “1-Small” means on this specific EC2 resource. For this example, “m1.small” is selected as the size. Defaults can also be specified for the image choice, the security groups, and so on.
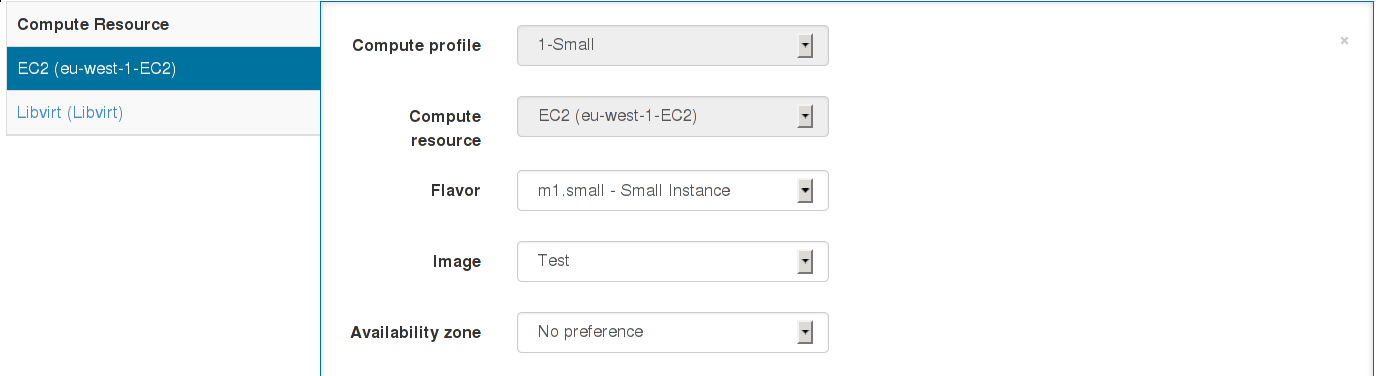
The changes are submitted, and on returning to the profile list, the new EC2 defaults will be shown.
Libvirt
In a very similar manner, the Libvirt resource can be clicked upon, and some defaults assigned. For this example, since this is the “1-Small” profile, 1 CPU, 512MB of RAM, a single bridged network device, and a 5GB disk are selected.
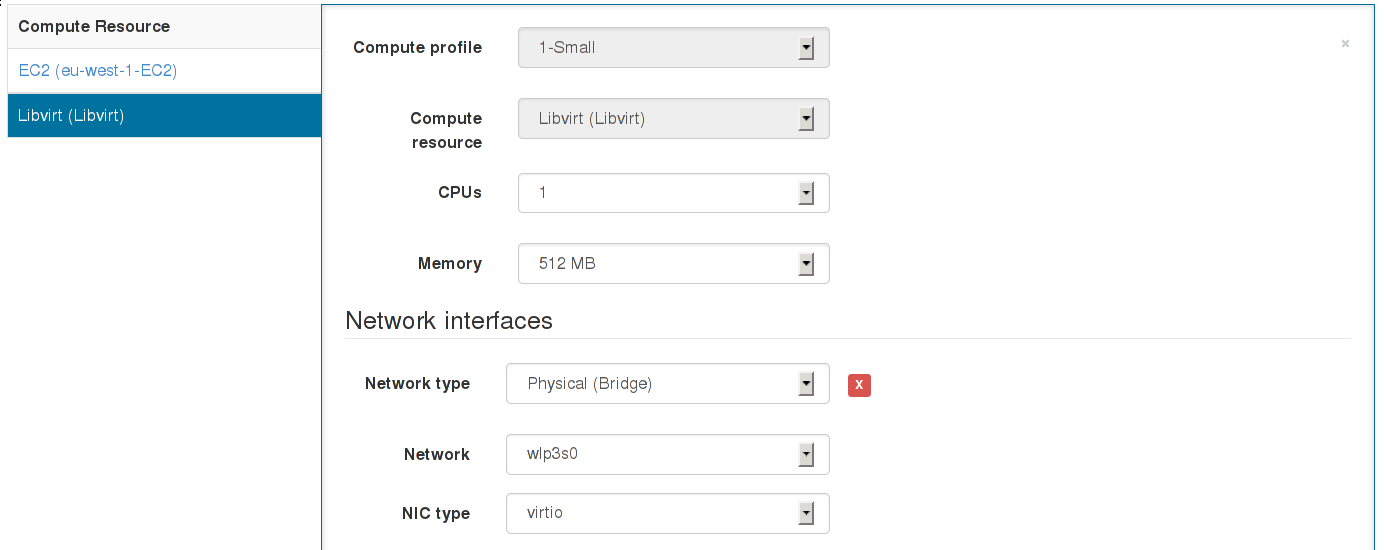
Again, the changes are submitted.
Applying a Compute Profile
Now visit Hosts > New Host. At first, things look exactly as before, but once a compute resource is selected which has at least one compute profile, a new combo-box will appear. This permits the user to select a profile to apply to this host. For this example, the Libvirt resource is selected, followed by the “1-Small” profile.
Once the profile is selected, the Virtual Machine tab will automatically update to use the defaults configured in the “1-Small” profile.
Assuming the defaults are suitable, the host has now been defined solely by selecting a host group and a profile. It’s also possible to associate a profile with a host group in the host group edit page, which will automatically select that profile when the host group is selected.
5.2.3 EC2 Notes
- Add a provisioning template of either type finish or user_data which will be executed on the new image.
- ‘finish’ templates complete the provisioning process via SSH - this requires Foreman to be able to reach the IP of the new host, and that SSH is allowing connections from Foreman. This uses the SSH key which Foreman uploaded to your compute resource when it was added to Foreman.
- ‘user_data’ templates instead provision by cloud-init (or similar meta-data retrieving scripts). This will not require Foreman to be able to reach the host, but the host must be able to reach Foreman (since user_data execution is asynchronous, the host must notify Foreman that the build is complete).
- Ensure AMIs are added under the Images tab on the compute resource
- Ensure the correct username is set for Foreman to SSH into the image (if using SSH provisioning).
- Tick the user_data box if the image is capable of using user_data scripts (usually because it has cloud-init installed).
- Enabling use_uuid_for_certificates in Administer > Settings is recommended for consistent Puppet certificate IDs instead of hostnames.
- VPC subnets and security groups can be selected on the Network tab when creating a host.
- The Managed IP dropdown menu allows selection between using the public and private IP address for communication from Foreman to the instance.
- Ensure that the selected template is associated to the OS (on the Associations tab) and is set as the default for the operating system too.
A finish-based example for configuring EC2 provisioning is given on the Foreman blog: EC2 provisioning using Foreman.
5.2.4 Google Compute Engine Notes
- Requires client e-mail address of an authorised google cloud console client ID is entered in the new compute resource screen and its associated .p12 private key file is manually transferred to the foreman server.
- The certificate must be stored in a location the foreman user account has permission to read.
- If your server enforces SELinux ensure the context is suitable or relabel it using restorecon -vv /usr/share/foreman/yourkey.p12 to
- Specify the location on the foreman server as the certificate path value e.g /usr/share/foreman/yourkey.p12
- Ensure images are associated under the Images tab on the compute resource.
- Add a provisioning template of type finish which will be executed over SSH on the new image.
- Ensure the finish template is associated to the OS (on the Associations tab) and is set as the default for the operating system too.
- Enabling use_uuid_for_certificates in Administer > Settings is recommended for consistent Puppet certificate IDs instead of hostnames.
- The External IP checkbox means the public IP address (rather than private IP) will be used for communication with the instance from Foreman.
5.2.5 Libvirt Notes
- Currently only supports KVM hypervisors.
- VM consoles will be configured by default to listen on 0.0.0.0, change this via libvirt_default_console_address in Administer > Settings > Provisioning.
- libvirt’s DNS and DHCP server (dnsmasq) can be disabled and replaced by BIND and ISC DHCPD (managed by Foreman) by creating a new virtual network and disabling DHCP support.
To connect to the hypervisor using SSH:
- Configure SSH keys (ssh-keygen) for the ‘foreman’ user on the Foreman host to connect fully automatically to the remote hypervisor host.
- Change to the ‘foreman’ user, test the connection and ensure the remote host has been trusted.
- If connecting to the hypervisor as a non-root user, set up PolicyKit to permit access to libvirt. Note that different versions of PolicyKit have different configuration formats. 1, 2.
- Add the compute resource with a URL following one of these examples:
qemu+ssh://root@hypervisor.example.com/systemto use the remote ‘root’ accountqemu+ssh://hypervisor.example.com/systemto use the remote ‘foreman’ account
To connect to the hypervisor over TCP without authentication or encryption (not recommended):
- Set the following options in libvirtd.conf:
listen_tls = 0listen_tcp = 1auth_tcp = "none"
- Enable libvirtd listening, e.g. set
LIBVIRTD_ARGS="--listen"in /etc/sysconfig/libvirtd - Add the compute resource with a URL following this example:
qemu+tcp://hypervisor.example.com:16509/system
If you have difficulty connecting, test access using the virsh command under the ‘foreman’ account on the Foreman host first, e.g. virsh -c qemu+ssh://hypervisor.example.com/system list.
5.2.6 OpenStack Notes
- Supports OpenStack Nova for creating new compute instances.
- Add a provisioning template of either type finish or user_data which will be executed on the new image.
- ‘finish’ templates complete the provisioning process via SSH - this requires Foreman to be able to reach the IP of the new host, and that SSH is allowing connections from Foreman. This uses the SSH key which Foreman uploaded to your compute resource when it was added to Foreman.
- ‘user_data’ templates instead provision by cloud-init (or similar meta-data retrieving scripts). This will not require Foreman to be able to reach the host, but the host must be able to reach Foreman (since user_data execution is asynchronous, the host must notify Foreman that the build is complete).
- Ensure Glance Images are added under the Images tab on the compute resource.
- Ensure the correct username is set for Foreman to SSH into the image (if using SSH provisioning).
- Tick the user_data box if the image is capable of using user_data scripts (usually because it has cloud-init installed).
- Security groups can be selected on the Virtual Machine tab when creating a host.
- The Floating IP Network dropdown menu allows selection of the network Foreman should request a public IP on. This is required when using SSH provisioning.
- Ensure that the selected template is associated to the OS (on the Associations tab) and is set as the default for the operating system too.
A finish-based example for configuring image-based provisioning is given on the Foreman blog, also applicable to OpenStack: EC2 provisioning using Foreman.
5.2.7 oVirt / RHEV Notes
- SPICE consoles are displayed using an HTML5 client, so no native XPI extension is necessary.
5.2.8 Rackspace Notes
- The compute resource URL refers to the identity API URL, e.g.
https://identity.api.rackspacecloud.com/v2.0
A full example for configuring image-based provisioning is given on the Foreman blog, also applicable to Rackspace: EC2 provisioning using Foreman.
5.2.9 VMware Notes
- Only VMware clusters using vSphere are supported, not standalone ESX or ESXi servers (#1945).
Consoles are provided using VNC connections from Foreman to the ESX server, which requires a firewall change to open the respective ports (TCP 5910 to 5930)
ssh root@esx-srv
vi /etc/vmware/firewall/vnc.xmlAdd the following file content:
<ConfigRoot>
<service id='0032'>
<id>VNC</id>
<rule id = '0000'>
<direction>inbound</direction>
<protocol>tcp</protocol>
<porttype>dst</porttype>
<port>
<begin>5910</begin>
<end>5930</end>
</port>
</rule>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</service>
</ConfigRoot>Apply and check the firewall rule:
esxcli network firewall refresh
esxcli network firewall ruleset list | grep VNCLastly, make the rule persistent:
cp /etc/vmware/firewall/vnc.xml /vmfs/volumes/datastore1/vnc.xml
vi /etc/rc.local
# At end of file:
cp /vmfs/volumes/datastore1/vnc.xml /etc/vmware/firewall/
esxcli network firewall refresh- The account that foreman uses to communicate with VCenter is assumed to have the ability to traverse the entire inventory in order to locate a given datacenter. A patch is required to instruct foreman to navigate directly to the appropriate datacenter to avoid permission issues (#5006).
5.3 Install Locations
Missing content. Consider contributing, you kind soul!
5.4 Securing Communications with SSL
The Foreman web application needs to communicate securely with associated smart proxies and puppet masters, plus users and applications connecting to the web interface. This section details recommended SSL configurations.
5.4.1 Securing Puppet Master Requests
In a typical ENC-based setup with reporting, puppet masters require access to Foreman for three tasks:
- Retrieval of external nodes information (classes, parameters)
- Uploading of host facts
- Uploading of host reports
All traffic here is initiated by the puppet master itself. Other traffic from Foreman to the puppet master for certificate signing etc. is handled via smart proxies (SSL configuration covered in the next section).
Configuration options
The Foreman interface authorizes access to puppet master interfaces based on its list of registered smart proxies with the Puppet feature, and identifies hosts using client SSL certificates.
Five main settings control the authentication, the first are in Foreman under Settings, Auth:
- require_ssl_puppetmasters (default: true), requires a client SSL certificate on the puppet master requests, and will verify the CN of the certificate against the smart proxies. If false, it uses the reverse DNS of the IP address making the request.
- restrict_registered_puppetmasters (default: true), only permits access to hosts that have a registered smart proxy with the Puppet feature.
- trusted_puppetmaster_hosts, a whitelist of hosts that overrides the check for a registered smart proxy
And two in config/settings.yaml:
- login (default: true), must be enabled to prevent anonymous access to Foreman.
- require_ssl (default: false), should be enabled to require SSL for all communications, which in turn will require client SSL certificates if require_ssl_puppetmasters is also enabled. If false, host-based access controls will be available for HTTP requests.
Enabling full SSL communications
Using Apache HTTP with mod_ssl and mod_passenger is recommended. For simple setups, the Puppet certificate authority (CA) can be used, with Foreman and other hosts using certificates generated by puppet cert.
- Set Foreman’s require_ssl_puppetmasters, restrict_registered_puppetmasters and require_ssl to true.
- The mod_ssl configuration must contain:
- *SSLCACertificateFile* set to the Puppet CA
- *SSLVerifyClient optional*
- *SSLOptions +StdEnvVars*
- ENC script (e.g.
/etc/puppet/node.rb) should have these settings:
- *:ssl_ca* set to the Puppet CA
- *:ssl_cert* set to the puppet master's certificate
- *:ssl_key* set to the puppet master's private key
- Report processor (e.g.
/usr/lib/ruby/site_ruby/1.8/puppet/reports/foreman.rb) should have these settings:
- *$foreman_ssl_ca* set to the Puppet CA
- *$foreman_ssl_cert* set to the puppet master's certificate
- *$foreman_ssl_key* set to the puppet master's private key
Troubleshooting
Warning messages will be printed to Foreman’s log file (typically /var/log/foreman/production.log) when SSL-based authentication fails.
- No SSL cert with CN supplied indicates no client SSL certificate was supplied, or the CN wasn’t present on a certificate. Check the client script has the certificate and key configured and that mod_ssl has SSLVerifyClient set.
- SSL cert has not been verified indicates the client SSL certificate didn’t validate with the SSL terminator’s certificate authority. Check the client SSL certificate is signed by the CA set in mod_ssl’s SSLCACertificateFile and is still valid. More information might be in error logs.
- SSL is required indicates the client is using an HTTP URL instead of HTTPS.
- No smart proxy server found on $HOST indicates Foreman has no smart proxy registered for the source host, add it to the Smart Proxies page in Foreman. A common cause of this issue is the hostname in the URL doesn’t match the hostname seen here in the log file - change the registered proxy URL to match. If no smart proxy is available or can be installed, use trusted_puppetmaster_hosts and add this hostname to the whitelist.
Advanced SSL notes
A typical small setup will use a single Puppet CA and certificates it provides for the Foreman host and puppet master hosts. In larger setups with multiple CAs or an internal CA, this will require more careful configuration to ensure all hosts can trust each other.
- Ensure the Common Name (CN) is present in certificates used by Foreman (as clients will validate it) and puppet master clients (used to verify against smart proxies).
- Foreman’s SSL terminator must be able to validate puppet master client SSL certificates. In Apache with mod_ssl, the SSLCACertificateFile option must point to the CA used to validate clients and SSLVerifyClient set to optional.
- Environment variables from the SSL terminator are used to get the client certificate’s DN and verification status. mod_ssl’s SSLOptions +StdEnvVars setting enables this. Variable names are defined by ssl_client_dn_env and ssl_client_verify_env settings in Foreman.
Reduced security: HTTP host-based authentication
In non-SSL setups, host-based authentication can be performed, so any connection from a host running a puppet smart proxy is able to access the interfaces.
- Set restrict_registered_puppetmasters to true.
- Set require_ssl_puppetmasters and require_ssl to false.
No security: disable authentication
Entirely disabling authentication isn’t recommended, since it can lead to security exploits through YAML import interfaces and expose sensitive host information, however it may be useful for troubleshooting.
- Set require_ssl_puppetmasters, restrict_registered_puppetmasters and require_ssl to false.
5.4.2 Securing Smart Proxy Requests
Foreman makes HTTP requests to smart proxies for a variety of orchestration tasks. In a production setup, these should use SSL certificates so the smart proxy can verify the identity of the Foreman host.
In a simple setup, a single Puppet Certificate Authority (CA) can be used for authentication between Foreman and proxies. In more advanced setups with multiple CAs or an internal CA, the services can be configured as follows.
Proxy configuration options
/etc/foreman-proxy/settings.yml contains the locations to the SSL certificates and keys:
--- # SSL Setup # if enabled, all communication would be verified via SSL # NOTE that both certificates need to be signed by the same CA in order for this to work # see https://projects.theforeman.org/projects/smart-proxy/wiki/SSL for more information :ssl_certificate: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/FQDN.pem :ssl_ca_file: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem :ssl_private_key: /var/lib/puppet/ssl/private_keys/FQDN.pem
In this example, the proxy is sharing Puppet’s certificates, but it could equally use its own.
In addition it contains a list of hosts that connections will be accepted from, which should be the host(s) running Foreman:
# the hosts which the proxy accepts connections from # commenting the following lines would mean every verified SSL connection allowed :trusted_hosts: - foreman.corp.com #- foreman.dev.domain
Configuring Foreman
For Foreman to connect to an SSL-enabled smart proxy, it needs configuring with SSL certificates in the same way.
The locations of the certificates are managed in the Settings page, under Provisioning - the ssl_ca_file, ssl_certificate and ssl_priv_key settings. By default these will point to the Puppet locations - for manually generated certificates, or non-standard locations, they may have to be changed.
Lastly, when adding the smart proxy in Foreman, ensure the URL begins with https:// rather than http://.
Sharing Puppet certificates
If using Puppet’s certificates, the following lines will be required in puppet.conf to relax permissions to the puppet group. The foreman and/or foreman-proxy users should then be added to the puppet group.
[main]
privatekeydir = $ssldir/private_keys { group = service }
hostprivkey = $privatekeydir/$certname.pem { mode = 640 }
Note that the “service” keyword will be interpreted by Puppet as the “puppet” service group.
5.5 Backup, Recovery and Migration
This chapter will provide you with information how to backup and recover your instance. All commands presented here are just examples and should be considered as a template command for your own backup script which differs from one environment to other.
It is possible to perform a migration by doing backup one one host and recovery on a different host, but in this case pay attention to different configuration between the two hosts.
This can be applied to the Foreman application itself, but pay attention when migrating smart-proxy and services because things like different IP addresses or hostnames will need manual intervention.
5.5.1 Backup
This chapter will provide you with information how to backup a Foreman instance.
Database
PostgreSQL
The pg_dump command can be used to backup the contents of a PostgreSQL
database to a text file. The most reliable way of backing up PostgreSQL
database is:
su postgres -c "pg_dump -Fc foreman > foreman.dump"
MySQL database
The mysqldump command can be used to backup the contents of your MySQL
database to a text file.
mysqldump --opt foreman > foreman.sql
Please follow MySQL documentation about other options for doing backups.
SQLite database
To backup SQLite database perform this simple step:
sqlite3 /path/to/foreman/db/production.db .dump > foreman.dump
SQLite databases are all contained in a single file, so you can back them up by copying the file to another location, but it is recommended to shut down the instance first, or at lest verify the integrity of the created archive using sqlite3 command. The dump command above is preferred.
Configuration
On Red Hat compatible systems issue the following command to backup whole /etc directory structure:
tar --selinux -czvf etc_foreman_dir.tar.gz /etc/foreman
For all other distribution do similar command:
tar -czvf etc_foreman_dir.tar.gz /etc/foreman
Puppet master
On the puppet master node, issue the following command to backup Puppet certificates on Red Hat compatible systems
tar --selinux -czvf var_lib_puppet_dir.tar.gz /var/lib/puppet/ssl
For all other distribution do similar command:
tar -czvf var_lib_puppet_dir.tar.gz /var/lib/puppet/ssl
DHCP, DNS and TFTP services
Depending on used software packages, perform backup of important data and configuration files according to the documentation. For ISC DHCP and DNS software, these are located within /etc and /var directories depending on your distribution as well as TFTP service.
5.5.2 Recovery
Recovery process is supposed to be performed on the same host the backup was created on on the same distribution and version.
If you planning to migrate Foreman instance, please read remarks in the beginning of this chapter.
Note: Foreman instance must be stopped before proceeding.
PostgreSQL
The pg_restore command can be used to recover contents of your PostgreSQL
database from the database dump. The most reliable way PostgreSQL
database is:
su postgres -c "pg_restore -C -d postgres foreman.dump"
MySQL database
The mysql command can be used to recover contents of your MySQL database
from the database dump in SQL format.
mysql < dump.sql
Please follow MySQL documentation about other options for data recovery.
SQLite database
To recover from SQLite dump perform this simple step:
sqlite3 /path/to/foreman/db/production.db < foreman.dump
It is possible just to copy db file, but Foreman instance must be stopped.
Configuration
On Red Hat compatible systems issue the following command to restore whole /etc directory structure:
tar --selinux -xzvf etc_foreman_dir.tar.gz -C /
For all other distribution do similar command:
tar -xzvf etc_foreman_dir.tar.gz -C /
It is recommended to extract files to an empty directory first and inspect the content before overwriting current files (change -C option to an empty directory).
Puppet master
On the puppet master node, issue the following command to restore Puppet certificates on Red Hat compatible systems
tar --selinux -xzvf var_lib_puppet_dir.tar.gz -C /
For all other distribution do similar command:
tar -xzvf var_lib_puppet_dir.tar.gz -C /
It is recommended to inspect the content of the restore first (see above).
DHCP, DNS and TFTP services
Depending on used software packages, perform recovery of important data and configuration files according to the documentation. This depends on the software and distribution that is in use.
5.6 Rails Console
Foreman is a Ruby on Rails application, which provides an interactive console for advanced debugging and troubleshooting tasks. Using this allows easy bypass of authorization and security mechanisms, and can easily lead to loss of data or corruption unless care is taken.
To access the Rails console, choose the method below appropriate to the installation method.
RPM and Debian installations
As root, execute:
yum install foreman-console
foreman-rake consoleSource installations
As the user running Foreman and in the source directory, execute:
RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rails cSet up
To assume full admin permissions in order to modify objects, enter in the console:
User.current = User.admin5.7 SPNEGO authentication
The following tutorial explains how to set up authentication with mod_auth_kerb and any IPA server. We will use an external IPA server and install mod_auth_kerb in the Foreman machines.
We assume the Foreman machine is IPA-enrolled:
ipa-client-installOn the IPA server, we create the service:
ipa service-add HTTP/<the-foreman-hostname>On the Foreman machine, we get the keytab for the service:
ipa-getkeytab -s ipa.example.com -k /etc/http.keytab -p HTTP/$( hostname )
chown apache /etc/http.keytab
chmod 600 /etc/http.keytabOn the Foreman machine, we install mod_auth_kerb:
yum install -y mod_auth_kerbOn the Foreman machine, we configure it to be used by Apache:
# add to /etc/httpd/conf.d/auth_kerb.conf
<Location /users/extlogin>
AuthType Kerberos
AuthName "Kerberos Login"
KrbMethodNegotiate On
KrbMethodK5Passwd Off
KrbAuthRealms EXAMPLE.COM
Krb5KeyTab /etc/http.keytab
KrbLocalUserMapping On
require valid-user
ErrorDocument 401 '<html><meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0; URL=/users/login"><body>Kerberos authentication did not pass.</body></html>'
# The following is needed as a workaround for https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1020087
ErrorDocument 500 '<html><meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0; URL=/users/login"><body>Kerberos authentication did not pass.</body></html>'
</Location>On the Foreman machine, we tell Foreman that it is OK to trust the authentication done by Apache by adding to /etc/foreman/settings.yaml or under Adminster > Settings:
:authorize_login_delegation: trueOn Foreman machine, restart Apache:
service httpd restartNow in your browser, if you kinit to obtain a ticket, accessing Foreman’s WebUI should not ask for login/password and should display the authenticated dashboard directly.
Enable auto-creation of externally authentication users
Foreman can auto create users already existing in your IPA server. When a new user is created on login, a page asking for the email address of this user will be shown. To enable this feature add:
:authorize_login_delegation_auth_source_user_autocreate: Externalto /etc/foreman/settings.yaml or under Adminster > Settings.
Namespace separation
If clear namespace separation of internally and externally authenticated users is desired, the KrbLocalUserMapping should be off:
# in /etc/httpd/conf.d/auth_kerb.conf
<Location /users/extlogin>
AuthType Kerberos
...
KrbLocalUserMapping Off
</Location>Then the @REALM would be part of the username and it would be clear that bob is INTERNAL-authenticated and bob@EXAMPLE.COM is different user, EXTERNAL-authenticated. The admin then can manually create another admin@EXAMPLE.COM user (with administrator privileges) and even the admin can use Kerberos.
5.7.1 Populate attributes for externally authenticated users
IPA server, enroll Foreman machine, setup mod_auth_kerb
Follow Section 5.7 to enable Kerberos authentication and autopopulation of users in Foreman.
Configure sssd-dbus and mod_lookup_identity
Enable Jakub Hrozek’s repository which has the builds of sssd-dbus and mod_lookup_identity. At http://copr-fe.cloud.fedoraproject.org/coprs/jhrozek/identity_demo/ choose the correct .repo file. For example, for Foreman on RHEL 6,
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jhrozek-identity_demo.repo \
http://copr-fe.cloud.fedoraproject.org/coprs/jhrozek/identity_demo/repo/epel-6-i386/Install the packages:
yum install -y sssd-dbus mod_lookup_identityUpdate /etc/sssd/sssd.conf to enable the Infopipe feature of sssd.
--- /etc/sssd/sssd.conf.orig 2013-12-10 03:09:20.751552952 -0500
+++ /etc/sssd/sssd.conf 2013-12-12 00:52:30.791240631 -0500
@@ -11,8 +11,10 @@
chpass_provider = ipa
ipa_server = _srv_, ipa.example.com
dns_discovery_domain = example.com
+ldap_user_extra_attrs = mail, givenname, sn
+
[sssd]
-services = nss, pam, ssh
+services = nss, pam, ssh, ifp
config_file_version = 2
domains = example.com
@@ -28,3 +30,7 @@
[pac]
+[ifp]
+allowed_uids = 48, 0
+user_attributes = +mail, +givenname, +sn
+With new enough selinux-policy, set the following boolean:
setenforce 1
setsebool -P httpd_dbus_sssd onIf your policy doesn’t have httpd_dbus_sssd, set SELinux to permissive:
setenforce 0Configure mod_lookup_identity – for example, edit /etc/httpd/conf.d/lookup_identity.conf to have the following in it:
# cat >> /etc/httpd/conf.d/lookup_identity.conf <<EOF
LoadModule lookup_identity_module modules/mod_lookup_identity.so
<Location /users/extlogin>
LookupUserAttr mail REMOTE_USER_EMAIL " "
LookupUserAttr givenname REMOTE_USER_FIRSTNAME
LookupUserAttr sn REMOTE_USER_LASTNAME
</Location>
EOFRestart sssd and Apache:
service sssd restart
service httpd restartAs admin, remove any previously autopopulated users from Foreman, so they can be created again, now with attributes.
Now, when you use Kerberos obtained from the IPA server to log in to Foreman, you should see the full name of the user instead of the login name in the top right corner of the screen, and if you inspect user’s details, the email address should be there as well.
6. Plugins
Plugins are tools to extend and modify the functionality of Foreman. The core of Foreman is designed to be lean, to maximize flexibility and minimize code bloat. Plugins offer custom functions and features so that each user can tailor their environment to their specific needs. Foreman plugins are implemented as rail engines that are packaged as gems and thus easily installed into Foreman.
6.1 Install a Plugin
Foreman plugins are implemented as gems in Ruby on Rails. See below for the different installation methods, which depend on your platform.
RPM installations
A limited number of plugins are available fully packaged from our yum repositories for ease of use. The number of these is increasing, so check the wiki to see if a package is available yet. If it’s a useful or popular plugin and not yet packaged, please file a feature request in the packaging project. The repos are available at yum.theforeman.org/plugins. Separate repos are available for each Foreman release, containing plugins that are compatible with that particular version. Packages are not currently GPG signed.
Configure the repo by creating /etc/yum.repos.d/foreman_plugins.repo:
[foreman-plugins] name=Foreman plugins baseurl=http://yum.theforeman.org/plugins/1.4/el6/x86_64/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
Find the package for the plugin: <pre>yum search rubygem-foreman</pre>
Install the package, e.g. <pre>yum install ruby193-rubygem-foreman_discovery</pre>
Restart Foreman with service foreman restart
Some plugins (e.g. foreman_column_view) may also require configuration in /usr/share/foreman/config/settings.plugins.d/, check for any .example files.
Debian installations
A limited number of plugins are available fully packaged from our deb repositories for ease of use. The number of these is increasing, so check the list of plugins to see if a Debian package is available yet. If it’s a useful or popular plugin and not yet packaged, please file a feature request in the packaging project.
The repo is available at http://deb.theforeman.org plugins <component>. Separate repos are available for each Foreman release, containing plugins that are compatible with that particular version. They are signed with the Foreman APT key.
- Add a source line like this:
deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ plugins 1.4to Apt - Find the package for the plugin:
apt-cache search ruby-foreman - Install the package, e.g.
apt-get install ruby-foreman-discovery - Restart Foreman:
touch ~foreman/tmp/restart.txtorservice apache2 restart
Some plugins (e.g. foreman_column_view) may also require configuration in /usr/share/foreman/config/settings.plugins.d/, check for any .example files.
Advanced: installing from gems
Not recommended, as it’s possible for the ‘gem’ command to try and install newer versions of Rails which can cause problems. Do note the install without dependencies below to avoid this problem. Ensure the plugin you want is available from rubygems.org as a gem. Plugins that aren’t published (just git repos) can’t be installed with this method without being built as a gem.
If on EL6, run <pre>scl enable ruby193 bash</pre> first for an SCL-enabled shell (not needed on Fedora)
Install without dependencies: <pre>gem install –ignore-dependencies foreman_column_view</pre>
If you need other dependencies (see the rubygems.org page), check the yum repo above (e.g. deface, nokogiri) or install the same way with ‘gem’
Add to the bundler.d/Gemfile.local.rb file as detailed below.
Restart Foreman with service foreman restart
If you hit problems, uninstall the added gems with <pre>gem uninstall -v VERSION GEM</pre>
Debian package or “from source” installations
It is recommended to use ~foreman/bundler.d/Gemfile.local.rb so that it is not overwritten by future upgrades.
If it’s published on rubygems.org, just add the name and the latest released version will be downloaded. Add to bundler.d/Gemfile.local.rb:
gem 'foreman_sample_plugin'
Or bundler can install the plugin from a git repository. Add to bundler.d/Gemfile.local.rb:
gem 'foreman_sample_plugin', :git => "https://github.com/example/foreman_sample_plugin.git"
Next, as a Foreman user (not root), run the following command:
$ bundle update foreman_sample_plugin
Then restart Foreman with touch ~foreman/tmp/restart.txt
6.2 Plugin List
An up-to-date plugin list is kept in the wiki
7. Troubleshooting
7.1 NoVNC
Foreman uses the excellent javascript VNC library noVNC, which allows clientless VNC within a web browser. When a console is opened by the user’s web browser, Foreman opens a connection to TCP Port 5910 (and up) on the hypervisor and redirects that itself.
Requirements
- Recent web browser
- Open network connection from the workstation where the web browser runs on to your Foreman server and from your Foreman server to the hypervisor on TCP ports 5910 - 5930.
Known issues
- Currently only unencrypted connections are possible, even if you connect to Foreman via HTTPS.
- Keyboard mappings are currently fixed to English only.
- When using Firefox, if you use Foreman via HTTPS, Firefox might block the connection. To fix it, go to about:config and enable network.websocket.allowInsecureFromHTTPS
Troubleshooting Steps
- Check for a “websockify.py” process on your Foreman server when opening the console page in Foreman
- If websockify.py is missing, check /var/log/foreman/production.log for stderr output with logging increased to debug
- Look at the last argument of the process command line, it will have the hypervisor hostname and port - ensure you can resolve and ping this hostname
- Try a telnet/netcat connection from the Foreman host to the hypervisor hostname/port
- The penultimate argument of websockify.py is the listening port number, check if your web client host can telnet to it
- If using Firefox, check the known issues above and set the config appropriately
7.2 Getting Help
Please check the Troubleshooting wiki page for solutions to the most common problems. Otherwise, there are two primary methods of getting support for the Foreman: IRC and mailing lists.
IRC
We work on the libera.chat servers. You can get general support in #theforeman, while development chat takes place in #theforeman-dev.
Mailing lists
Mailing lists are available via Google Groups. Much like IRC, we have a general users (support, Q/A, etc) lists and a development list: